Tag: Pain
-

Acute Thoracic Pain
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * suspicious signs , apart from an obvious clinical picture: – history of coronary heart disease. – pains that last for several seconds at least. – pain dependent on breathing. – Pain not reproducible by palpation and mobilization of the rib cage. – associated digestive symptoms. – risk factors for thromboembolic disease. * signs of gravity :…
-
Non-cancerous pain
“Pain is a perceptive, unpleasant, multidimensional, sensory, emotional phenomenon that signals the possibility of physical harm. (Executioner) After 3 to 6 months of progression, a pain passes from the state of acute symptom to the state of chronic symptom. We distinguish 3 components in a painful phenomenon: – The nociceptive component : The pain responds to…
-
Chronic abdominal pain
It is abdominal pain that persists, repeats itself and become chronic outside of an emergency context. Irritable bowel or functional colopathy are the most common pathologies. The rarer causes are numerous and difficult to diagnose, the obsession of the general practitioner and the urgent request of the painful patients will lead to the realization of many complementary…
-

Acute abdominal pain of the child
Acute abdominal pathology in children is a common cause of admission to emergencies. Interrogation (of the child and his entourage) and a complete clinical examination are essential for the diagnosis, which is quite often difficult because of certain hazards: absence of anamnesis, difficulty of the examination conditions, absence of control an ingestion or inhalation of…
-

Acute abdominal pain of the adult
Acute abdominal pain in adults is common. Their support still remains difficult today and source of error due to: – the multiplicity of etiologies: more than a hundred disorders; – the clinic sometimes incomplete, atypical or misleading: extradigestive affections, “aberrant” irradiations or variables in time; – in general medicine, the initial clinical examination must make it…
-

Post-exercise muscle pain
—
by
Introduction: Aches are frequent during the practice of physical activities and sports. They occur after intense and / or unusual eccentric muscle exercise, within 12 to 48 hours. The exact term used in the literature is that of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) or delayed onset muscle pain. Clinical signs: Interrogation: Pains occur 12 to 48 hours…
-
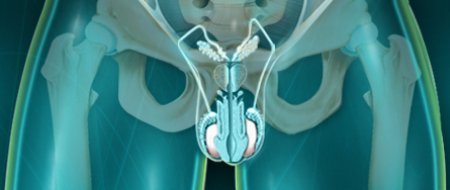
Testicular Pain
—
by
Testicular pain may be testicular irradiation or represent a usually retroperitoneal disease. Acute testicular pain should discuss first twisting of the spermatic cord, absolute surgical emergency. Chronic scrotal pain, that is to say manifesting for more than six months, can have multiple causes within a rigorous clinical approach. Physiology: “The genital-femoral nerve from the sacral…
-
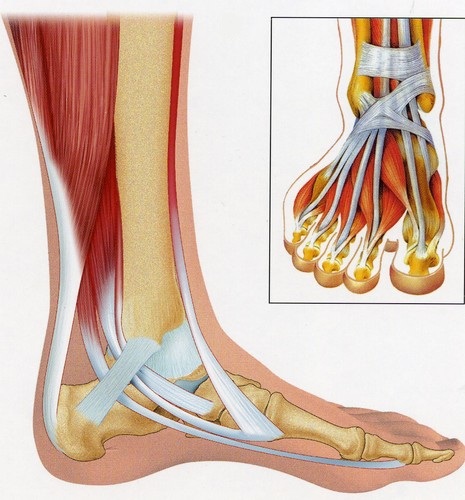
Foot Pain and Ankle
—
by
FOOT OSTEOARTHRITIS: All joints of the ankle and foot may have a degenerative disease. Outside of hallux rigidus, primary osteoarthritis is exceptional in the foot. Osteoarthritis is secondary to trauma (fractures, dislocations, sprains with osteochondral fracture) to strain (chronic ankle instability), to primitive static or acquired disorders or destructive arthropathy (inflammatory, infectious, neurological, metabolic, hemophilic,…
-
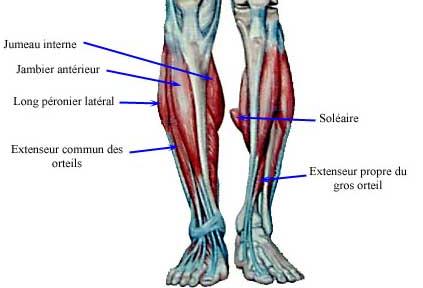
Calf Pain
—
by
This pain is usually muscle and its mechanism may be ischemic, inflammatory, or metabolic. For understanding the pain of muscular origin, we can also see chapter Myalgia and cramps. But sometimes the pain of bone origin or joint. Three situations are possible: – The pain is acute and brutal, and it is often a medical…
You must be logged in to post a comment.