Tag: Fibrillation
-
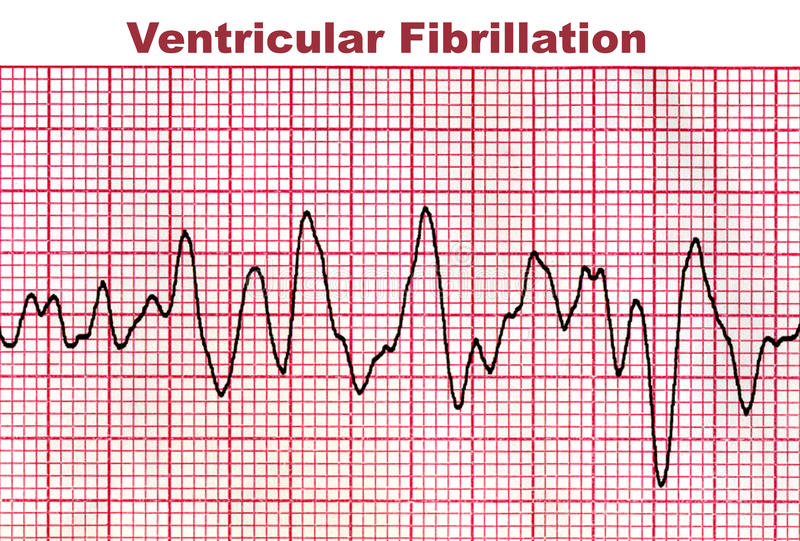
Ventricular Fibrillation
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * brutal loss of consciousness and circulatory arrest chart: – loss of pulse and high blood pressure. – disappearance of the noises of the heart. – then respiratory arrest and mydriasis confirming brain death. * syncope if transient fibrillation. ETIOLOGY: * complications of infarction or acute coronary insufficiency. * worsening of a TV, a torsade de pointe. * Digitalis intoxication. * hyperkalemia . * advanced…
-

Atrial Fibrillation
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * irregular heartbeat more or less fast between 60 and 160 / min with variable amplitudes, permanent or paroxysmal. * no functional signs. * or asthenia and moderate dyspnea. * or palpitations or oppressions unpleasant, paroxysmal. * or inaugural lipolysis or even syncope type Adams-Stokes. * look for signs of valvulopathy (especially mitral) on auscultation. * complications : Functional or organic angina…
-
Arrhythmias, Antiarrhythmic Treatment
—
by
Warning: • The use of anti-arrhythmic (AAR) requires a specialist opinion: indications, against-indications, cardiac side effects and extracardiac, surveillance. • All antiarrhythmic has pro-arrhythmic effects, negative inotropic, humps conduction, sometimes bradycardia. • Carefully assess the risk / benefit of treatment AAR. • Specialist advice is necessary for explorations (echo, Holter, etc): . assess the severity…
-
Myocardial infarction
—
by
1- Early complications: A- rhythm disorders (very common in the early hours): – Sinus bradycardia, especially in cases of inferior infarction with sweat, pallor, fall in blood pressure (vagal syndrome); reversible under atropine and fluid replacement. – Sinus tachycardia: common suggestive of left ventricular failure, extensive necrosis. – AC / FA: frequent and transient risk…
-

Vitamin K antagonist
– The VKA act through competitive inhibition of hepatic synthesis of certain clotting factors vitamin K-dependent: prothrombin (II); proconvertin (VII); factor IX; Factor X (X). – Protein C and Protein S (coagulation inhibitors) are also vitaminic-K-dependent. – Two families derivatives indandione (fluindione or Previscan) and coumarin (acenocoumarol or Sintrom®; warfarin or Coumadin®). – Fixing to…
You must be logged in to post a comment.