Tag: Troubles
-

Psychic Troubles
—
by
Before symptoms of psychiatric pace, think about organic causes: neurological disorders can make believe psychosis, hyperthyroidism can manifest as an anxiety condition, hypoglycemia by a state of agitation, etc. Conduct a careful clinical examination, with particular attention to somatic history, even and especially if the patient is “known” to have a psychiatric history. Conversely, somatic…
-

Taste disorders (dysgeusia)
—
by
PHYSIOLOGICAL BASES: Taste strict sense is the sense that perceives the taste of dissolved substances in saliva. The perception of each individual flavor has a prime seat: the bitter and acid are especially seen in the soft palate, salty the anterior two thirds of the tongue and the sweet on any language. Sensory receptors are…
-

Gait disorders and falls in the elderly
—
by
INTRODUCTION: The physiological walking requires the smooth functioning of afférentiels sensory systems, vestibular, visual, peripheral nerves, muscles, and the integrity of the motor structures, extrapyramidal and cerebellar. Despite its complexity, it is an essentially automatic activity involving a vast system of controls and checks. Too common in the elderly, falls should always be considered a…
-

Troubles monthlies
—
by
Menstrual cycle disorders are a very frequent reason for consultation, from puberty to menopause. The pathophysiological mechanisms are multiple, requiring semiological analysis cycle disorder. Some setting reminders are needed (Box 1) Box 1. Definitions Amenorrhoea: it is defined by the lack of monthlies for more than three months. It is called primary when the patient…
-
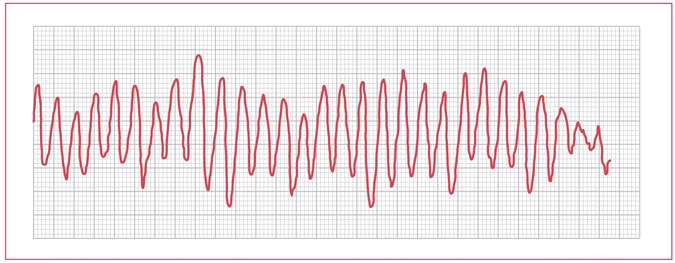
ECG heart rhythm disorders
1- Premature atrial: – The premature born prematurely, the P wave is different morphology of the wave normal P; – The following QRS complex is fine, except in case of branch block (organic or functional) or and preexcitation. – ESA is followed by compensatory rest – Sometimes when ESA occurs very early, it is blocked…
-
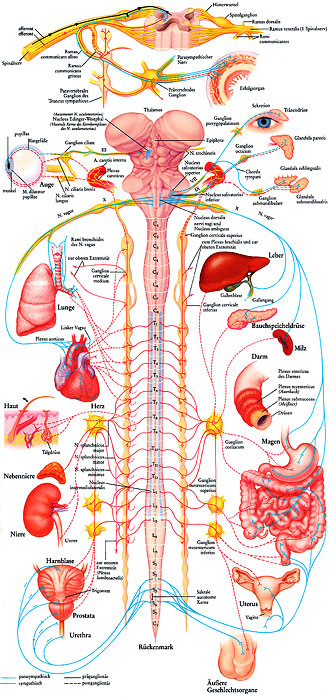
Vegetative functions
1- pupillary disorders: Argyll-Robertson syndrome (syphilis): small pupils, irregular, uneven, the pupillary light reflex is abolished (direct and consensual), while the accommodation-convergence is preserved. * Adie Syndrome: unilateral pupillary areflexia tendon + anomalies. The affected pupil is moderately dilated, direct and consensual RPM is completely or almost completely abolished. Slow pupillary contraction and relaxation. *…
You must be logged in to post a comment.