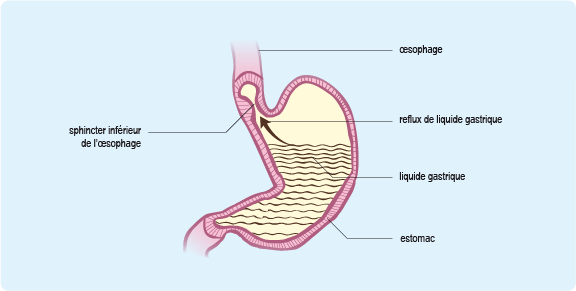
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Clinical signs:
Burning stomachache or heartburn, generally relieved by antacids; acid regurgitation (often postural: ante-bending or supine). In the absence of dysphagia (oesophageal stenosis), these events are benign.
Treatment:
– In first intention, encourage the patient to avoid alcohol, tobacco, and give aluminum hydroxide PO: 1.5 to 3 g / day in 3 divided doses one hour after meals or 500 mg during crises painful.
“The aluminum hydroxide may decrease the absorption of drugs ingested simultaneously meet an average of two hours between taking aluminum hydroxide and that of other drugs. “
– If antacids are insufficient: omeprazole PO 20 mg / day in the morning for 3 days or, failing that, cimetidine PO, 400 mg / once daily at bedtime for 3 days
– In small children: no drug treatment, rest and sleep on an incline (30-45 °).
Peptic ulcers
Clinical signs:

Epigastric pain type of burning or cramps between meals, waking the patient at night, especially characteristics they return periodically by episodes of a few days and when accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
The most common complications are perforation and bleeding.
Treatment of uncomplicated ulcer:
– At an isolated thrust:
• Find NSAIDs, acetylsalicylic acid; stop
• Encourage the patient to avoid alcohol and tobacco
• omeprazole PO: 20 mg / day in the morning for 7 to 10 days or, failing that, cimetidine PO: 800 mg / once daily at bedtime for 7 to 10 days
– If frequent recurrences, unrelated to NSAID use and requiring repeated anti-secretory treatment: see eradication ofHelicobacter pylori.
Treatment of complicated ulcers:
Perforation:
The mention if intense epigastric pain and brutal, especially when there is abdominal defense. The risk of peritonitis is particularly important that the perforation occurs on a full stomach.
– Start with:
• to strict fasting patient; insert a gastric tube, suction if possible
• Insert an IV line and hydrate (alternate 5% glucose and Ringer’s lactate)
• hyoscine butylbromide IV or IM: 10 to 20 mg to be repeated every 8 hours if necessary
• omeprazole IV infusion: 40 mg / day to spend 20 to 30 minutes or, failing that, IV cimetidine 1600 mg by continuous infusion over 24 hours
– Refer to the surgeon if the patient has eaten within 6 hours of pain or no improvement within 12 hours despite medical treatment.
– Continue this treatment for 3 days then resume oral feeding if the perforation occurs on an empty stomach and the patient’s condition improves within 12 hours. Can undertake a PO treatment to eradicate Helicobacter pylori (see below).
Gastrointestinal Bleeding:
Externalization of black stools (melena) and / or vomiting blood (haematemesis).
In 80% of cases, stopping the bleeding is spontaneous.
– Insert a gastric tube suction and intravenous (16G).
If the hemodynamic status is good (normal pulse and TA):
– Hydrate (Ringer Lactate), monitor, let fasting 12 hours.
– In the absence of active bleeding, resume feeding after 12 hours.
Gastric lavage with cold water is not essential but may help evaluate persistence of bleeding.
If bleeding persists (haematemesis) and / or if the haemodynamic state deteriorates (rapid pulse, low BP):
– Intensive care and transfusion according to the extent of bleeding.
– Emergency surgical treatment.
Most ulcers related to infection by Helicobacter pylori. If the diagnosis is vraissemblable ulcer, eradication of the germ should be considered for patients with frequent recurrences requiring repeated anti-secretory treatment or in case of complicated ulcers (perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding) to eliminate the risk of recurrence .
Once past the acute phase, prescribe one of the following treatments:
“Metronidazole PO can be replaced by tinidazole PO: 1 g / day in 2 divided doses. “
Remarks:
– Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and NSAIDs (indomethacin, ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc.) are cons-indicated in patients suffering or having a history of ulcer.
– Omeprazole is as effective PO in IV.
Dyspeptic disorders
Clinical signs:
Epigastric discomfort or pain occurring at mealtimes, often accompanied by bloating, feeling of heaviness, nausea.
These disorders are usually functional in nature, possibly related to stress but not with the level of stomach acid (antacids and antisecretory are ineffective). Their resolution is spontaneous general.
Treatment:
If symptoms persist, symptomatic short-term treatment may be considered:
Metoclopramide PO in 3 divided doses, 1/2 hour before meals for 2 to 3 days
can be useful especially in cases of nausea, vomiting, bloating, etc.
Children over 20 kg: 0.4 mg / kg / day
Adult: 15 to 30 mg / day
In adults, hyoscine butylbromide PO: 30 mg / day in 3 divided doses, 1/2 hour before meals for 2 to 3 days may be useful, particularly in cases of spasmodic pain.
Note: find and deal with possible intestinal parasites (taeniasis, ascariasis, hookworm, giardiasis, amoebiasis).

You must be logged in to post a comment.