I – Introduction:
A- Causes of conjunctivitis:
 The causes of conjunctivitis can vary, but are often associated with factors such as infections, allergies, and environmental irritants. Viral conjunctivitis is usually caused by viruses such as those that cause the common cold or flu, while bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilus influenzae. Allergies can also cause conjunctivitis, in response to allergens such as dust, dust mites, animal hair and pollens. Also, environmental irritants such as smoke, dust, chemicals used for contact lenses, and cosmetics can also cause conjunctivitis. Certain pre-existing medical conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and immune deficiency can also increase the risk of developing conjunctivitis. It is important to determine the underlying cause of conjunctivitis for proper treatment and effective management of the condition.
The causes of conjunctivitis can vary, but are often associated with factors such as infections, allergies, and environmental irritants. Viral conjunctivitis is usually caused by viruses such as those that cause the common cold or flu, while bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilus influenzae. Allergies can also cause conjunctivitis, in response to allergens such as dust, dust mites, animal hair and pollens. Also, environmental irritants such as smoke, dust, chemicals used for contact lenses, and cosmetics can also cause conjunctivitis. Certain pre-existing medical conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and immune deficiency can also increase the risk of developing conjunctivitis. It is important to determine the underlying cause of conjunctivitis for proper treatment and effective management of the condition.
B- Importance of treating conjunctivitis:
It is important to treat conjunctivitis because of its potentially negative effects on vision and overall eye health. Conjunctivitis can cause eye irritation and pain, as well as redness and excessive secretion. If left untreated, conjunctivitis can also lead to an increased risk of more serious eye infections, such as uveitis, keratitis, and endophthalmitis. In addition, conjunctivitis can cause discomfort and reduced quality of life due to eye pain and irritation, as well as difficulty seeing clearly. It is therefore important to consult a doctor for prompt diagnosis and treatment of conjunctivitis, in order to minimize the risks to eye health and improve the quality of life of patients. Treatment may include medications such as antibiotics, antihistamines, and corticosteroids, as well as home remedies to relieve symptoms. Finally, it is important to prevent the spread of conjunctivitis by practicing good eye hygiene, avoiding close contact with people with conjunctivitis, and washing your hands regularly.
II- Symptoms of conjunctivitis:
A- Redness of the eye:
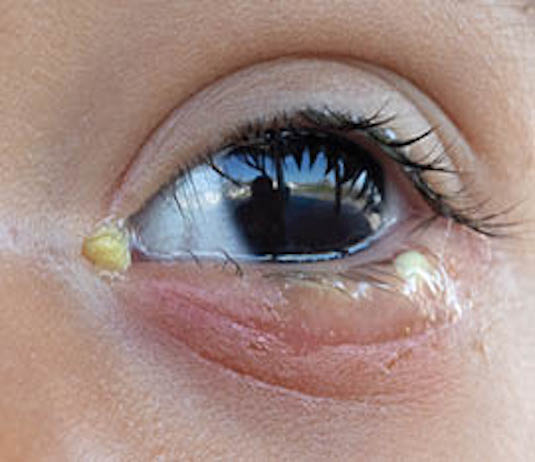
Eye redness is a common symptom of conjunctivitis, but can also be caused by other eye conditions such as eye irritation, eye allergies, and eye infections. The redness is often accompanied by other symptoms such as irritation, pain, itching and excessive eye secretion. In many cases, eye redness can be treated at home with home remedies such as hot and cold compresses and soothing eye drops. However, it is important to see a doctor if the redness persists or worsens, as this may indicate a more serious condition requiring medical treatment.
In addition, redness can also be caused by factors such as fatigue, lack of sleep, excessive alcohol consumption, and reaction to certain medications. It is therefore important to consider all potential factors to determine the underlying cause of eye redness. Sometimes the redness can also be a sign of a systemic condition such as multiple sclerosis or sarcoidosis, so it’s important to see a doctor for a complete eye exam. Finally, to prevent eye redness, it is important to practice good eye hygiene, regulate the amount of time spent in front of screens, and protect the eyes from environmental irritants.
B- Eye secretions:
Oily eyes are a common symptom of conjunctivitis, but can also be caused by other conditions such as eye allergies, eye infections, and environmental irritants. Secretions can be clear and watery or thicker and yellowish. They can cause irritation, pain and discomfort, as well as temporary vision problems.
It is important to treat eye secretions promptly to prevent their spread and potential complications. Treatments can include medications such as antihistamines, antibiotics, and corticosteroids, as well as home remedies such as hot and cold compresses and soothing eye drops. Also, to prevent oily eyes, it is important to practice good eye hygiene, wash your hands regularly, and avoid environmental irritants.
It is also important to note that secretions from the eye can be a sign of more serious conditions such as iridocyclitis, keratitis and uveitis, so it is important to seek medical attention if the secretions persist or worsen. Finally, to prevent discharge from the eye, it is important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention when needed for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
C- Eye irritation:
Eye irritation is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, such as conjunctivitis, eye allergies, environmental irritants, and eye infections. Symptoms of eye irritation may include itching, burning, pain, and redness of the eye. In some cases, the irritation can also lead to excessive eye secretion.
It is important to treat eye irritation to prevent potential complications and to improve quality of life. Treatments can include medications such as antihistamines, antibiotics, and corticosteroids, as well as home remedies such as hot and cold compresses and soothing eye drops. Also, to prevent eye irritation, it is important to practice good eye hygiene, wash your hands regularly, and avoid environmental irritants.
In some cases, eye irritation can also be caused by factors such as fatigue, lack of sleep, excessive alcohol consumption, and reaction to certain medications. It is therefore important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Finally, to prevent eye irritation, it is important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention when needed for prompt and effective treatment.
D- Sensitivity to light:
Light sensitivity, also known as photophobia, is a common symptom associated with various eye conditions, including conjunctivitis, eye infections, eye injuries, and migraines. This sensitivity can cause pain and discomfort when a person is exposed to light, including bright light or sunlight.
Light sensitivity can negatively impact a person’s quality of life by limiting daily activities and disrupting sleep. It is therefore important to treat the underlying cause of light sensitivity to prevent potential complications and improve quality of life.
Treatment for light sensitivity will depend on the underlying cause and may include medication such as anti-inflammatories, anticonvulsants and painkillers, as well as home remedies such as goggles and cold compresses for pain. eyes. Also, to prevent light sensitivity, it is important to practice good eye hygiene, protect yourself from bright light, and avoid environmental irritants.
Finally, to prevent light sensitivity, it is important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention when needed for proper diagnosis and treatment. Prompt and effective treatment can help prevent potential complications and improve a person’s quality of life.
III- Risk factors for conjunctivitis:
A- Recurrent eye infections:
Recurrent eye infections can cause a great deal of discomfort and incapacity for those who have them. These are infections that come back frequently and can be caused by various conditions, such as conjunctivitis, allergies, tear gland disorders, and corneal conditions.
Recurrent eye infections can lead to many symptoms such as itching, eye pain, redness, eye discharge, and increased sensitivity to light. Besides causing discomfort, recurring eye infections can also lead to more serious complications such as bacterial infections, Korean ulcers, and loss of vision if not treated properly.
It is important to see a doctor if eye infections recur to identify and treat the underlying cause. Treatment may include medications such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, as well as interventions such as surgery to correct tear gland disorders.
Finally, to prevent recurrent eye infections, it is important to practice good eye hygiene, protect yourself from environmental irritants, and avoid behaviors that can compromise eye health, such as sharing eye care items. By taking the appropriate measures, it is possible to prevent recurrences of eye infections and maintain good vision health.
B- Contact with allergens:
Contact with allergens can be a major factor in causing allergic conjunctivitis. Allergens can include pollens, dust mites, molds, pets, chemicals such as cosmetics and cleaning products, and foods. When an individual is exposed to one of these allergens, the immune system reacts by producing antibodies called immunoglobulin E, which can cause an allergic response.
Symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis can include itching, eye pain, redness, eye discharge, and increased sensitivity to light. If left untreated, these symptoms can worsen and cause more serious complications such as bacterial infections, ulcers, and loss of vision.
It is important to consult a doctor in case of ocular allergic reactions in order to obtain an adequate diagnosis and treatment. Treatment may include medications such as antihistamines to relieve symptoms, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and anti-allergy eye drops to prevent allergic reactions.
Finally, to prevent contact with allergens, it is important to consider risk factors such as season, climate and activities that may cause allergic reactions. By taking the proper steps to avoid allergens, allergic reactions can be prevented and good eye health can be maintained.
C- Wearing contact lenses:
Wearing contact lenses can be a risk factor for conjunctivitis. Contact lenses can easily collect bacteria and germs, which can lead to eye infection. Infections can include bacterial, fungal or viral conjunctivitis which can cause symptoms such as itching, eye pain, redness, eye discharge and increased sensitivity to light.
People who wear contact lenses should follow a number of precautions to minimize the risk of infections. This may include regularly cleaning lenses, regularly replacing lenses, using cleaning solutions recommended by an ophthalmologist, and suspending lens wear if you experience eye symptoms.
It is also important to see a doctor if you experience eye symptoms for proper diagnosis and treatment. Medications may include antimicrobial eye drops to treat infections, antihistamines to relieve symptoms, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Finally, to prevent eye infections related to contact lens wear, it is important to follow the lens wearing instructions recommended by an ophthalmologist and not to wear lenses for longer than recommended. By taking the proper steps to prevent contact lens-related infections, it is possible to maintain good eye health and enjoy the comfort and freedom that contact lens wear brings.
D- Pre-existing medical conditions:
Pre-existing medical conditions can increase the risk of conjunctivitis. Certain conditions such as allergies, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, atopic dermatitis and dry eyes can weaken the immune system and leave the eyes more vulnerable to infections.
Additionally, certain conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, and epithelial dystrophy can lead to increased dry eyes, which can cause symptoms such as itching, eye pain, redness, eye discharge, and tenderness. increased in light.
It is important to see a doctor if you have any pre-existing medical conditions and develop symptoms of conjunctivitis. Your doctor may recommend medications such as moisturizing eye drops to treat dry eye and relieve symptoms, or medications such as antihistamines to treat allergies.
Finally, to prevent conjunctivitis related to pre-existing medical conditions, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for managing your condition, use recommended moisturizing eye drops, and maintain a good level of general health. By taking the appropriate measures to prevent conjunctivitis related to pre-existing medical conditions, it is possible to maintain good eye health and limit the risk of infections.
IV- Diagnosis of conjunctivitis:
A- Ophthalmological examination:
The ophthalmological examination is an important examination for diagnosing and treating conjunctivitis. During the exam, the ophthalmologist will examine the eyes to assess the health of the conjunctiva and cornea. He will also inspect the eyelids to look for signs of infections or other problems.
The ophthalmologist can perform tests such as biometrics to measure eye shape and depth, tonometry to measure intraocular pressure, and pachymetry to measure corneal thickness.
In addition to the physical examination of the eyes, the ophthalmologist may also perform additional diagnostic tests such as light sensitivity tests, pupillary reflex tests, and fluorescence tests to assess corneal health and the conjunctiva.
If conjunctivitis is caused by an infection, the eye doctor may also perform a conjunctival smear to look for signs of bacteria or viruses.
The ophthalmological examination is important to correctly diagnose conjunctivitis and recommend the appropriate treatment. It is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist if you develop symptoms of conjunctivitis to avoid deterioration of eye health and prevent potential complications.
B- Additional diagnostic tests:
In addition to the eye examination, some cases of conjunctivitis may require additional diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause. The most common tests include:
1- Allergy screening tests: These may include skin tests, blood tests, and breath tests to determine if conjunctivitis is caused by an allergic reaction.
2- Imaging tests: Techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluoresceinography can be used to assess the condition of the cornea and conjunctiva.
3- Culture test: If the ophthalmologist suspects an infection, a conjunctival smear can be taken for bacterial or viral culture.
4- Blood test: In some cases, a blood test may be necessary to determine the presence of an underlying medical condition that may be causing conjunctivitis.
Additional diagnostic tests are important to determine the underlying cause of conjunctivitis and to recommend effective treatment. It is important to consult an ophthalmologist to discuss additional diagnostic tests that may be needed in your particular case.
V- Treatment of conjunctivitis:
A- Drug treatment:
Treatment for conjunctivitis depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, drug treatment is recommended to relieve symptoms and cure the condition. The most common drugs used to treat conjunctivitis include:
1- Antibiotic eye drops or ointments: If conjunctivitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be prescribed.
2- Antihistamine eye drops: If conjunctivitis is caused by an allergic reaction, antihistamine eye drops can be used to relieve symptoms and prevent future reactions.
3- Corticosteroid eye drops: In severe cases of allergic conjunctivitis, corticosteroid eye drops may be prescribed to relieve symptoms and prevent future reactions.
4- Antiviral eye drops: If conjunctivitis is caused by a viral infection, antiviral eye drops may be prescribed.
It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions about using these medications and not to stop the medication before the prescribed time has elapsed, even if the symptoms have disappeared. Medications can help cure the condition and prevent future recurrences.
B- Home remedies to relieve symptoms:
There are several home remedies that can help relieve the symptoms of conjunctivitis. Although these remedies are generally considered safe, it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. The most commonly used home remedies include:
1- Warm compresses: Warm compresses can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Simply soak a clean cloth in warm water and lay it over your closed eyes for 10-15 minutes.
2- Green tea: Green tea bags can be used to create cool compresses for the eyes. The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties of green tea can help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms of conjunctivitis.
3- Sea buckthorn oil: Sea buckthorn oil can help heal eye infections due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Just put a few drops of oil on a cotton ball and apply it on the eyes.
4- Aloe vera: The moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera can help relieve the symptoms of conjunctivitis. Just cut a leaf of aloe vera and squeeze the juice on a cotton ball to make eye compresses.
5- Eye wash: The eyes can be washed with a saline solution to remove irritants and reduce inflammation. It is important to wash your hands before washing your eyes to avoid transmission of infection.
It is important to remember that home remedies cannot cure conjunctivitis, but can simply help relieve symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention for proper treatment.
C- Prevention of conjunctivitis:
Prevention of conjunctivitis is important to avoid complications and recurrences. Here are some preventative measures to consider:
1- Wash your hands frequently: This can help reduce the risk of eye infection by killing germs and bacteria on your hands.
2- Avoid touching your face: Avoid touching your eyes, nose or mouth without washing your hands.
3- Avoid contact with people with conjunctivitis: Avoid sharing personal items with people with conjunctivitis, such as towels or eye drops.
4- Do not wear soft contact lenses: If you have conjunctivitis, it is best not to wear soft contact lenses. Lenses can trap bacteria and germs, which can make infection worse.
5- Avoid environmental irritants: Avoid irritants such as cigarette smoke, dust and pollution.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing conjunctivitis or getting it again. It is always important to consult a doctor in case of persistent or recurring symptoms in order to receive appropriate treatment.
VI- Conclusion:
A- Summary of key information:
Conjunctivitis is a common eye condition that can cause redness, eye discharge, irritation, and sensitivity to light. There are several causes of conjunctivitis, such as recurrent eye infections, contact with allergens, wearing contact lenses, and pre-existing medical conditions.
An eye exam is needed to diagnose conjunctivitis, and additional diagnostic tests may be needed to determine the underlying cause. Drug treatment for conjunctivitis depends on the underlying cause, but may include topical medications, such as eye drops or ointments.
Home remedies can help relieve symptoms of conjunctivitis, such as wearing sunglasses to reduce sensitivity to light and placing a warm compress on the eyes to reduce irritation. Prevention of conjunctivitis can be achieved by following simple measures such as frequent hand washing, avoiding environmental irritants, and avoiding contact with people with conjunctivitis.
In summary, conjunctivitis is a common eye condition that can be caused by several different factors and requires an ophthalmological examination for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment options include topical medications, home remedies, and preventative measures to reduce the risk of recurrence.
B- Importance of prevention and rapid treatment of conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis is a common eye condition that can cause significant pain and irritation. If not treated quickly, it can also cause permanent damage to eyesight. Therefore, it is important to prevent the onset of conjunctivitis and to seek immediate treatment if symptoms occur. Prevention can include simple measures such as washing your hands regularly, avoiding touching your eyes with your fingers, and sharing personal items such as towels or glasses. If a person has symptoms of conjunctivitis, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. At the end of the day,
C- Advice to avoid the transmission of conjunctivitis:
The transmission of conjunctivitis can be prevented by adopting certain strict hygienic practices. Here are some tips to avoid the transmission of conjunctivitis:
1- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before touching your eyes.
2- Avoid touching your eyes with your fingers, tissues and other objects.
3- Avoid sharing personal items such as glasses, towels or cosmetics.
4- Do not use cosmetic products that have been in contact with infected eyes.
5- During the healing period, avoid contact with other people, especially children and vulnerable people.
6- Wear protective goggles to avoid contact with allergens and irritants.
7- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when sneezing or coughing.
8- Do not use contact lenses until conjunctivitis is cured.
By following these tips, you can reduce the risk of conjunctivitis transmission and maintain good eye hygiene. It is important to consult a doctor if symptoms of conjunctivitis occur in order to obtain adequate treatment.
Leave a Reply