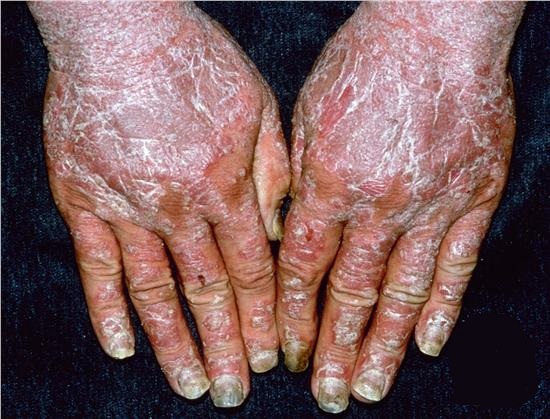
The exfoliative dermatitis is characterized by a generalized confluent erythema with desquamation affecting all integument.
The main causes are drug eruptions, psoriasis, eczema, cutaneous lymphoma and scabies.
DIAGNOSIS:
Main symptoms:
Erythroderma is a rare syndrome. The trend may last several weeks with waves and poor general condition.
The rash is widespread, inflammatory, purplish with sloping points accompanied by a fine desquamation or in large shreds, with thickening of the skin folds (pachydermia).
Mucous membranes can be achieved with cheilitis, conjunctivitis and stomatitis. Eyelashes, hair and eyebrows are becoming scarce, and even fall in a few weeks. There may be swelling of the face.
Nail growth is disturbed with the presence of Beau’s lines and even nail loss.
Associated symptoms:
The main symptoms are:
– Fever: oscillating often, it is related to the thermal dysregulation and does not mean infection; it is often accompanied by chills;
– Pruritus: often fierce, with skin pulling sensation that can be painful;
– The polyadenopathies: Although not specific, they should move towards a CTCL epidermotropic (Sezary syndrome);
– Hemodynamic disorders, electrolyte and signs related to decompensation of pre-existing defects: heart failure, kidney, etc.
TO DO:
If the diagnosis of erythroderma is suspected on the presence of the above symptoms, hospitalization in a specialized urgently needed in most cases. Symptomatic treatment (local care with daily warm baths, applying non-alcoholic antiseptic, emollient creams or topical steroids) is conducted in conjunction with the general treatment (electrolyte balancing, correction of any defects decompensation, stopping unnecessary medications , antihistamines, etc.) and the etiological approach, in which the interview and clinical examination plays a big role.Skin histology is often non-specific.
ETIOLOGIES:
Drug erythroderma:
Diagnosis:
Erythroderma appears at least one week after the introduction of medicament. A later time (two to six weeks) evokes a drug hypersensitivity syndrome or DRESS (Drug Rash with Hypereosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms).
The most charged drugs are gold salts, antibacterial sulfonamides, antiepileptic, allopurinol and beta-lactams, in particular minocycline in the subject of black skin.
Treatment:
The due process must be stopped as soon as possible, subject to the accident said pharmacovigilance. The trend is mostly supportive treatment after discontinuation of the suspect drug.
Erythrodermic psoriasis:
Diagnosis:
The following criteria are in favor of erythrodermic psoriasis:
– Personal and family history of psoriasis;
– Withdrawal of corticosteroids;
– Erythematous, scaly lesions limited well characterized;
– Pustules.
The pustules are follicular and amicrobiennes.
The achievement of nails (punctuation pitting, salmon spots) as well as the scalp (squamous helmet) can move towards psoriasis.
In addition to the withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids, taking certain medications such as beta blockers promoting can be found.
Treatment:
Treatment is initiated in a specialized environment.
In addition to the therapeutic measures discussed above and topical corticosteroids, treatment with retinoids (less than 20 mg / day) or immunosuppressive (methotrexate in small doses, 10 mg / week), is established.
Phototherapy is against inappropriate.
Eczema:
Diagnosis:
The following criteria are in favor of eczema:
– Atopic dermatitis or eczema history;
– Vésiculosuintantes lesions.
It often occurs with atopy or follows the application of a topical.
Treatment:
Treatment involves the eviction of the triggering factor, symptomatic measures already detailed and application of topical corticosteroids most often (Diprosone® cream with decreasing doses for example: 1 application per day on the body for seven days, and every two day for two weeks and then twice weekly for two weeks and then stop).
CTCL epidermotropic or Sezary syndrome:
Diagnosis:
The following criteria are in favor of a Sezary syndrome:
– On more than 60 years;
– Chronic exfoliative dermatitis, itchy, infi filtered;
– Polyadenopathies;
– Palmoplantar keratoderma important.
The suspected diagnosis on clinical is often confirmed by histology late. Abnormal cells circulating in the convoluted nucleus, and significant title (Sezary cells, greater than 10%) can be observed. Looking for a T clone in the blood and skin (study of rearrangement of the gene encoding the receptor T) should be performed, and a radiological assessment (discussed modalities).
Other blood diseases may be associated with erythroderma (malignant lymphoma Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s, leukemia, myelodysplasia).
Treatment:
According to the importance of achieving and stage, treatment varies from local application of chlormethine (Caryolysine®) to interferon or to polychemotherapies.
Norwegian scabies:
Diagnosis:
The following criteria are in favor of Norwegian scabies:
– Mealy erythroderma, crusted, hyperkeratotic;
– Elderly, debilitated, living in community.
Scabies is highly contagious. The diagnosis is confirmed by looking for mites on skin scrapings product.
Treatment:
Hospitalization with isolation dermatological medium is necessary. Treatment involves the repeated application of whitewash of Ascabiol®, treatment of clothing with a solution paraticide or administration of oral ivermectin (Stromectol®, 200 mcg / kg single dose). The contacts must be identified, assessed and treated.
HIV:
The following criteria must be suspected HIV (virus immunodeficiency active):
– Young subject;
– Drug addiction;
– Multiple sexual partners;
– Unprotected sex.
Must be removed before any HIV erythroderma.
Other causes:
Rarer causes these mainly concern:
– Graft disease against the host: sclerodermiform appearance in a marrow graft;
– Pityriasis rubra pilaris: although limited papular lesions, scaly, orange-yellow;
– Lichen planus;
– Some of pemphigus;
– Erythrodermas paraneoplastic solid cancers: lung, esophagus, stomach, prostate, thyroid, breast, ovary, rectum.
Erythrodermas without cause found:
They correspond to 10-40% of cases of erythroderma. Regular dermatological monitoring is required, the number of cases progressing to lymphoma.

You must be logged in to post a comment.