* Tobacco: high risk beyond 20 PA; Carcinogenic: benzopyrene and polycyclic hydrocarbons; nitrosamines;phenols; arsenic.
* Other FDR: asbestos (amphibole overcoats, for little or no chrysotile); arsenic; nickel; chromium; iron oxide;hydrocarbons; beryllium; ionizing radiation.
* Genetic factors: HLA B12 group.
* Late effects of tuberculosis -> adenocarcinoma
A- Pathology:
1- squamous carcinomas:
– 40-50% of lung cancers
– Bronchial lobar or segmental> bronchi
– Bud with obstructive infiltration of the bronchial wall; frequent central necrosis
– Differentiation squamous +/- marked (intercellular bridges and / or keratinization)
– Cytokeratin (CSC); ACE negative or weakly positive
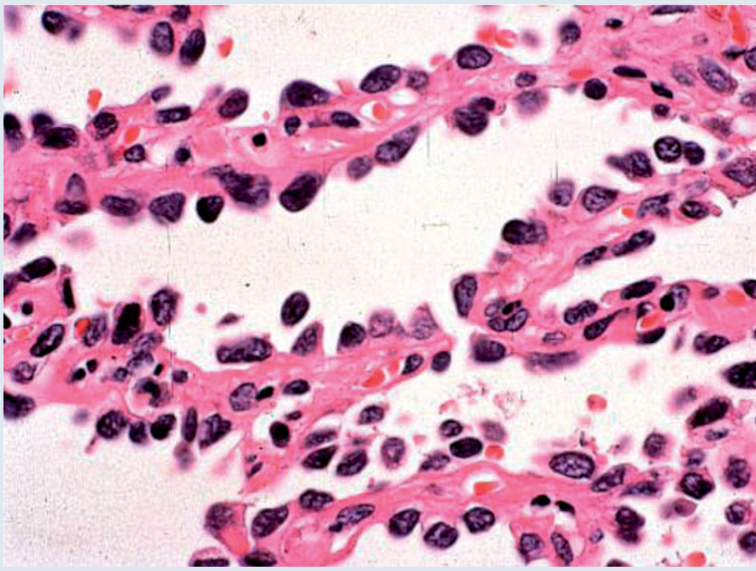
2- Adenocarcinoma:
– 20% of lung cancer
– Subpleural peripheral tumors with destruction of structures
– The bronchoalveolar form is little or no destructive with alveolar dissemination (cough with copious expectoration).
– Immunohistochemistry: ACE, surfactant (Clara cell differentiation); SAP; keratin.
B- Clinical Syndromes:
1- Pancoast tumor:
– Tumors of the apex with
– Neuralgia C8-D1
– Horner’s syndrome ipsilateral
– Lyse rib of the posterior arch of the first 2 ribs.
– Atrophy of the muscles of the hypothenar
– Risk of vertebral and spinal extension
2- paraneoplastic syndromes:
– Clubbing
– Hypercalcemia, repeated phlebitis; SIADH
– Hypertrophic pulmonary arthropathy Osteopathy Pierre-Marie with:
* Clubbing
* Arthropathy and soft tissue thickening +/- joint pain
* Periostosis radiological sheathing
* Especially the fact Kc squamous
3- Other events:
– Superior vena cava syndrome (less common than for small cell Kc) with:
* Edema in cape of the face, neck and MS
* Venous circulation collateral
* Risk of cerebral edema ++
– Phrenic paralysis -> hiccups …
– Mediastinal syndrome: left recurrent laryngeal paralysis (bitonal voice); Dysphagia
– Recurrent pneumonitis; hemoptysis …
Diagnostic features
– Chest X-ray and CT scan: tumor opacity Central reached (perihilar) or peripheral +/- excavated and irregular boundaries
– Fibroscopy with bronchial bronchial aspiration and biopsies of the lesions (sprouting aspect, infiltrating …).
– If endoscopy can confirm the diagnosis before an abnormal chest image (atelectasis, excavated opacity round image parenchymal) => thoracotomy is indicated in doubt.
Treatment C:
Surgery is the treatment of choice; hypercapnia is a cons-indication to any act of excision
a- TNM:
1- T (primary tumor):
– Tx: presence of tumor cells in sputum without further radiological signs or bronchoscopic
– T1: ≤ 3cm; no more proximal lobar bronchus attained only
– T2:> 3cm; more than 2 cm from the hull; atelectasis of not reaching all the lung; achieving the visceral pleura.
– T3: achieving the chest wall; the diaphragm; the mediastinal pleura; pericardium within 2 cm of the hull without reaching it.
– T4: achievement of the trachea or carina; mediastinum; the heart and great vx; esophagus; secondary tumor nodule in the same lobe as the original; reached the vertebral body; neoplastic pleurisy histologically proven
2- N (regional lymph nodes) and M (distant metastasis):
– N1: ipsilateral hilar reached
– N2: ipsilateral mediastinal involvement and / or under carinaire
– N3: contralateral disease (hilar and / or mediastinal); scalene or supraclavicular lymph node
– M1: included tumor nodule in another lobe that primitive (metastasis)
b- occult carcinoma: TXN0M0
Stage 0: TisN0M0 (in situ tumor) -> Treatment: Photodynamic; cryotherapy or endobronchial brachytherapy
Stage IA: T1N0 -> Survival to 5 years:> 70% -> Treatment: Surgical treatment / No radiation so complete surgical … / chemotherapy if inoperable (+/- radiotherapy)
Stage IB: T2N0 -> Survival to 5 years: 60% -> Treatment: Surgical treatment / No radiation so complete surgical … / chemotherapy if inoperable (+/- radiotherapy)
Stage IIA: T1N1 -> Survival to 5 years: 50% -> Treatment: Surgical treatment / No radiation so complete surgical … / chemotherapy if inoperable (+/- radiotherapy)
Stage IIB: T2N1; T3N1 -> Survival to 5 years: 30-40% -> Treatment: Surgical treatment / No radiation so complete … surgery / chemotherapy if inoperable (+/- radiotherapy)
Stage IIIA: T1N2; T2N2; T3N2 -> Survival to 5 years: 10-30% -> Treatment: Surgical treatment routine postoperative radiotherapy +.
Stage IIIB: T1N3; T2N3; T3N3; T4 -> Survival to 5 years <5% -> Treatment: Radiotherapy Thoracic
Stage IV: M1 -> Survival to 5 years: <1% -> Treatment: Radiotherapy analgesic; exclusive chemotherapy
– Secondary lung tumors: single or multiple nodules predominantly in the lower lobes; although limited;carcinomatous lymphangitis; excavated tumor …

You must be logged in to post a comment.