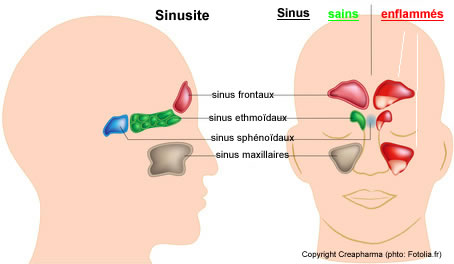
1- Acute ethmoiditis of the child:
The ethmoid sinus is present at birth. Mostly in children 2 to 3 years; complicates nasopharyngitis; germ: Haemophilus influenzae; Pneumococcus and staphylococcus.
A- non externalized acute ethmoiditis:
It is characterized by acute nasopharyngitis with high fever (39 ° C) in an asthenic child. The examination sometimes reveals a moderate moderates the inner corner of the eye associated with purulent rhinorrhea the same side. Middle meatus (opening of drainage ethmoid sinuses).
B- ethmoiditis acute externalized:
Fever of 39 ° C + evocative local signs. Painful inflammatory edema reaches the upper and lower eyelids.
Conjunctival edema (chemosis). Unilateral purulent rhinorrhea. Ophthalmologic complications; scan routine sinus
C- Complications:
* The ophthalmologic complications are the most common: orbital cellulitis; subperiosteal abscess (moves the eyeball down and out);orbital abscess (severe proptosis with immobility of the eyeball and alteration of the eyeball)
* Neurological complications thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus manifested by seizures, meningeal syndrome with impaired consciousness.
2- maxillary sinusitis:
The maxillary sinus is present at birth but is individualized only at the age of 6 years.
* Before the age of 6 years: the sinus reached integrates Table nasopharyngitis. Purulent rhinorrhea, cough productive night and morning. => (Rhinosinusitis)
* After the age of 6: frank reached individualized. Fever; nasal obstruction and purulent rhinorrhea; jaw pain increased by exercise, coughing and anteflexion of the head. Plain radiography (Blondeau) finds full opacity or liquid level.

Leave a Reply