I – Introduction:
A- Definition of sciatica:
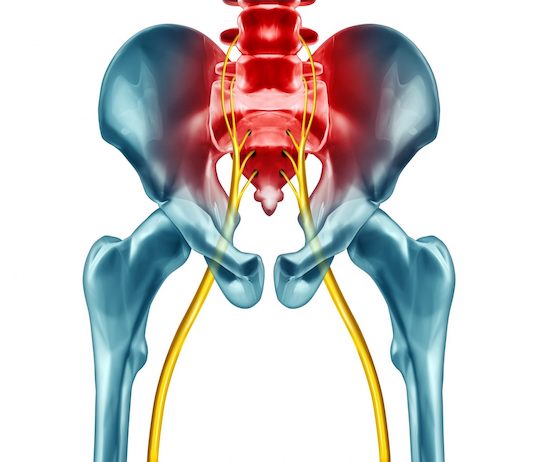
Sciatica is a painful disorder that affects the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the human body. This nerve runs from the lower back and runs through the buttocks to connect to the legs and feet. Sciatica can cause severe pain in the leg, numbness, weakness and burning sensations along the path of the sciatic nerve. It is often caused by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, muscle strain, or degenerative spine disease. However, other causes can include trauma, infections, tumors, and conditions like diabetes. Sciatica can have a huge impact on quality of life, limiting daily activities and causing pain when sitting or standing. It is therefore important to understand the causes,
B- Causes of sciatica:
 The causes of sciatica can vary, but most are related to spinal problems, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative arthritis, or spondylolisthesis. Herniated discs can occur when the soft tissue inside the disc moves and presses on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and symptoms. Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal that can compress the sciatic nerve. Degenerative arthritis can damage joints and discs in the spine, causing inflammation and nerve compression. Spondylolisthesis is a condition where one of the vertebrae in the spine shifts relative to the lower vertebra, which can also cause nerve compression.
The causes of sciatica can vary, but most are related to spinal problems, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative arthritis, or spondylolisthesis. Herniated discs can occur when the soft tissue inside the disc moves and presses on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and symptoms. Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal that can compress the sciatic nerve. Degenerative arthritis can damage joints and discs in the spine, causing inflammation and nerve compression. Spondylolisthesis is a condition where one of the vertebrae in the spine shifts relative to the lower vertebra, which can also cause nerve compression.
Other causes can include trauma such as spinal fractures, infections, tumors, or medical conditions such as diabetes that can impair nerve function. Finally, lifestyle factors such as being overweight, a sedentary lifestyle, poor posture or overexertion can also contribute to the onset of sciatica. It is important to see a doctor to establish the underlying cause of sciatica in order to determine the appropriate treatment.
C- Importance of understanding sciatica:
Understanding sciatica is important for several reasons. First, it helps to better diagnose and understand the underlying cause of the pain. Indeed, sciatica can be caused by various spinal conditions, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative arthritis, trauma, and infections. Understanding the underlying cause can help determine the most appropriate treatment to relieve pain and manage symptoms.
Additionally, understanding sciatica can also help prevent its recurrence. This can be done by adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining good posture, managing weight, and doing regular exercises to strengthen your back muscles. It’s also important to promptly treat any underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, that may be contributing to the onset of sciatica.
Finally, understanding sciatica can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Sciatica can cause severe pain and sensory disturbances, which can have a significant impact on daily activities. By understanding treatment options, patients can find the relief needed to manage pain and return to an active and functional life.
II- Symptoms of sciatica:
A- Pain in the leg:
Leg pain can be a symptom of many different conditions, ranging from simple injuries to serious medical conditions. This pain can manifest in a variety of ways, including sharp pains, dull aches, burning, numbness, and tingling. The severity of the pain can vary greatly, ranging from mild to very intense.
Leg pain can be caused by spinal problems, such as sciatica, or by injuries such as sprains or tendinitis. It can also be caused by conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, peripheral arterial disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Also, some medications can cause side effects that include leg pain.
It is important to see a doctor if you experience pain in your leg, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, redness or fever. A doctor can assess the cause of pain and recommend appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
B- Numbness and weakness:
Numbness and weakness can be alarming symptoms and can be caused by many different conditions. These symptoms can show up in one or more parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, hands, feet, and fingers. Numbness and weakness may also be associated with tingling, burning, and dull pain.
Numbness and weakness can be caused by spinal problems, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis, or by conditions such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, and peripheral neuropathy. Also, some medications can cause side effects such as numbness and weakness, and head trauma and spinal cord injury can also be responsible for these symptoms.
It is important to see a doctor if you experience persistent numbness or weakness, especially if these symptoms are associated with pain or sensory disturbances. A doctor can assess the cause of numbness and weakness and recommend appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
C- Pain that worsens when sitting or standing:
Pain that gets worse when sitting or standing can be a symptom of many different conditions, including spinal problems, musculoskeletal injuries, and serious medical conditions. This pain can manifest as sharp pains, dull aches, burning, numbness and tingling.
Spinal problems, such as sciatica, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis, can cause pain that is worse when sitting or standing. Musculoskeletal injuries such as sprains, tendonitis, and plantar fasciitis can also lead to similar pain. Medical conditions such as peripheral arterial disease, deep vein thrombosis, and diabetic neuropathy can also be responsible for these pains.
It’s important to see a doctor if you experience pain that gets worse when sitting or standing, especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, weakness, swelling, or redness. A doctor can assess the cause of pain and recommend appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
D- Radiating pain in the buttock, thigh and calf:
Radiating pain in the buttock, thigh, and calf can be a symptom of many different conditions, such as sciatica, herniated discs, lower back sprains, and injuries to muscles and tendons in the area. The pain can be described as a sharp ache, dull ache, burning, or numbness.
Sciatica is a common condition that can cause radiating pain in the buttock, thigh, and calf. It occurs when the sciatic nerve, which runs through the lumbar region, is compressed or irritated. Disc herniations can also compress the sciatic nerve and cause similar pain. Lower back sprains and injuries to the muscles and tendons in the area can also lead to radiating pain.
It is important to see a doctor if you experience radiating pain in your buttock, thigh and calf, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, weakness, sensory disturbances or changes in posture. A doctor can assess the cause of pain and recommend appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
III- Risk factors for sciatica:
A – Age:
Age can play an important role in the development of certain medical conditions, including chronic diseases, mobility disorders and cognitive impairments. As we age, the body undergoes natural changes that can affect health and quality of life.
Older people are more likely to develop chronic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and respiratory disease. They may also face mobility challenges, such as osteoporosis, arthritis, and back problems. Cognitive disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, can also become more common as people age.
However, it is important to note that aging is not a disease in itself and older people can lead active, healthy and productive lives. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying active and taking care of their mental health, seniors can improve their quality of life and slow the effects of aging. Regular medical care can also help prevent or treat age-related medical conditions.
B- Overweight:
Overweight is a condition in which body weight is above normal for a person’s height, age, and sex. It can lead to many serious health problems, such as diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, respiratory disease, and certain types of cancer.
Being overweight can be caused by an unbalanced diet, lack of exercise, a sedentary lifestyle, genetic factors, hormonal disorders and mental health problems. Overweight people may also face psychological challenges such as depression, self-worth and social stigma.
It is important to understand that losing weight can help prevent or treat health problems associated with being overweight. Dietary changes, increased physical activity, and stress management can help achieve a healthy weight. Medical attention may also be needed to treat underlying medical conditions that may be causing or making the overweight worse. It is important to work with a doctor to develop a weight loss plan tailored to your individual needs.
C- Intense physical activity:
Vigorous physical activity is defined as a high level of exercise or physical exertion that can lead to muscle or heart fatigue. This can include activities such as jogging, weight training, cycling, soccer, and other competitive sports. Although intense physical activity is often associated with numerous health benefits, such as weight loss, improved physical fitness and reduced risk of chronic diseases, it can also be the cause of wounds.
Injuries related to strenuous physical activity can include muscle aches, sprains, broken bones, spinal injuries, tendonitis and joint pain. It is important to understand that these injuries can be prevented or minimized by taking a step-by-step approach and respecting your body’s limits. This may include proper warm-up, proper cool-down, use of protective gear, and practicing correct training techniques.
It’s also important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the level of physical activity that’s right for your individual needs. People with underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or respiratory disorders may need to limit strenuous physical activity to avoid any health risks. Ultimately, vigorous physical activity can be beneficial to health if done responsibly and under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
D- Incorrect posture:
Incorrect posture is defined as the abnormal position of the body which can cause long term pain and injury. This can include incorrect sitting posture, such as slouching in a chair, leaning forward on a computer, or supporting your weight on only one side of your body. Incorrect posture can also include inappropriate standing positions, such as hunching, balancing on one leg, or carrying heavy loads unbalanced.
The negative effects of incorrect posture can include pain in the back, shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees, as well as poor blood circulation and impaired breathing. People with incorrect posture may also experience fatigue more quickly, as their body has to work extra hard to maintain an incorrect posture.
It is important to understand the importance of correct posture in preventing pain and injury. Tips for good posture include setting up an ergonomic work environment, taking frequent breaks to relax and stretch the body, and using breathing and relaxation techniques to help maintain healthy posture. . It is also recommended that you work with a medical professional to identify the underlying causes of incorrect posture and determine ways to correct it. Ultimately, adopting good posture can improve overall health, quality of life, and physical performance.
E- Sedentary work:
Sedentary work involves spending long hours sitting at a desk, in front of a computer, or driving. This sedentary lifestyle can contribute to pain and injury, including to the spine, shoulders, elbows, hips, and legs. Additionally, a study has shown that spending long hours sitting can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Sedentary work can also lead to decreased blood circulation, muscle tension and deterioration of posture. People with chronic pain may also find that their condition worsens due to long periods of time spent in a sitting position.
It is important to understand the negative health effects of sedentary work to avoid pain and injury. Solutions include establishing an ergonomic work environment, taking frequent breaks to relax and stretch the body, and adopting a regular exercise routine to improve blood circulation and strengthen muscles. . People with chronic pain may also find improvement by working with a medical professional to determine the underlying cause of their pain and ways to relieve it. Ultimately, reducing the time spent in a sedentary position and adopting healthy practices can improve overall health and prevent pain and injury.
IV- Diagnosis of sciatica:
A- Physical examination:
Physical examination is an important step in diagnosing sciatica. This is an examination performed by a healthcare professional that may include movement tests, reflex tests and sensitivity tests.
During the physical exam, the healthcare professional may ask questions about your symptoms, your medical history, and potential risk factors such as lifestyle and injury history. They may also inspect your posture, body, and spine to look for signs of health issues.
Movement tests may include flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral movement of the spine. Reflex tests can help assess nerve function, while sensitivity tests can help assess pain and sensation in the leg.
Ultimately, the physical exam can help identify the causes of sciatic pain, which can help in developing an effective treatment plan. It can also help determine if additional tests, such as medical images, are needed to make a more accurate diagnosis.
It is important to see a medical professional for a physical exam if you have symptoms of sciatica to avoid serious complications.
B- Medical imaging (MRI, PET, x-rays):
Medical imaging can be used to help diagnose sciatica and assess its extent. The most common types of medical imaging include MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging), PET scans (computed tomography), and x-rays.
MRI is often considered the most accurate imaging tool for evaluating spinal problems. It can help visualize intervertebral discs, nerves, and nerve roots, which can help identify the causes of sciatic pain.
PET scans can help assess blood flow to the affected area and can be used to detect vascular abnormalities that may be contributing to sciatic pain. X-rays can help visualize the bones of the spine, but are not as accurate as MRIs or PET scans for evaluating spinal or nerve problems.
When you see a healthcare professional for symptoms of sciatica, they may recommend one or more of these medical imaging modalities based on your medical history and symptoms. By using these tools, he can get a complete picture of your condition and help develop an effective treatment plan.
C- Assessment of pain and function:
The assessment of pain and function is an important part of the diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. This may include a series of physical tests and an assessment of your level of pain and how it affects your quality of life.
The doctor may start by asking you questions about your symptoms, medical history, and family history. He may also perform a physical exam, including checking for tenderness, muscle strength, and nerve function in the affected area.
Additional tests may include posture and mobility assessments, reflex tests, and nerve tests. The severity of pain and how it affects your ability to perform daily activities can also be measured using tools such as pain scales and quality of life questionnaires.
Assessing pain and function can help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and formulate a treatment plan that takes into account your individual needs. By working closely with the doctor, you can help develop a treatment plan that aims to reduce pain, improve function, and maximize your quality of life.
V- Treatment of sciatica:
A- Medical treatment:
Medical treatment for sciatica can include a combination of medications, therapies, and lifestyle modifications. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent symptoms from worsening.
Medications commonly used to treat sciatica include pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and nerve pain medications. Steroid injections can also be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Therapies such as physiotherapy, acupuncture, and chiropractic can help improve mobility and reduce pain. Patients may also be asked to perform specific exercises and stretches to strengthen muscles and improve posture.
Lifestyle modifications such as losing weight, modifying work posture, and adopting good postural habits may also be recommended to help prevent symptoms of sciatica.
It is important to work closely with a doctor to determine the best treatment plan for your individual condition. Treatments can be adjusted over time to ensure you get the maximum pain relief and improved function.
B- Physical therapy:
Physical therapy is an important part of treatment for sciatica. Physiotherapists are medical professionals trained to help treat back pain and nerve disorders.
Physical therapy for sciatica may include strengthening exercises, stretching, traction, and manual therapy to improve mobility and flexibility. Physiotherapists can also help patients adopt good postural habits to prevent relapses.
Strengthening exercises target the muscles that support the back and spine, while stretching helps loosen tight and sore muscles. Traction can help relieve pressure on the sciatic nerves, while manual therapy can help improve spinal mobility and function.
Physical therapy can help relieve pain, improve mobility, and prevent relapses. It is important to work closely with a physical therapist to determine the best treatment plan for your individual condition. Sessions can be adapted over time to ensure you get the maximum pain relief and improved function.
C- Surgery:
Surgery is considered a last resort treatment for sciatica, only recommended when medical treatments and physical therapy have failed to relieve the pain.
There are several types of surgeries that can be used to treat sciatica, including microdiscectomy, laminectomy, and spinal stabilization. The choice of surgery will depend on the underlying cause of the sciatica and the severity of the condition.
Microdiscectomy is the most common procedure for treating sciatica. This is a minimally invasive procedure that involves removing a small part of the intervertebral disc that puts pressure on the sciatic nerve. Laminectomy is a larger procedure that involves removing part of the bone from the spinal canal to relieve pressure on the nerves.
The goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve and improve spinal function. However, it is important to note that surgery can come with risks and complications, including post-operative pain, prolonged recovery, and temporary loss of strength and feeling.
It is important to discuss treatment options with your doctor to determine if surgery is the best option for your specific condition. If surgery is deemed necessary, it is important to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to maximize the chances of success.
D- Lifestyle changes:
Lifestyle modifications can be a key part of treating sciatica. People with sciatica may need to make adjustments in their daily life to help relieve pain and prevent a recurrence. Simple changes such as improving posture, reducing time spent sitting, and exercising regularly can help relieve pain and strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Wearing comfortable shoes and orthotic insoles can also help improve posture and reduce pain. Sciatica sufferers may also benefit from alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic to relieve pain and strengthen muscles. At the end of the day,
VI- Prevention of sciatica:
A- Warming up before exercise:
Warming up before exercise is important to prevent injury and maximize the benefits of exercise. This is especially true for people with sciatica, who may be more susceptible to injury due to pain and weakness in their leg. A proper warm-up can help increase blood circulation and body temperature, which can make muscles more flexible and responsive. It can also help reduce the risk of injury by strengthening muscles and preparing them for exercise. It is important to dedicate at least 5-10 minutes to warming up before exercise, focusing on the muscle groups that will be used during the exercise. Warm-ups may include light stretching exercises,
B- Correction of the posture:
Posture correction is an important aspect of sciatica treatment and prevention. Poor posture can cause or worsen pain in the spine, hips, and legs. Prolonged static positions, such as sedentary work, can lead to tension and compression of the intervertebral discs and spinal nerves, which can cause or worsen sciatica. Correcting posture involves becoming aware of body position and correcting bad posture habits. Therapists and trainers can help people with sciatica identify their bad posture habits and learn how to adopt healthier postures. Posture correction can also include the use of support devices such as ergonomic chairs or headrests, as well as muscle-strengthening exercises to strengthen the muscles that support the spine. By correcting posture, people with sciatica can relieve pain, improve function, and prevent recurrences of the condition.
C- Avoidance of repetitive movements that can cause pain:
Avoiding repetitive movements that can cause pain is an important aspect of preventing or relieving sciatica. Activities that may cause pain or pressure on the spine include heavy lifting, prolonged driving, prolonged computer use, and other activities that may cause prolonged bending or excessive rotation back. It is important to remember that sciatica can also be caused by repetitive movements of everyday life such as painting, gardening, and cleaning. It is advisable to take regular breaks and stretch often to avoid pain. Moreover, reducing strenuous physical activity and using heavy-duty support devices can also help reduce pressure on the spine. Finally, it is important to consult a doctor to assess the cause of the pain and recommend the most appropriate means to prevent or relieve it.
D- Maintain a healthy weight:
Maintaining a healthy weight is important to minimize the risk of getting sciatica or worsening the symptoms if you already have it. Being overweight can increase pressure on spinal discs and joints, which can cause pain and inflammation. By losing weight, you can reduce the pressure on your back and relieve the pain associated with sciatica. In addition to eating a balanced, healthy diet, exercising regularly can help maintain a healthy weight and strengthen back muscles to prevent injury. If you have weight issues, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to develop a food and exercise plan that’s right for you.
VII- Conclusion:
A- Summary of sciatica:
Sciatica is a painful disorder that affects the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the human body. It extends from the spine to the leg and foot. The pain is often described as radiating to the buttock, thigh, and calf, and may be worse when sitting or standing. Causes of sciatica can include age, being overweight, strenuous physical activity, incorrect posture, and sedentary work. Treatments for sciatica include medication, physical therapy, surgery, and lifestyle modifications, such as warming up before exercise, correcting posture, and avoiding repetitive motions that can cause pain. pain. By maintaining a healthy weight and taking care of your body,
B- Importance of understanding and treating sciatica:
Sciatica is a common health problem that can cause significant pain and functional limitations. That’s why it’s important to understand sciatica and the different treatments available to manage the symptoms. By understanding the underlying cause of sciatica, steps can be taken to prevent or reduce symptoms in the future. Treatment for sciatica can include medical interventions such as medication or physical therapy, as well as lifestyle modifications such as correcting posture and maintaining a healthy weight. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Regardless of the treatment chosen, it is important to work with a healthcare professional to manage the symptoms of sciatica effectively and safely. Ultimately, prompt and appropriate treatment for sciatica can help reduce functional limitations and improve the overall quality of life for those affected by this disorder.
C- Tips to prevent sciatica in the future:
Prevention of sciatica is important to avoid the pain and complications associated with this condition. There are several tips you can follow to minimize the risk of developing sciatica. It is important to maintain a healthy weight, as being overweight can put excessive pressure on the spine and nerves. Additionally, correct posture can help reduce pressure on the nerves, so it’s important to make sure you maintain good posture during daily activities. Also avoid repetitive movements that can cause pain, such as heavy lifting without adequate support. Finally, a proper warm-up before exercise can help minimize the risk of injury and soreness.
Leave a Reply