Tag: Atrial
-
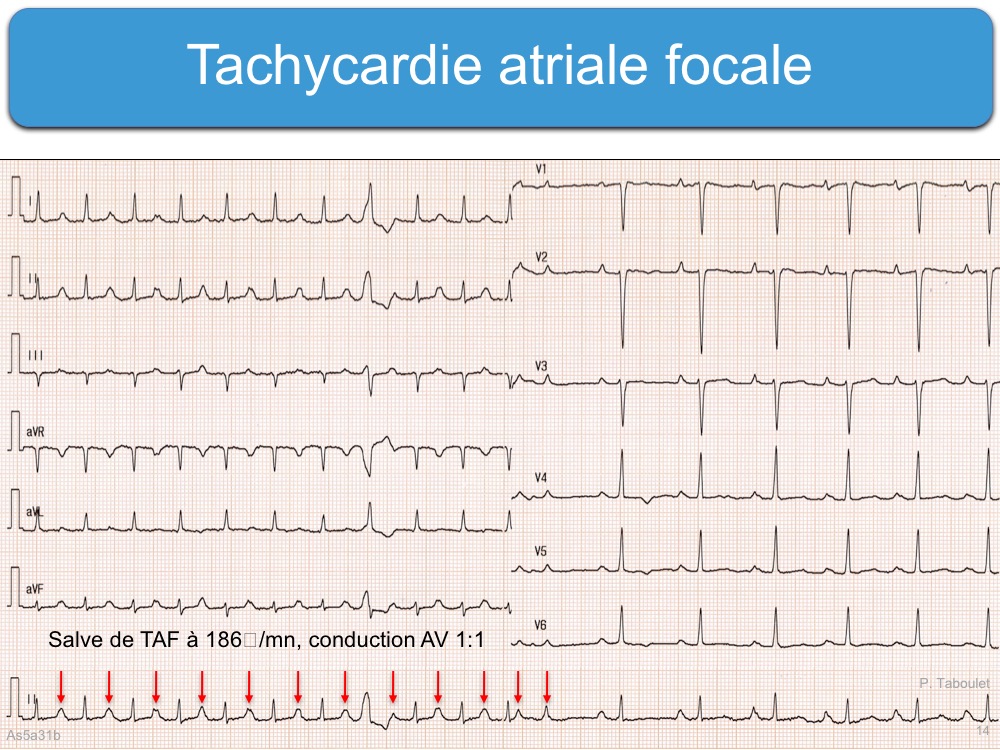
Atrial Flutter and Atrial Tachysystole
—
by
ATRIAL FLUTTER: CLINICAL SIGNS: * none. * or asthenia and moderate dyspnea, palpitations or uncomfortable chest tightness. * or inaugural lipothymia or even syncope of Adams-Stokes. * paroxystic tachycardia, by access or permanent, regular at 150 / min (in the mode 2/1) or 100 / min (3/1). * slowed by the massage of a single carotid sinus for 20 seconds. * complications: the…
-

Atrial Fibrillation
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * irregular heartbeat more or less fast between 60 and 160 / min with variable amplitudes, permanent or paroxysmal. * no functional signs. * or asthenia and moderate dyspnea. * or palpitations or oppressions unpleasant, paroxysmal. * or inaugural lipolysis or even syncope type Adams-Stokes. * look for signs of valvulopathy (especially mitral) on auscultation. * complications : Functional or organic angina…
-

Vitamin K antagonist
– The VKA act through competitive inhibition of hepatic synthesis of certain clotting factors vitamin K-dependent: prothrombin (II); proconvertin (VII); factor IX; Factor X (X). – Protein C and Protein S (coagulation inhibitors) are also vitaminic-K-dependent. – Two families derivatives indandione (fluindione or Previscan) and coumarin (acenocoumarol or Sintrom®; warfarin or Coumadin®). – Fixing to…
You must be logged in to post a comment.