* Plasmodium vivax, P. malariae. P. ovale never give a pernicious and are still susceptible to antimalarial drugs.
* The duration of erythrocytes cycle explains the frequency of febrile illness (48 hours for all species except P. malariae that lasts 72 hours -> quartan).
* In a subject having stayed in endemic areas malaria should be suspected in any table regardless of the associated symptoms.
* Incubation may be several months for P. vivax and P. ovale.
* Intermittent plustres Access: move in 3 phases, rigors (1h), high fever (4h), profuse sweating and remission.
Periodically repeating: mild fever thirds (every 2 days); quartan (every 3 days).
* For P. falciparum periodicity is often less clear (third malignant fever).; there is no real forgiveness between the peaks.
* The renaissance of access may subsequently reappear after a few years (to 20 years for P. malariae) for all species except P. falciparum (no re-experiencing).
* The pernicious (neuropalustre) is manifested by neurological signs (acute encephalitis); anemia; jaundice (hemolysis); renal failure;cytolysis; metabolic acidosis; DIC; hypoglycemia …
* Severity criteria for access plustre: ground; vomiting +; fever ++ tray;rate of erythrocytes parasitized ≥ 5%; severe anemia and hemoglobinuria; clinical jaundice; hypoglycemia; the rest is obvious.
* The thin film is the examination of emergency referral (MGG staining).
The thick film is more sensitive than smear but requires 12 to 24 hours drying before staining
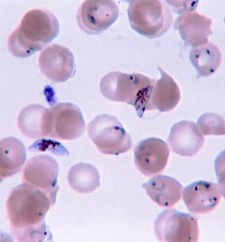
* On smear P. falciparum is suggested by the following: faux-shaped gametocytes; exclusive presence of ring trophozoites (no schizont or rosette body) a red blood cell invasion by several trophozoites (polyparasitism)parasitaemia can be intense (> 5%).
* In a strong clinical suspicion treatment is instituted emergency even if negative smears.
* Thrombocytopenia is not a sign of seriousness (even important); leukopenia.
* All antimalarials are schizontocidal (active only on intra-GR shape); Quinine is the only one that is natural.
* Antimalarial curative treatment only: quinine, Fansidar (sulfadoxine pyrimethamine);
* The AP prophylactic and curative treatment: mefloquine, halofantrine, chloroquine (Nivaquine®).
* Cyclins and macrolides have antimalarial action and can be used in combination with quinine in some pernicious.
* Chemoprophylaxis prevents clinical access, but does not prevent the malaria infection.
Should be started the day before departure and continued four weeks after the return (if chloroquine).



Leave a Reply