I – Introduction:
A- Presentation of erysipelas and its symptoms:
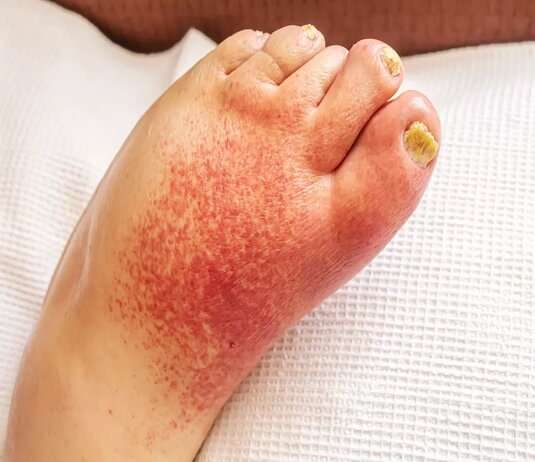
Erysipelas is a bacterial skin infection that can be very painful and cause serious complications if not treated quickly. It is usually manifested by a sharp and hot redness of the skin, accompanied by swelling, pain and a sensation of heat. This redness often spreads rapidly, forming an inflammatory plaque that can reach several centimeters in diameter. Erysipelas can affect any part of the body, but is most common on the legs, arms, face or neck. Other symptoms may also occur, such as chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, or severe fatigue. If in doubt,
B- Importance of treating this skin infection quickly:
 It is essential to treat erysipelas quickly because this skin infection can cause serious complications if not treated in time. If the infection spreads, it can reach the lymph nodes, blood, or subcutaneous tissue, leading to life-threatening complications such as sepsis. Additionally, erysipelas can recur if not treated properly, with repeated infection potentially causing permanent damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Additionally, the pain and discomfort associated with erysipelas can have a significant impact on the affected person’s quality of life, leading to temporary or permanent inability to work, as well as significant stress and anxiety. In sum,
It is essential to treat erysipelas quickly because this skin infection can cause serious complications if not treated in time. If the infection spreads, it can reach the lymph nodes, blood, or subcutaneous tissue, leading to life-threatening complications such as sepsis. Additionally, erysipelas can recur if not treated properly, with repeated infection potentially causing permanent damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Additionally, the pain and discomfort associated with erysipelas can have a significant impact on the affected person’s quality of life, leading to temporary or permanent inability to work, as well as significant stress and anxiety. In sum,
C- Objective of the article: inform about erysipelas and its treatments:
The purpose of this article is to educate about erysipelas and its treatments, providing accurate and helpful information to help those affected by this skin infection understand the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. We want to offer a comprehensive and reliable resource on this topic to help people affected by erysipelas make informed decisions about their health, understanding the benefits and risks of each treatment option. In addition, we aim to raise awareness about erysipelas among the general public, so that everyone can recognize the symptoms of this skin infection and take the necessary steps to prevent or treat it quickly. In summary, our goal is to offer a comprehensive and accessible resource on erysipelas and its treatments,
II- What is erysipelas?
A- Definition of erysipelas:
Erysipelas is a skin infection caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pyogenes. It is manifested by a sharp and hot redness of the skin, which can quickly spread to form an inflammatory plaque. Erysipelas is most commonly seen on the legs, but can also affect other parts of the body such as the arms, face, or neck. This infection is common in people with damaged skin, impaired blood circulation, or weakened immune systems. Common symptoms of erysipelas include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, pain, and swelling. Diagnosis is usually based on the patient’s symptoms and medical history, as well as laboratory tests if necessary. Treatment for erysipelas usually involves the use of antibiotics, along with measures to relieve symptoms. It is important to treat erysipelas promptly to avoid potentially serious complications.
B- Causes of infection:
Erysipelas is caused by a bacterium called Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. This bacterium is usually spread by contact with an infected person, or through an open wound on the skin. Infection can also occur when the bacteria enters the skin through cracks, cuts, or scratches, or when the skin is damaged by insect bites, burns, or rashes. People with impaired blood circulation, venous insufficiency, or weakened immune systems are more likely to develop Streptococcus pyogenes infection. Additional risk factors include obesity, diabetes, malnutrition, smoking, and intravenous drug use. In summary,
C- Risk factors:
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing erysipelas. One of the main factors is the presence of the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes in the skin, which can be spread by direct contact with an infected person, or through an open wound on the skin. People with impaired blood circulation, venous insufficiency, or weakened immune systems are more likely to develop Streptococcus pyogenes infection. Additional risk factors include obesity, diabetes, malnutrition, smoking, and intravenous drug use. People who have had surgery or have an open wound on their skin are also more likely to develop erysipelas. In addition, some professions, such as agricultural workers or people working in humid or dusty environments, may be at higher risk of infection. It is important to understand the risk factors for erysipelas in order to take steps to prevent or treat infection early.
D- Common symptoms:
Symptoms of erysipelas can vary from person to person, but there are some common symptoms that can help identify the infection. Early signs of erysipelas include bright redness and swelling of the skin, often accompanied by pain or tenderness. Affected areas may also become warm to the touch, and nearby lymph nodes may be swollen. Symptoms may appear quickly and worsen within hours, and blisters or blisters may also form. In more severe cases, fever, chills, fatigue, and nausea may also be present. It’s important to see a doctor if you have symptoms of erysipelas, as prompt treatment can help avoid complications and speed healing.
III- How to diagnose erysipelas?
A- Physical assessment and observation of symptoms:
Physical assessment and observation of symptoms are key to diagnosing erysipelas. The doctor will begin by examining the affected skin for signs of redness, swelling, and pain. It may also be helpful to check for swollen lymph nodes in the affected area. The doctor may also measure the body temperature to check if the patient has a fever. In addition to the physical exam, the doctor may also do blood tests or skin cultures to identify the presence of bacteria. Physical evaluation is an important process to determine if symptoms are caused by erysipelas or another condition. It is important to see a doctor as soon as possible if you have symptoms of erysipelas,
B- Complementary examinations:
In addition to the physical exam, additional tests may be needed to diagnose erysipelas and help determine the appropriate treatment. Blood tests may be done to check for bacteria in the blood and to monitor levels of inflammation. Tissue samples may also be taken for laboratory analysis to determine the species of bacteria responsible for the infection. Also, X-rays may be done to rule out the possibility of complications such as an underlying abscess or pneumonia. Additional tests can also be useful to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and ensure that the infection is not spreading. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for additional tests to facilitate the process of diagnosing and treating erysipelas. Prompt detection and management of infection can contribute to rapid recovery and a reduction in potential complications.
1- Bacteriological sampling:
Bacteriological sampling is a commonly used test to diagnose erysipelas and identify the species of bacteria responsible for the infection. The swab is usually done using a sterile swab that is rubbed over the surface of the affected skin. The samples taken are then cultured in the laboratory to allow identification of the pathogen. The results of bacteriological sampling are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis of erysipelas and help determine the appropriate treatment. It is important to note that carrying out a bacteriological sample may take a few days to provide definitive results. During this time, the doctor is likely to start treatment based on symptoms and physical exam. Bacteriological sampling is generally carried out in patients whose symptoms are severe or who present with possible complications. If you have symptoms of erysipelas, it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
2- Ultrasound:
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of the body’s internal organs. In the case of erysipelas, an ultrasound can be useful to detect potential complications, such as an underlying abscess. This exam can help the doctor determine the extent of the infection and plan the appropriate treatment. During the ultrasound, a medical imaging technician applies a gel to the area to be examined and uses a probe to emit sound waves. The sound waves bounce off internal organs and create images which are then examined by a radiologist. Ultrasound is a non-invasive and safe procedure that does not require x-rays. It can be performed on an outpatient basis and usually only takes a few minutes.
3- Scanner:
CT scan, also called computed tomography (CT), is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and a computer to produce detailed images of the body’s internal organs. In the case of erysipelas, a CT scan can be helpful in detecting complications such as an abscess or necrotizing fasciitis, a rare but serious form of soft tissue infection. The CT scan can also help the doctor determine the extent of the infection and plan the appropriate treatment. During the procedure, the patient lies on a table that slides through a donut-shaped ring, while the scanner emits X-rays to create images. The CT scan is a noninvasive procedure, but it does involve exposure to X-rays, so it’s important to discuss the potential risks with your doctor.
IV- Treatment of erysipelas:
A- Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are the main treatment for erysipelas. They are used to eliminate the bacterial infection that causes this skin condition. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics to treat erysipelas are penicillins and cephalosporins, which are effective against gram-positive bacteria. In some cases, broader-spectrum antibiotics can be used to treat more complicated bacterial infections. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding the dose, duration and frequency of taking antibiotics. Full antibiotic treatment is needed to prevent the infection from coming back. It is also important to take extra precautions to prevent the spread of infection, such as frequent hand washing and covering infected areas with a clean bandage. If you are diagnosed with erysipelas, it is important to take the antibiotics prescribed by your doctor and follow all recommendations for a full recovery.
1- Choice of drugs:
The choice of drugs to treat erysipelas depends on the severity of the infection, the patient’s response to antibiotics, and the patient’s medical history. Oral antibiotics are often used to treat milder cases of erysipelas, while intravenous antibiotics may be needed to treat more serious infections. Penicillins, such as penicillin G or flucloxacillin, are often the first choice for treating erysipelas because of their effectiveness against gram-positive bacteria. However, penicillin-allergic patients may be given cephalosporins, such as ceftriaxone or cefazolin, which are also effective against Gram-positive bacteria. In some cases, broad-spectrum antibiotics can be used to cover gram-negative bacteria or anaerobes, especially if complications are suspected. The choice of drugs should be made by a competent medical professional, taking into account the medical history and current condition of the patient.
2- Duration of treatment:
The duration of treatment for erysipelas depends on the severity of the infection and the patient’s response to treatment. In most cases, patients are treated with antibiotics for 10-14 days. Antibiotics are often given by mouth, but in more severe cases, hospitalization with intravenous administration may be required. If the patient responds well to antibiotic treatment, they may be allowed to go home and continue oral treatment. It is important that patients complete their full course of antibiotics, even if they feel better before the end of treatment. Stopping treatment prematurely can lead to a relapse of the infection and increase the risk of serious complications. In some cases, longer antibiotic treatment may be needed to prevent a relapse. Follow-up with a medical professional is essential to monitor the healing of the infection and ensure that no complications develop.
3- Precautions:
There are certain precautions you can take to avoid getting erysipelas. First of all, it is important to maintain good personal hygiene and treat small cuts and wounds quickly. Avoiding going barefoot outdoors can also help prevent infection. People with lymph edema or venous insufficiency should take steps to treat these conditions and reduce their risk of getting erysipelas. It is also important to follow antibiotic prescription instructions and complete the full treatment to avoid relapses and antibiotic resistance. If you have been diagnosed with erysipelas, avoid close contact with others to avoid spreading the infection. Finally, if you have symptoms of erysipelas,
B- Symptomatic measures:
In addition to antibiotics, there are certain symptomatic measures that can help relieve the symptoms of erysipelas. It is important to rest and elevate the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Applying cold or hot compresses can also help relieve discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce pain, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help reduce inflammation. It is also important to stay hydrated and follow a healthy diet to help the body fight infection. If erysipelas affects the legs, it may help to wear compression stockings to reduce swelling. Also, it is important to carefully monitor the affected area for any signs of complications, such as spread of infection or abscess formation. If you have symptoms of erysipelas, seek prompt medical attention for early diagnosis and treatment, and follow these symptomatic measures to relieve symptoms.
1- Rest:
Rest is an important measure to treat erysipelas, which is a potentially serious skin infection. The body needs time to fight infection, and rest allows the immune system to focus on this task. Also, rest reduces stress on the body, which can help prevent the spread of infection. In case of erysipelas, it is recommended to rest as much as possible and to limit physical activities. If the infection affects the legs, it may help to elevate the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Rest is also important to prevent complications, such as the spread of infection or abscess formation. In sum,
2- Raising the leg:
Leg elevation is a recommended measure to help treat erysipelas, a skin infection that can cause inflammation and pain in the affected area. Raising the leg helps reduce pressure in blood vessels and tissues, which can help reduce swelling and pain. This measure can be particularly useful in case of erysipelas of the lower extremities, because prolonged standing or sitting can aggravate swelling and cause blood stagnation. It is recommended to elevate the affected leg above the level of the heart, for example using a pillow or cushion. This measure can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as antibiotics or painkillers, to help relieve the symptoms of erysipelas. In sum,
3- Analgesics:
Painkillers are often used to help relieve pain associated with erysipelas, a skin infection that can cause inflammation and tenderness in the affected area. Pain relievers can be taken by mouth or applied directly to the skin as a cream or gel. The most common pain relievers used to treat erysipelas pain are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, which can help reduce inflammation and pain. Opioids can also be used for severe pain, but are often reserved for the most severe cases due to their potential for side effects. It is important to follow the dosage and duration of use instructions recommended by your doctor or pharmacist to minimize side effects and maximize treatment effectiveness. In summary, analgesics can help relieve the pain associated with erysipelas, but their use should be supervised by a healthcare professional.
C- Prevention of recurrences:
Preventing recurrences of erysipelas is important because this skin infection can come back in some people, even after effective treatment. To reduce the risk of recurrence, it is recommended to maintain good skin hygiene and take care of wounds or cuts to avoid infection. If you are prone to skin infections, it is important to take extra precautions, such as wearing loose clothing and protecting your skin from insect bites and wounds. It is also recommended to watch for signs of skin infection such as redness, swelling and pain and seek medical attention immediately if erysipelas is suspected. Finally, if you have ever had an episode of erysipelas,
1- Prophylactic treatments:
Prophylactic treatment is a preventative approach that involves giving long-term antibiotics to people who have a history of recurrent erysipelas. This approach is used to reduce the frequency of recurrences. However, the decision to prescribe prophylactic treatment depends on several factors, including the number of previous recurrences, the severity of symptoms, general health, and the patient’s ability to tolerate treatment. Commonly used antibiotics for the prophylactic treatment of erysipelas include penicillin V, erythromycin, and clindamycin. It is important to emphasize that prophylactic treatment should only be prescribed by a qualified healthcare professional and that adherence to treatment is essential to avoid relapses. Besides,
2- Hygiene of life:
Healthy living is important to prevent skin infections such as erysipelas. To avoid recurrences of this disease, it is recommended to follow certain hygiene measures such as washing your hands regularly, avoiding contact with people suffering from skin infections and taking care of your skin. It is also advisable not to scratch the irritated or infected areas and to wear loose and comfortable clothes to avoid any friction of the skin. A healthy, balanced diet can also help boost the immune system and prevent infections. Additionally, regular physical activity can help maintain good blood circulation, which is important for preventing skin infections. By following these lifestyle tips,
V- Tips to prevent erysipelas:
A- Personal hygiene:
Body hygiene is essential to prevent skin infections, including erysipelas. It is recommended that you shower or bathe regularly and wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. It is also important to keep the nails clean and to cut them regularly. Avoid sharing towels or clothes with other people and wear comfortable shoes to avoid injuries that can lead to infection. If you have open wounds, it is important to clean them and cover them with a clean, dry dressing. Personal hygiene is a key part of preventing skin infections and should be practiced regularly to reduce the risk of infection.
B- Wound care:
Wound care is essential to prevent infections and speed up healing. For people with erysipelas, it is important to clean the wound thoroughly with mild soap and water. It is recommended to use a sterile compress to clean the wound and to avoid touching the affected area with dirty hands or contaminated objects. Once the wound has been cleaned, it is advisable to apply an antibiotic cream and cover it with a sterile dressing. It is important to change the dressing regularly to avoid contamination. If the wound continues to get worse despite care, it is essential to see a doctor for proper treatment.
C- Prevention of insect bites:
Preventing insect bites is essential to avoid contracting certain insect-borne diseases, such as malaria or dengue fever. It is recommended to use repellents containing DEET, which is very effective against mosquitoes, ticks and other insects. It is also important to wear long clothing and hats to reduce exposure to bites, especially when traveling to risk areas. It is also advisable to sleep under an insecticide-treated mosquito net to prevent mosquito bites at night. Finally, it is important to consider environmental conditions, such as standing water, which can promote the proliferation of insects and contribute to the spread of disease.
D- Strengthen the immune system:
Strengthening the immune system is important for preventing infections and reducing the risk of disease. To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to follow a healthy and balanced diet, rich in fruits and vegetables. It is also important to exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight. Sleep is also key to boosting the immune system, as the body regenerates and repairs itself during sleep. It is important to limit stress and have stress management strategies such as meditation or deep breathing. Avoiding bad habits such as excessive alcohol and tobacco consumption can also help boost the immune system. Finally,
VI- Conclusion:
A- Summary of the key points of the article:
In this article, we have discussed the different aspects related to infections and treatments. Risk factors, common symptoms, physical assessments and symptom observations were explained. We also discussed additional examinations such as bacteriological samples, ultrasounds and scanners. Antibiotics, their choice, their duration of treatment and the precautions to be taken were also discussed. Symptomatic measures including rest, leg elevation, and analgesics were presented. We also discussed the prevention of recurrences, prophylactic treatments, lifestyle, body hygiene and wound care. Finally, we explained how to prevent insect bites and strengthen the immune system.
B- Importance of consulting a doctor as soon as symptoms appear:
It is important to consult a doctor as soon as symptoms appear in order to receive adequate treatment and avoid any complications or aggravation of the disease. Some illnesses can be treated more easily when detected early, which also reduces the risk of spreading infection. In addition, a doctor can assess symptoms and determine if further tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis or to rule out other conditions. It is also important to note that some symptoms may be signs of a more serious condition that requires urgent medical intervention. In summary, it is crucial to consult a doctor as soon as symptoms appear for rapid and effective management of the disease.
C- Encouragement to take preventive measures to avoid recurrence of erysipelas:
Erysipelas is a potentially serious skin infection that can recur if preventive measures are not taken. To avoid a recurrence, it is important to take preventive measures at the first symptoms of erysipelas such as redness, pain and swelling of the skin. Preventive measures include proper personal hygiene, early treatment of wounds and skin lesions, proper care for insect bites, and measures to strengthen the immune system. It is also important to follow the prophylactic treatments prescribed by a doctor, such as antibiotics, to prevent the recurrence of the infection. If you have ever suffered from erysipelas, it is important to consult your doctor at the first signs of recurrence in order to take the necessary measures to avoid any complications. By taking these steps, you can help prevent recurrences of erysipelas and maintain good skin health.
Leave a Reply