Warning:
• The PAO can be fatal (asphyxia, serious rhythm disorder) hospitalize ++.
• Treatment is symptomatic and etiologic (underlying heart disease and triggering factor).
• It is a turning during the development of heart disease.
Clinic:
– Dyspnea asphyxia often beginner night, preceded by paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea episodes with cough, laryngeal crackles, orthopnea, chest tightness.
– Expectoration frothy, hémoptoïque, airy.
– Find signs of seriousness: tachypnea, drawing, cyanosis, impaired consciousness, slow pulse.
– Bilateral crackles sometimes going back to the heights.
– Usual Tachycardia, gallop left, functional mitral regurgitation (except mitral stenosis).
Additional tests at the bedside:
– ECG: regular sinus tachycardia; sometimes signs directing to a cause: Quick AF, signs of necrosis or ischemia … not disconnect the patient ++ (electrodes to 4 members).
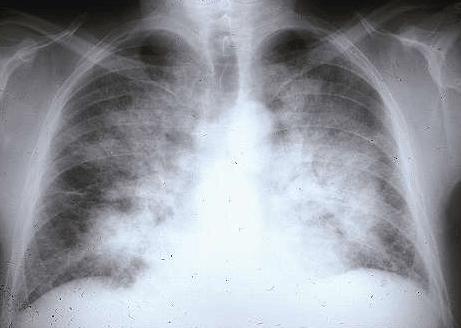
– Chest X-ray (if performed): alveolar edema in butterfly wings, pleurisy, possible cardiomegaly.
– Arterial blood gas (if performed): shunting with hypoxemia, hypocapnia, respiratory alkalosis or early acidosis.
To behave:
– Calm the patient.
– Implementation sitting, legs dangling.
– NATISPRAY [NTG], 0.30, 2 puffs sublingual.
– Lasix [furosemide], an intravenous, 80 mg (4 bulbs).
– Oxygen mask.
– Call the ambulance for admission in ICU.
OAP “standard”:
– Turning the scope, chest X-ray.
– Oxygen 6 l / min.
– Stop negative inotropic drugs.
– Infusion for injection Lasix [furosemide] or Burinex [bumetanide] IVD according to clinical response, urine output and blood pressure.
– Supplementation potassium.
– RISORDAN IV: 2 to 5 mg / time.
– Heparin low molecular weight for prevention of thromboembolism.
– Treatment of myocardial ischemia (possibly revascularization angioplasty type), arrhythmia (slow fast ACFA), a thrust of HTA …
– Relais diuretics IV: passing per os.
– Strict salt-free regime.
OAP serious, even asphyxia:
– Anyway, resuscitation idem, more power is positive inotropic drugs.
– If hypotension, no nitrates.
– Intubation-ventilation if necessary.
– Or even use norepinephrine against drive-by intra-aortic balloon …

You must be logged in to post a comment.