RA is an autoimmune inflammatory disease of the overall connective tissue predominantly synovium. It is the most common chronic inflammatory rheumatism. The female is strong (sex ratio 1/4). The peak frequency is premenopausal.
1- Clinic:
– Adverse distal joint, bilateral and symmetrical (arthritis)
– The most frequently affected joints: wrists, hands (metacarpophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal), the front feet, knees and sometimes métatarsophalagiennes The distal interphalangeal (DIP) are met.
– Tenosynovitis flexors (swelling of the palms, crepitus in palmar flexion, sd carpal tunnel)
– Insidious and progressive beginning. Must be advanced for more than 6 weeks. Chronic if> 3 months
– Usually the thoracolumbar spine and sacroiliac are respected
– Gradually joint and ligament injuries lead to permanent deformation
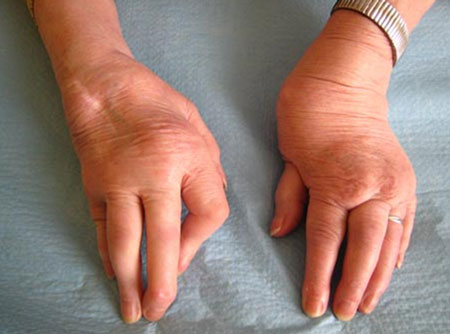
– Deformation of the hand posterior subluxation of the ulnar head with mobility piano key (threatening the extensor tendons); gooseneck finger (the most common and most annoying); deviation of the fingers Ulnar wind
– There is a risk of tendon rupture (extensors)
– Infringement of the foot (90%): hallux valgus deformity of the big toe and claw of the other toes (foot triangular characteristic)
– The TMJ arthritis (TMJ) are highly suggestive of PR
– Involvement of the cervical spine is common (posterior neck pain). C1-C2 subluxation is typical, it evolves into an anterior dislocation. But neurological complications are rare (occipital neuralgia, spinal cord compression).
2- Biology and Histology:
– VS biological inflammatory syndrome with high leukocytosis normal or high (25%). Normal VS (10%) does not eliminate the diagnosis. A hyperthrombocytose is found in 20% of cases.
– Rheumatoid factor: self-Ac IgG IgM (Fc). They are not specific to the PR. Often negative in the first months of evolution. Latex Test (1 / 80th); Waaler-Rose (1/64 °). They may sensitive (80% after 2 years) and low specificity. It can be detected in other connective (lupus syndrome Sjogren) or chronic infectious diseases (endocarditis Osler, hepatitis C, Kala-azars)
– Anti-keratins Ac (antistratum corneum or anti-fillagrin) are highly specific (99%) but inconstant (sensitivity 44%)
– Other self-Ac Ac antiperinuclear (sensitive and specific enough); antinuclear factor (FAN); anti-RA ac 33
– HLA typing: HLA DR4 is present in 60% of RA. It has a prognostic value
– Synovial fluid: inflammatory types; the complement assay (which is low) and rheumatoid factor has no interest. The ragocytes are PNN with cytoplasmic inclusions). A variegated form lymphocyte dominance can be met.
– Biopsy of synovial: only useful in atypical forms (mono-arthritis). Synovitis is nonspecific and is characterized by hypertrophy of synovial villi and multiplication of fringes. Hyperplasia of synovial villi. The presence of rheumatoid nodules intrasynoviaux is exceptional.
3- Radiological signs:
– Often absent at the beginning (is visible only 1 or 2 years of evolution)
– Then fusiform thickening of soft tissue periarticular
– And increased radiation transparency of the epiphysis (demineralization or osteoporosis band)
– More late (but more evocative) -> periarticular erosions (blurred or notched) to capsular synovial insertion (4th, 5th metatarsal, ulnar styloid, scaphoid)
– The subchondral geodes are sometimes early (first sign to appear)
– Finally, the overall narrowing of the joint space translates cartilage destruction
– Bone condensations and ostéophytoses are absent (except stage arthropathy late sequelae)
– F specific radiological elms
* Rheumatoid carpite: first causes demineralization, pinching interlining, geodes. Then carpite amalgamating with osteolysis and condensation.
* Hand in spyglass (shriveled fingers): very advanced form with osteolysis of the metacarpals and phalanges.
4- Extra-articular manifestation:
– Rheumatoid nodules (15%), subcutaneous (swelling firm and painless to the hands, Achilles tendon …). The visceral nodules are rare.
– Vasculitis: Raynaud’s syndrome; necrotizing vasculitis; purpura, ulcers; mononeuritis
– Felty’s syndrome (splenomegaly leukoneutropenia +);
– Leukemia
– Caplan syndrome: pneumoconiosis (silicosis with intrapulmonary rheumatoid nodules)
– Interstitial diffuse (20%)
– Bronchiectasis (DDB) are common in CT (30%)
– Violations of the serous (pleural, pericardial effusion)
– Sjögren’s syndrome (15%)
– Secondary Amyloidosis AA (5%) late complications
5- Background processing:
– The basic treatment should be started as soon as possible; it blocks the disease; verify the efficacy after 3 months; if no efficiency must increase the dose, change treatment or to an association
– Methotrexate: against-indicated in pregnancy, infection or chronic liver disease (hepatotoxic). Regular monitoring of albuminuria and creatinine and the transaminasémie (risk of cytolytic hepatitis). effective contraception.
– Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil®): synthetic antimalarial; risk of damage to the retina (electroretinogram systematic the first year and examination of color vision every 3 months). Is always used in combination
– Sulfasalazine (Salazopyrine®) monitoring counts liver function tests and platelet counts
– Gold salts (Allochrysine®) control proteinuria and platelet count before each injection
– D-penicillamine (thiol compounds)
– Anti-TNF: these side effects are serious infections, an induced lupus, an abortion
– The crenotherapy is against-indicated thrust
Biotherapy is effective
Pejorative factors:
* Acute onset polyarticular
* Extra-articular Achievement
* Early radiographic bone erosion
* VS and very high CRP
* EN early (<6 months) and high
* HLA-DR ß1 04
* Poor response to DMARD therapy
* High socioeconomic status
+ Diagnostic ACR criteria: arthritis affecting at least 3 joints (PIP, MCP, MTP, wrist, knee, ankle or balanced) lasting for at least 6 weeks, morning stiffness of more than 1 hour (> 6 weeks ), rheumatoid factor, rheumatoid nodules and radiographic changes (osteoporosis band erosions). 4 positive signs are sufficient for diagnosis
Pannus -> synovial proliferation

You must be logged in to post a comment.