Tag: Meningococcal
-
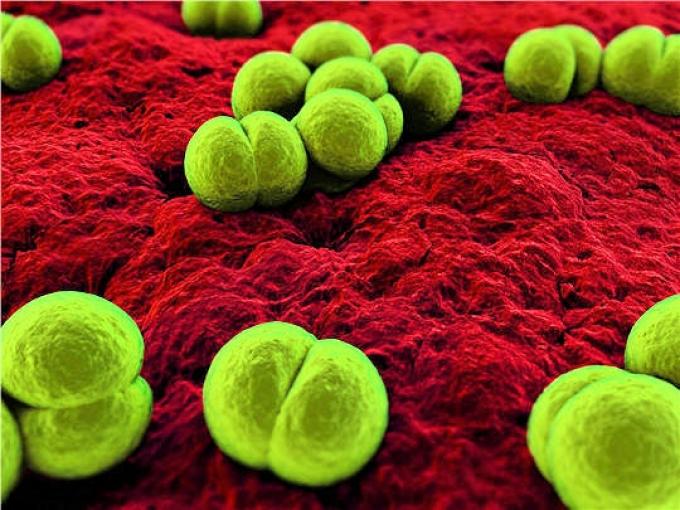
Prophylaxis of meningococcal disease
—
by
Meningococcus is a bacterium responsible for about 30% of bacterial meningitis in France. Mortality of this infection is far from negligible despite the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. A well conducted prophylaxis in the entourage of a case should prevent the occurrence of secondary cases.However, the epidemiology of this infection is often not known and…
-
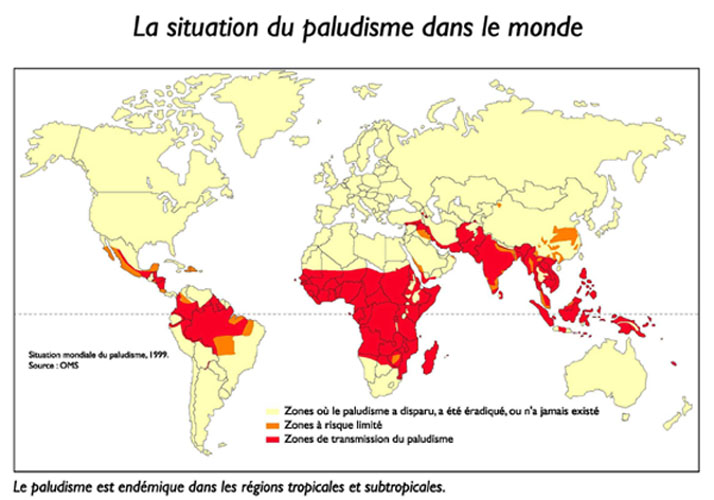
Bacterial and Parasitic Infections
* Diphtheria: it is due to the lysogénée bacteria strain that produces exotoxin. C. The diphtheria that do not produce exotoxin may be responsible for angina false membranes, but also septicemia (and secondary locations: endocarditis) but do not induce the disease diphtheria. Diphtheria is a little immunizing disease which justifies vaccination for convalescent patients. *…
You must be logged in to post a comment.