I – Introduction:
A- Definition of phlebitis:
Phlebitis is a common medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein deep in the body, usually in the legs. This can lead to obstruction of blood flow and can be very painful. Phlebitis can also increase the risk of developing a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition where a blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs. Risk factors for phlebitis include advanced age, physical inactivity, obesity, smoking, heart disease, and autoimmune disease. Symptoms of phlebitis include pain and swelling in the affected leg, localized redness and warmth, bruising, and fever. The diagnosis of phlebitis can be established by a clinical examination, laboratory tests and imaging techniques. Treatment for phlebitis usually includes blood thinners, anti-inflammatories, and painkillers, as well as surgery if necessary. Prevention of phlebitis can include regular exercise, healthy eating, and quitting smoking.
B- Importance of phlebitis as a public health problem:
 Phlebitis is a major public health problem due to its high incidence and potentially serious health consequences. It is estimated that about one to two percent of the population will develop phlebitis in their lifetime, and incidence rates increase with age. Phlebitis can lead to significant pain and temporary disability, which can negatively impact the quality of life of those affected. Additionally, phlebitis can increase the risk of developing a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition. The costs of phlebitis are high, both in terms of medical costs and indirect costs associated with lost productivity and disability. Consequently, it is important to recognize and treat phlebitis quickly to minimize its consequences for public health and for the individuals affected. Preventing phlebitis, including promoting healthy lifestyles, can help reduce the incidence of this condition and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Phlebitis is a major public health problem due to its high incidence and potentially serious health consequences. It is estimated that about one to two percent of the population will develop phlebitis in their lifetime, and incidence rates increase with age. Phlebitis can lead to significant pain and temporary disability, which can negatively impact the quality of life of those affected. Additionally, phlebitis can increase the risk of developing a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition. The costs of phlebitis are high, both in terms of medical costs and indirect costs associated with lost productivity and disability. Consequently, it is important to recognize and treat phlebitis quickly to minimize its consequences for public health and for the individuals affected. Preventing phlebitis, including promoting healthy lifestyles, can help reduce the incidence of this condition and improve the quality of life for those affected.
C- Objective of the article:
The purpose of this article is to provide complete and up-to-date information on phlebitis, a common and potentially serious condition that can affect affected individuals’ quality of life and overall health. This text is intended for a wide audience, including healthcare professionals, patients and their relatives, as well as anyone who wants to know more about phlebitis. The aim is to describe the definition, causes, symptoms, diagnoses and treatments of phlebitis, as well as its importance as a public health problem. Readers will also learn tips on preventing phlebitis and what to do if symptoms occur. At the end of the day,
II- Causes of phlebitis:
A- Risk factors:
Risk factors for phlebitis are multiple and can include lifestyle factors, general health, and certain medical conditions. Advanced age is a significant risk factor for phlebitis because the veins become more fragile over time. A sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and smoking can also increase the risk of phlebitis, as these factors can affect blood circulation and blood clotting. People with heart conditions, such as heart failure or atrial fibrillation, are also at higher risk of developing phlebitis. Finally, people with certain autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, may be more susceptible to developing phlebitis due to the disruption of blood clotting that can occur in these conditions. It is important to consult a doctor to assess the risk of phlebitis and to develop an adequate treatment plan if necessary.
1- Hereditary factors:
Hereditary factors can also play an important role in the development of phlebitis. Some people may be predisposed to phlebitis due to their family history or the presence of certain genetic abnormalities that affect blood clotting. For example, abnormalities in the gene that codes for activated protein C, an important clotting factor, can increase the risk of phlebitis. Similarly, abnormalities in the gene for protein S, another clotting factor, can increase the risk of phlebitis. It is important to note that although hereditary factors can increase the risk of phlebitis, they are usually not the only cause. Environmental factors, such as lifestyle and medical conditions, can also contribute to the development of phlebitis. Accordingly, a comprehensive approach that considers both hereditary and environmental factors is needed to assess the risk of phlebitis and develop an adequate treatment plan.
2- Sedentary lifestyle:
Physical inactivity is an important risk factor for the development of phlebitis. People who sit or stand for long periods without moving can develop venous stasis, which can cause blood to pool in the veins. This buildup can promote the formation of blood clots, which can be a trigger for the development of phlebitis. A sedentary lifestyle can also affect blood circulation by reducing the pressure in the veins, which can lead to stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs. As a result, it is important to maintain regular physical activity to help prevent phlebitis. Simple activities, such as walking, jogging or bicycling can help improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of phlebitis.
3- Obesity:
Obesity is another important risk factor for the development of phlebitis. People with obesity have an increased risk of developing venous stasis, which can lead to blood pooling in the veins. This buildup can promote the formation of blood clots, which can be a trigger for the development of phlebitis. Also, obesity can increase the pressure on the veins of the legs, which can lead to reduced blood circulation and stagnation of blood in the veins. This stagnation can also increase the risk of developing varicose veins, which can lead to an increased risk of phlebitis. It is therefore important to maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of phlebitis. Weight loss programs that include a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of phlebitis and help maintain a healthy weight. In addition, moderate alcohol consumption and rejection of tobacco can also help reduce the risk of phlebitis by improving blood circulation.
4- Smoking:
Smoking is an important risk factor for the development of phlebitis. Tobacco can affect blood circulation by reducing the flexibility of vascular walls and increasing blood clotting. This can lead to stagnation of blood in the veins and an increased risk of blood clots forming. Smokers also have an increased risk of developing varicose veins, which can increase the risk of phlebitis. Also, smoking can cause damage inside blood vessels, which can reduce blood flow and increase the risk of phlebitis. It is therefore important for smokers to quit cigarettes to reduce the risk of phlebitis and other serious health problems. Smoking cessation programs, such as nicotine patches, nicotine gums and medications can help smokers quit and reduce the risk of phlebitis. Also, regular physical activity and a healthy diet can help improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of phlebitis.
5- Hormonal treatment:
Hormonal treatment can also be a risk factor for the development of phlebitis. Women who take birth control pills may have an increased risk of developing phlebitis due to the increased blood clotting that can occur with this type of treatment. Likewise, pregnant women may be at a greater risk of phlebitis due to the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. Women who have a family history of phlebitis or who have other risk factors for phlebitis, such as obesity or reduced physical activity, may be at higher risk of developing phlebitis while on hormone therapy. It is therefore important to discuss treatment options with a doctor to reduce the risk of phlebitis. Treatment options may include a change in birth control, regular physical activity, and a healthy diet. Also, blood thinners may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots forming and prevent the development of phlebitis.
B- Associated diseases:
There are several associated diseases that can increase the risk of developing phlebitis. Certain autoimmune diseases, such as Wegener’s disease and lupus, can affect blood clotting and increase the risk of phlebitis. Likewise, blood diseases such as thrombocythemia and sickle cell anemia can increase the risk of blood clots forming. People with cancer may also have an increased risk of phlebitis due to the need to undergo treatments that can affect blood clotting. Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, can also increase the risk of phlebitis by disrupting the body’s ability to manage blood clotting. It is therefore important for people with these diseases to discuss with their doctor their risk of phlebitis and the preventive measures that can be taken to reduce this risk. Options may include regular physical activity, healthy eating, and taking blood thinners under medical supervision.
1- Heart diseases:
Heart disease can also increase the risk of developing phlebitis. People with heart conditions such as heart failure, angina, and myocardial infarction may have an increased risk of blood clots. Cardiac surgeries such as coronary bypass surgery or valve replacement surgery can also increase the risk of phlebitis. People with heart disease should therefore be aware of their increased risk of phlebitis and take steps to reduce this risk. Options may include regular physical activity, healthy eating, weight management, and taking blood thinners under medical supervision. It is important to discuss treatment options with a doctor to reduce the risk of phlebitis in heart disease. Blood thinners may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots forming and prevent the development of phlebitis.
2- Cancer:
Cancer can also increase the risk of developing phlebitis. People with cancer may have an increased risk of phlebitis due to treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which can affect blood clotting. In addition, tumors can impair blood circulation, which can increase the risk of blood clots. People with cancer should be aware of their increased risk of phlebitis and discuss with their doctor the preventive measures that can be taken to reduce this risk. Options may include regular physical activity, healthy eating, weight management, and taking blood thinners under medical supervision. It is also important to consult a doctor before taking blood thinners, because some cancer treatments can be affected by taking blood thinners. Preventing phlebitis is important for people with cancer because it can reduce potential complications such as pulmonary embolism and improve quality of life.
3- Autoimmune diseases:
Autoimmune diseases can also increase the risk of developing phlebitis. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis can affect blood clotting and increase the risk of blood clots forming. People with autoimmune diseases may also be more vulnerable to phlebitis-related complications, such as pulmonary embolism. It is important for people with autoimmune diseases to discuss preventive measures with their doctor to reduce the risk of phlebitis. Options may include regular physical activity, healthy eating, weight management, and taking blood thinners under medical supervision. It is also important to consult a doctor before taking blood thinners, as some medications for autoimmune diseases can be affected by taking blood thinners. Preventing phlebitis is important for people with autoimmune diseases because it can reduce potential complications and improve quality of life.
III- Symptoms of phlebitis:
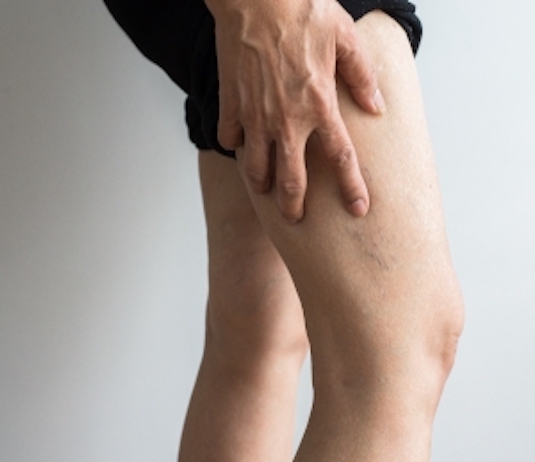
A- Pain and swelling in the leg:
Leg pain and swelling are common symptoms of phlebitis. The pain may be described as a dull ache, burning sensation, or sharp pain and may travel down the leg. The swelling may be visible and may affect part or all of the leg. The skin may also be red and hot to the touch, indicating inflammation. If the pain and swelling are associated with a fever, dry cough, wheezing or chest pain, it may be a pulmonary embolism and it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of phlebitis can be similar to other medical conditions, so it is important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and proper treatment. Treatment may include blood thinners to prevent new blood clots from forming, as well as anti-inflammatories to relieve pain and swelling. Prompt management of phlebitis can help prevent potential complications, such as pulmonary embolism.
B- Redness and localized heat:
Localized redness and warmth are common symptoms of phlebitis. The skin may become red and hot to the touch, especially on the affected leg. Redness and warmth are signs of inflammation, indicating that the body is responding to injury or infection. However, in the case of phlebitis, the redness and warmth are caused by pooling of blood and the body’s reaction to a blood clot in the vein. If the redness and warmth are associated with other symptoms such as pain, swelling and fever, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment for phlebitis may include blood thinners to prevent new blood clots from forming, as well as anti-inflammatories to relieve redness and warmth. Prompt management of phlebitis can help prevent potential complications such as pulmonary embolism. It is important to consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis and adequate treatment.
C- Bruising:
Bruising is a common skin lesion that can occur with phlebitis. They are characterized by blue or purple patches on the skin and are the result of blood leaking under the skin due to ruptured small blood vessels. Bruises can occur anywhere on the leg affected by phlebitis, but they are often associated with areas of pressure or friction, such as the ankles or knees. Bruising is often a sign of severe phlebitis and may indicate that the blood clot has grown to a large size. Phlebitis treatment should therefore be initiated as soon as possible to minimize the risk of complications such as pulmonary embolism.
D- Fever:
Fever can be a symptom associated with phlebitis. However, it is important to note that fever is usually a sign of the inflammation or infection that accompanies phlebitis rather than a direct result of blood clot formation. When phlebitis is caused by an infection, fever can be an important warning sign. Fever can also be a symptom of deep phlebitis, which is a severe form of the condition. In this case, the clot may have reached deeper into the veins and may cause high fever in addition to pain and swelling in the affected leg. If you experience symptoms of fever in addition to those associated with phlebitis, it is important to seek medical attention promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
IV- Diagnosis of phlebitis:
A- Clinical examination:
Clinical examination is a key element in diagnosing phlebitis. The doctor will usually start by asking about the patient’s symptoms and medical history, including the presence of risk factors such as physical inactivity, smoking, heart disease, and autoimmune diseases. He will also perform a thorough physical examination of the affected leg, including palpation for pain and swelling, and observation of the skin for signs of localized redness and warmth or bruising. If the doctor suspects phlebitis, they may also recommend laboratory tests such as blood tests to measure the level of blood clotting or images to visualize the presence of a blood clot. Imaging techniques such as venous ultrasound or computed tomography can also be used to confirm the diagnosis of phlebitis and assess the severity of the condition. Finally, it is important to point out that the clinical examination can help rule out other diagnoses such as superficial thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis, which may present with similar symptoms.
B- Laboratory tests:
Lab tests can be used to help diagnose phlebitis and assess the severity of the condition. One of the most common tests is the blood clotting test, which measures the blood’s ability to clot. An abnormal result may indicate an increased risk of blood clots and therefore phlebitis. Other lab tests may include blood tests to measure inflammation levels, lipid levels, glucose levels, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and D-dimer levels, which are indicators the formation of blood clots. Additionally, laboratory tests can also be used to rule out other potential diagnoses, such as bacterial infections and venous disease. Finally,
1- Complete blood count:
The complete blood count is a laboratory test that measures the different types of blood cells in the body. This exam can be used to help diagnose phlebitis and assess the severity of the condition. A normal blood count includes a balanced proportion of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. However, in cases of phlebitis, there may be an increase in white blood cells, which can help fight off possible infection, as well as a decrease in red blood cells, which can be broken down due to blood clots. Additionally, complete blood counts can also measure C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, which are indicators of inflammation. Finally,
2- Clotting time:
Clotting time is a lab test that measures how quickly blood forms clots. This exam can be used to assess the risk of phlebitis and determine the severity of the condition. In general, a normal clotting time is between 10 and 15 minutes. However, in case of phlebitis, the clotting time can be accelerated, which means that the blood is more likely to form clots. This phenomenon can lead to obstruction of blood vessels and increase the risk of serious complications such as pulmonary embolism. It is important to note that the clotting time can be affected by a number of factors such as the use of anticoagulant medications, hereditary diseases and chronic conditions such as cancer. At the end of the day,
3- D-dimer test:
The D-dimer test is a laboratory test that measures the amount of D-dimer, fragments of clotting proteins, in the blood. It is often used to assess the risk of phlebitis and pulmonary embolism. In general, high levels of D-dimer may indicate increased activation of the blood clotting system and an increased risk of clot formation. However, it is important to note that high levels of D-dimer can also be caused by other conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, pneumonia, and lung injury. Ultimately, the D-dimer test can be a useful tool to assess the risk of phlebitis and to determine the measures needed to prevent potential complications. However,
C- Imaging techniques:
Imaging techniques are another important tool for diagnosing phlebitis. They help visualize the blood flow in the veins and identify blood clots that may be causing the condition. The most common imaging techniques used for phlebitis include computed tomography (CT), venous ultrasound, and magnetic resonance (MRI). CT uses x-rays to produce images of veins and arteries, while venous ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time images of blood flow. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of veins and arteries. At the end of the day,
1- Venous ultrasound:
Venous ultrasound is a common imaging technique used to diagnose phlebitis. It allows to visualize the deep and superficial veins and to determine if a blood clot is present. This examination is non-invasive and does not require any special preparation. It is also inexpensive and can be done quickly. Venous ultrasound is particularly helpful in diagnosing phlebitis in patients with symptoms such as pain and swelling in the leg. Also, it can be used to monitor the progress of phlebitis and determine if treatment is working. In general, venous ultrasound is considered a reliable tool for the diagnosis of phlebitis and is widely used in clinics and hospitals around the world.
2- MRI:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a medical imaging test used to diagnose phlebitis. This technique uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of the human body. MRI is particularly useful in diagnosing phlebitis because it can visualize blood vessels in detail, including deep veins, which is not always possible with other imaging methods. Additionally, MRI does not require the use of X-rays or other radioactive substances, making it a safer option for patients. The images produced by MRI can also help determine the extent of the phlebitis and any damage to the affected veins, which can help plan the right treatment.
3- CT:
CT, or computed tomography, is a medical imaging test used to diagnose phlebitis. This is a scan that uses X-waves and a magnetic field to produce detailed images of blood vessels and surrounding tissue. CT can help identify venous obstructions, abnormal dilatations and thrombosis, which is crucial for the diagnosis and management of phlebitis. However, it is important to note that CT is not always the first choice for diagnosing phlebitis, as other tests such as venous ultrasound may be more effective and less invasive. Ultimately, the choice of imaging technique will depend on physician preference and each patient’s clinical situation.
V- Treatment of phlebitis:
A- Medicines:
Treatment for phlebitis usually involves the use of medications, in addition to recommended lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors. Blood thinners are often used to reduce blood clots and prevent potential complications such as pulmonary embolism. Commonly used anticoagulants include warfarin, heparin, and newer oral anticoagulants such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation in the affected leg. In some cases, medications for pain management or fever are also used.
1- Anticoagulants:
Blood thinners are medicines that are used to prevent blood clots from forming in veins and arteries. They are often prescribed to people with phlebitis because this disorder can cause dangerous blood clots to form in the deep veins of the leg. Blood thinners are often used in combination with other treatments to relieve symptoms and prevent potential complications, such as the clot spreading to the lungs. The most commonly used anticoagulants are warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban and rivaroxaban. It’s important to talk with a doctor to determine the most appropriate medication for each individual case, as each can have potential side effects and usage restrictions.
2- Anti-inflammatories:
Anti-inflammatories are often used to treat phlebitis and reduce the pain and inflammation associated with the condition. This type of medication works by blocking the production of pro-inflammatory substances, which can help reduce pain and speed healing. The most common anti-inflammatories used to treat phlebitis include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac. It is important to remember that anti-inflammatories can also cause side effects, such as stomach upset or kidney problems, so it is important to consult a doctor before using them. Also, anti-inflammatories cannot prevent blood clots from forming, which is a key goal of treating phlebitis.
3- Analgesics:
Analgesics are a type of medicine used to relieve pain. They may be prescribed to treat the symptoms of phlebitis, such as pain and inflammation in the affected leg. The most common painkillers used to treat phlebitis include paracetamol, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Although these medications are generally considered safe, it is important to use them as directed by your doctor and to consider possible side effects and interactions with other medications. Analgesics should not be used to replace blood thinners, which are needed to prevent blood clots from forming in the veins, but can be used in addition to relieve pain and inflammation.
B- Surgical interventions:
Surgical interventions may be necessary in cases of severe phlebitis or in the presence of complications such as deep vein thrombosis. Surgical options include clot resection, vein stripping, and thrombectomy. Clot resection involves the removal of the blood clot using a small surgical incision. Vein stripping is a procedure that involves removing the affected vein using a small incision. Thrombectomy is a procedure that involves the removal of the blood clot using a special catheter. However, these surgeries are often only recommended in severe cases and are subject to strict criteria in terms of necessity and patient selection.
C- Prevention:
Prevention is crucial to avoid the occurrence of phlebitis. Certain steps can be taken to reduce the risk of developing phlebitis, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding sitting or standing for long periods of time, and exercising regularly. It is also important to monitor risk factors for associated diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, and to manage them appropriately. If you have a family history of phlebitis, you should see a doctor for regular examination and monitoring. Finally, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of phlebitis, including pain and swelling in the leg, and to seek medical attention immediately if phlebitis is suspected. By taking these preventive measures,
1- Regular exercise:
Regular exercise is a key factor in the prevention of many diseases, including heart disease, diabetes and some forms of cancer. It can also help reduce joint pain, improve blood circulation and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise can be as simple as walking 30 minutes a day or doing more vigorous activities such as running or biking. It’s important to find an activity that suits your tastes and fitness level, so that you can maintain it for the long term. Also, it is important to consult a doctor before beginning a new exercise regimen, especially if one has any medical history or health problems.
2- Healthy food:
Diet plays a crucial role in the prevention of many diseases, including heart disease, diabetes and obesity. A healthy diet includes a variety of nutritious foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. It is important to limit the consumption of foods high in saturated fat, added sugars and salt. Also, regular consumption of alcoholic beverages should be moderate. People who follow a healthy diet can reduce their risk of developing many chronic diseases and improve their overall health. It is recommended that you consult a healthcare professional to discuss your nutritional needs and receive personalized advice on how to maintain a healthy diet.
3- Smoking cessation:
Quitting smoking is one of the most important ways to prevent many diseases, including heart disease and cancer. Tobacco is the leading cause of preventable death worldwide and contributes to many other health problems, such as addiction, lung disease and skin problems. To quit smoking, it’s important to understand why you smoke and find ways to manage the cravings and challenges of quitting. It may be helpful to talk with a doctor, social worker, or smoking cessation counselor to find the best ways for you. There are also nicotine medications and substitutes that can help reduce withdrawal symptoms.
VI- Conclusion:
A- Summary of key information:
Summarizing key information is a crucial aspect of understanding a topic or issue. It allows you to summarize the most important points of complex information in a more concise and easy to understand form. Key information is often used to give a quick update on a situation, for a presentation in a meeting, or to quickly convey important information to someone. To be effective, the summary of key information must be precise, concise and detailed. It should include the most relevant and important points while excluding superfluous or less important details. Preparing a summary of key information is a great way to make sure you really understand a topic and prepare you to talk about it or make important decisions.
B- Importance of prevention and rapid treatment of phlebitis:
Phlebitis is a serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the circulatory system and increase the risk of developing diseases such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and heart failure. It is therefore very important to prevent and treat phlebitis quickly. Prevention includes measures such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and quitting smoking. If phlebitis is diagnosed early, it can be effectively treated with blood thinners, anti-inflammatories and painkillers. If drug treatment is not effective, surgery may be required. In general, phlebitis is a treatable condition and, with prompt and adequate management, most patients can fully recover and avoid potentially serious complications. It is therefore important to consult a doctor quickly if symptoms of phlebitis appear.
C- Final message for patients and the general public:
The final message for patients and the general public is that it is crucial to take charge of their vein health and to watch carefully for potential symptoms of phlebitis, which can include localized pain, swelling and redness in the leg. . It is also important to follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly and stop smoking to reduce the risk of developing phlebitis. If symptoms are detected, it is crucial to seek medical attention quickly in order to receive proper diagnosis and treatment. Early use of blood thinners, anti-inflammatories and painkillers can help reduce the risk of serious complications such as pulmonary embolism.
Leave a Reply