Category: News & Events
-
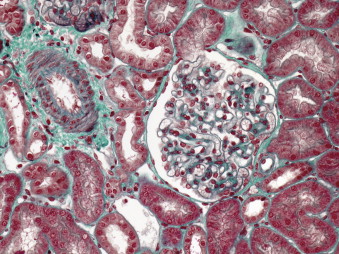
Lipoid Nephrosis
1- Biology: A- Definition: Massive proteinuria> 50 mg / kg / day (40 mg / m² / h); clear Hypoproteinemia and hypoalbuminemia (<30 g / L) Hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia B- Protein: α2-globulins still high (-> 30% plasma protein) Gamma globulins are low High coagulation factors Reduce protein vector => anemia (decreased transferrin) hypothyroidism … C-…
-

Urinary tract infection
1- radiological information: Ultrasound: Systematic dice the first episode of UTI (boy or not) CUM (retrograde cystography): Episode 2 in girls; from the 1st episode in boys IVU: in case of anomalies on ultrasound, the MUC Before any abnormality of the urinary tract systematically search for VUR by CUM 2- vesicoureteral reflux: Most common in…
-
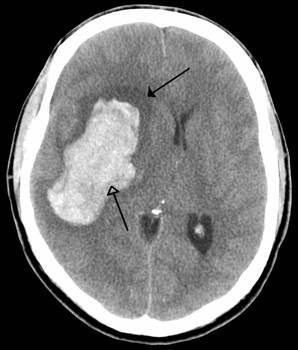
Hemorrhagic stroke
1- Clinical pictures: A- lens capsular hemorrhage (deep hematoma UCS): – Acute onset with headache and quickly disorders of consciousness; Hemiplegia + conjugate deviation of the head and eyes toward the lesion – Ventricular floods can occur characterized by generalized hypertension, seizures, signs decerebrate – A more gradual and less severe picture can be with:…
-
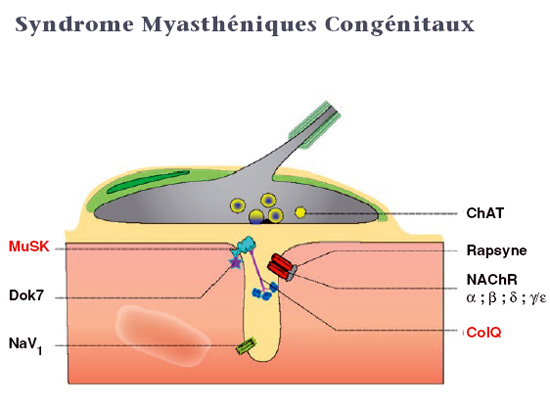
Congenital Myopathy
1- myotonias: A- Steinert disease: – Synonym: Myotonic dystrophy – If transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion. – The molecular abnormality in question is located in the gene encoding the protein kinase myotonine (DMPK) on ch.19 by abnormal amplification of a trinuclotidique sequence. – Atrophy predominant in the cephalic end responsible for a particular facies…
-
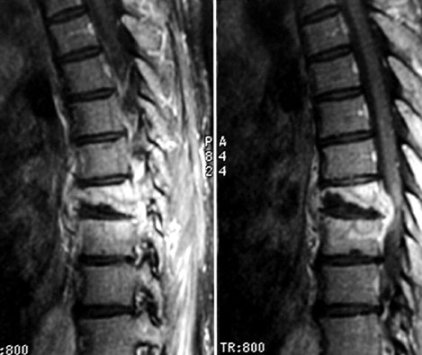
Pott’s disease
1- General: – Spinal tuberculosis is the most common location of osteoarticular tuberculosis – There are two forms: spondylitis (Pott’s disease) and spondylitis (without involvement of intervertebral discs). – The Pott’s disease is characterized by the achievement of the vertebral disc 2 adjacent vertebrae. – Tuberculous spondylitis is a tuberculous osteomyelitis of the vertebral body…
-

Semiotics of Sensitivity
1- lesions of the spinal cord: A- Syndrome cordonale post: * Paresthesia; Lhermitte’s sign (shock sensation-clenchée by flexing the neck) * Disorders discriminative sensitivity (position sense); astereognosis * Ataxic disorders B- syringomyelic Syndrome: * Responsible lesion is in the gray matter intramedullary * Achievement dissociated sensitivity on thermal and painful sensitivities and respecting the tactility…
-
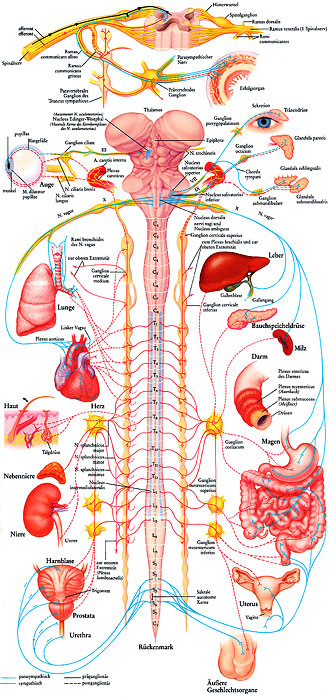
Vegetative functions
1- pupillary disorders: Argyll-Robertson syndrome (syphilis): small pupils, irregular, uneven, the pupillary light reflex is abolished (direct and consensual), while the accommodation-convergence is preserved. * Adie Syndrome: unilateral pupillary areflexia tendon + anomalies. The affected pupil is moderately dilated, direct and consensual RPM is completely or almost completely abolished. Slow pupillary contraction and relaxation. *…
-
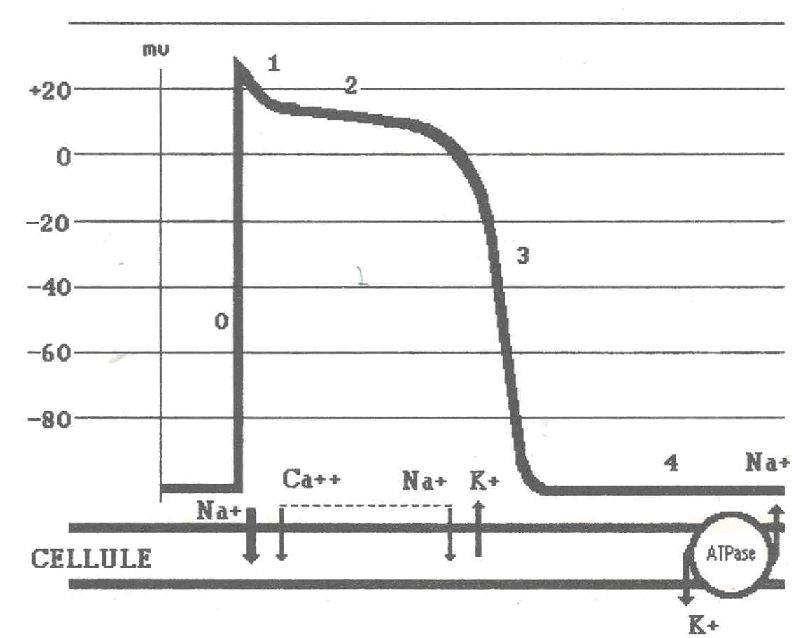
Antiarrhythmic
1- Classification of Vaughan Williams: * Class I: sodium channel inhibitors (+ membrane stabilizing effect) – Ia: quinidine; disopyramide (Rythmodan) – Ib: lidocaine; phenytoin; mexiletine – Ic: Cibenzoline, propafenone (Rythmol®) flecainide * Class II: Beta-blockers * Class III: inhibitors of potassium flux – Amiodarone (Cordarone) – Sotalol (Sotalex®) – Bretylium * Class IV: calcium channel…
-
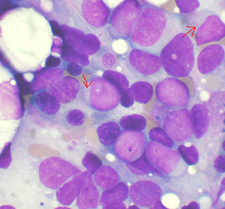
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are acute malignant diseases of proliferation and differentiation stop medullary precursors grainy lines, monocytic, erythroid, or platelet. Thus, we see that the term acute non-lymphoblastic leukemia, used by the Anglo-Saxons, would be more appropriate to name this disease that the term acute myelogenous leukemia usually used in France. The acute myeloid…
You must be logged in to post a comment.