I – Introduction:
A- Definition of tuberculosis:
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can affect different organs of the body, mainly the lungs, but also the lymphatic system, bones and joints. Tuberculosis is transmitted through respiratory droplets when infected people talk, cough or sneeze. The disease can be latent and show no symptoms, but can also develop into an active form which can cause fever, fatigue, weight loss, persistent cough and other symptoms. Treatment for TB usually involves taking antibiotic drugs for several months. Tuberculosis prevention can be achieved by raising awareness among at-risk populations, offering early detection tests, and avoiding living conditions that can promote disease transmission. It is also important to treat TB quickly to prevent it from spreading to other people.
B- Importance of tuberculosis as a public health problem:
 Tuberculosis is considered an important global public health problem. Indeed, according to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), around 10 million people developed an active form of tuberculosis in 2019, and nearly 1.5 million people died from this disease. Tuberculosis is particularly common in developing countries and can aggravate health inequalities in these regions. Tuberculosis can also be complicated by drug resistance, which makes treatment more difficult and expensive. In addition, TB can result in significant financial costs for sufferers and their families, in addition to health system costs.
Tuberculosis is considered an important global public health problem. Indeed, according to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), around 10 million people developed an active form of tuberculosis in 2019, and nearly 1.5 million people died from this disease. Tuberculosis is particularly common in developing countries and can aggravate health inequalities in these regions. Tuberculosis can also be complicated by drug resistance, which makes treatment more difficult and expensive. In addition, TB can result in significant financial costs for sufferers and their families, in addition to health system costs.
C- Objective of the article:
The aim of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of tuberculosis, including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The aim is to make readers aware of the importance of tuberculosis as a public health problem, as well as to inform them about the different aspects of the disease. By providing detailed information about TB, this article also aims to help people understand their risk of contracting the disease, as well as the steps they can take to protect themselves and help prevent its transmission. Finally, the article aims to encourage readers to discuss tuberculosis with their doctor and to get tested if necessary, to enable early diagnosis and treatment.
II- Causes of tuberculosis:
A- Bacteria responsible for tuberculosis:
Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacterium is a slowly multiplying germ that can be transmitted through respiratory droplets when infected people talk, cough or sneeze. The bacterium can infect different organs of the body, mainly the lungs, but also the lymphatic system, bones and joints. The majority of people infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria will not develop active symptoms of tuberculosis, but will be carriers of the disease in a latent state. However, some people can develop an active form of TB, especially if their immune system is weakened or if they are exposed to conditions that can make them susceptible.
B- How tuberculosis spreads:
Tuberculosis spreads when people infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria cough, talk or sneeze, releasing respiratory droplets that may contain the bacteria. People who are exposed to these respiratory droplets can then contract the disease by inhaling the bacteria. Tuberculosis can also spread in communities where the population is vulnerable, such as communities living in poverty, homes for the aged, prisons and care centers for people with mental disorders. People with weakened immune systems, such as people living with HIV/AIDS, are also more vulnerable to transmission of TB.
C- Risk factors for tuberculosis:
Risk factors for TB include living in densely populated communities, poverty, poor living conditions, a weakened immune system, exposure to people infected with TB, and travel to areas where TB is endemic. People living with HIV/AIDS are particularly vulnerable to TB because HIV attacks the immune system, which can make people more susceptible to contracting the disease. Smokers also have an increased risk of developing tuberculosis because smoking can damage the lungs and make people more susceptible to respiratory infections. Older people and children may also be more vulnerable to TB due to immature or weakened immune systems.
III- Symptoms of tuberculosis:
A- Common symptoms:
The most common symptoms of active TB include prolonged cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue, and coughing up blood. Symptoms may also include chest pain, shortness of breath, and night sweats. Tuberculosis can also spread to other parts of the body, such as bones and joints, and can cause joint pain, bone pain, and stiffness. The symptoms of tuberculosis can resemble those of other respiratory diseases, so it is important to seek medical attention if an infection is suspected. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent disease progression and prevent transmission to others.
B- Specific symptoms according to the parts of the body affected:
Tuberculosis symptoms can vary depending on the part of the body affected. When the lungs are affected, symptoms may include a prolonged cough, bloody cough, fatigue, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. If TB spreads to other parts of the body, such as bones and joints, it can cause joint pain, bone pain, stiffness, and muscle weakness. When TB affects the kidneys, it can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and frequent urination. If TB affects the central nervous system, it can cause severe headaches, dizziness, memory loss, blurred vision, and impaired coordination.
C- How tuberculosis can be confused with other diseases:
Tuberculosis can easily be confused with other diseases due to its similar symptoms. For example, symptoms such as prolonged cough, fever and night sweats are common to many other respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, pneumonia and asthma. Additionally, joint and bone pain can be similar to that caused by conditions such as arthritis or bone disease. It is also possible that tuberculosis is confused with infections such as HIV/AIDS, which can also cause similar symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue and night sweats. It is therefore important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
IV- Diagnosis of tuberculosis:
A- Diagnostic tests available:
There are several diagnostic tests available to detect tuberculosis. The first test is the tuberculin skin test (PPD), which involves injecting a small amount of substance into the skin to check the body’s reaction. If the person is infected with TB bacteria, a lump will appear at the injection site after 48 to 72 hours. The PPD test is a quick and inexpensive test, but it can give false positive results in people who have been previously exposed to the bacteria.
Another diagnostic test is the nucleic acid test (NAT), which uses DNA technology to detect the presence of TB bacteria DNA in sputum or body fluid samples. . This test is more accurate than the PPD test, but it is also more expensive and takes longer to get the results.
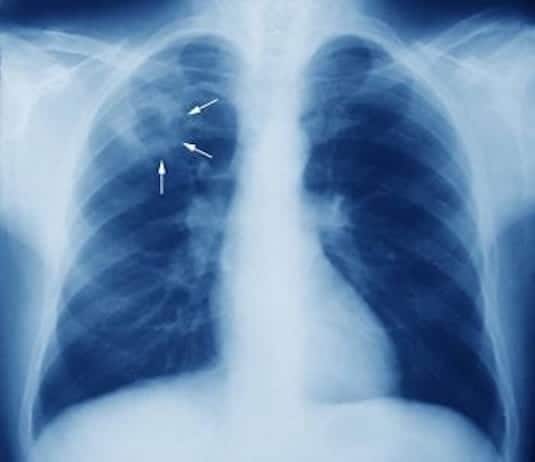
Finally, a chest x-ray test can be used to visualize lung damage caused by tuberculosis. However, this test cannot provide a definitive diagnosis of tuberculosis, but it can help rule out other potential causes of respiratory symptoms.
Ultimately, the choice of diagnostic test will depend on the symptoms presented and the availability of tests in the country or region. It is important to consult a doctor to determine the best test for a given situation.
B- How test results are interpreted:
The interpretation of TB diagnostic test results is a crucial process in establishing a diagnosis and determining the appropriate treatment. For the tuberculin skin test (PPD), a skin reaction of more than 5 mm is considered a positive result, indicating possible exposure to the tuberculosis bacteria. However, it is not a definitive diagnosis and further tests should be done to confirm the presence of active TB.
For nucleic acid screening (NAT) tests, results may vary depending on the type of test used. The results can be either negative, or positive, or even indeterminate. A negative result generally means that the bacterium was not detected in the samples, while a positive result indicates the presence of the bacterium’s DNA. Indeterminate results may require additional testing for more accurate interpretation.
For chest X-ray, the interpretation of the results depends on the type of lesions visible on the X-ray images. Suspicious lesions should be evaluated by a qualified physician to determine if they are caused by tuberculosis or another lung disease.
It is important to note that TB can hide in the body for years without producing symptoms. Therefore, even negative test results cannot guarantee the absence of tuberculosis. It is always best to see a doctor for a full evaluation and an accurate diagnosis.
C- Importance of diagnosing tuberculosis early:
Early diagnosis of tuberculosis is extremely important for effective treatment and prevention of the spread of the disease. If TB is not diagnosed in time, it can lead to serious complications and death. In addition, untreated TB can become multi-drug resistant, making treatment more difficult and more expensive.
Early diagnosis also helps minimize the time a person can spread the disease to others, which can help prevent an outbreak. People with TB should start treatment as soon as possible to increase their chances of full recovery.
It is important that people with symptoms of TB or risk factors, such as recent travel to countries with a high risk of TB, see a doctor for testing. Doctors may also perform regular screening tests for people at high risk, such as healthcare workers and immunocompromised people.
In summary, early diagnosis of tuberculosis is crucial for the well-being of the person affected, the prevention of the spread of the disease and the protection of the community in general.
V- Treatment of tuberculosis:
A- Types of drugs used to treat tuberculosis:
The treatment of tuberculosis generally involves the use of several drugs at the same time to completely eliminate the bacteria responsible for the disease. Drugs commonly used to treat tuberculosis include isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and streptomycin.
These drugs must be taken regularly for several months, often for six months or more, to ensure complete elimination of the TB bacteria. Treatment can be difficult because the drugs can cause serious side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, and weight loss.
It is important that people with TB follow their treatment strictly to avoid drug resistance, which can make treatment more difficult and more expensive. Doctors can adjust medications based on individual patient reactions to minimize side effects.
In conclusion, the drugs used to treat tuberculosis are essential in eliminating the bacteria responsible for the disease and helping those affected to recover fully. However, it is important to strictly follow the prescribed treatment to ensure effective healing and prevent drug resistance.
B- Duration of treatment:
The time it takes to treat TB depends on several factors, such as the severity of the disease, the drugs used, and the patient’s response to treatment. In general, treatment for tuberculosis lasts six to nine months, although some people may require longer treatment.
Treatment usually begins with a combination of drugs, called intensive therapy, which lasts two to six months. After this phase, patients may be directed to continued treatment, called maintenance therapy, which usually lasts another four to seven months.
It is important to note that the duration of treatment can vary depending on several factors, such as the severity of the disease, the presence of complications and the patient’s response to treatment. Doctors closely monitor patients to make sure TB is cleared up completely and treatment is working.
In conclusion, the duration of treatment for tuberculosis varies depending on several factors and can range from six to nine months or more. It is important that patients follow their treatment strictly to ensure complete recovery and prevent the disease from coming back.
C- Importance of completing the recommended treatment:
It is extremely important to complete the recommended treatment for tuberculosis. If a patient stops treatment too soon, they may develop a resistant form of the disease, which may be more difficult to treat and more contagious. It can also cause serious health complications, including the reappearance of tuberculosis and the progression of the disease to other parts of the body.
Also, non-completion of treatment can lead to increased transmission of TB to others. This can contribute to the progression of tuberculosis as a public health problem, making the disease more difficult to control and eliminate.
Following the recommended treatment is also important to ensure complete recovery and to minimize the risk of the disease coming back. Doctors closely monitor patients during the entire treatment to ensure that the tuberculosis is cleared up completely and the patient recovers fully.
In conclusion, it is crucial to complete the recommended treatment for tuberculosis. This helps to ensure complete recovery, minimize the risk of the disease coming back, and prevent transmission to others. Doctors can help patients follow their treatment and make sure the treatment is working.
VI- Prevention of tuberculosis:
A- Prevention measures for people at high risk:
There are several preventive measures for people considered to be at high risk of developing TB. These may include:
1- BCG vaccination: the BCG vaccine is given to people considered to be at high risk, including health care workers, people living in areas with a high incidence of tuberculosis and children born to mothers with tuberculosis.
2- Early diagnosis: people at high risk should undergo regular screening tests to detect tuberculosis early. This may include chest X-rays, blood tests, and swab tests.
3- Avoid infected people: People at high risk should avoid close contact with people infected with TB, including avoiding sharing personal items and wearing a face mask when in contact with people with TB. disease.
4- Prophylactic treatment: people at high risk may be prescribed prophylactic treatment to prevent the progression of tuberculosis in the event of exposure to the bacteria.
5- Good hygiene practices: Good hygiene practices, such as washing your hands frequently and covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the transmission of tuberculosis.
In conclusion, it is important to take preventive measures for people considered to be at high risk of developing tuberculosis. People at risk can speak with their doctor to assess their risk and develop a personalized prevention plan.
B- Prevention measures for the general population:
Tuberculosis prevention is important for the whole population, as it can help reduce the transmission of the bacteria responsible for the disease. There are several preventive measures that can be taken by the general population to minimize the risk of contracting TB. First, people should practice good personal hygiene by washing their hands regularly and covering their mouths when coughing or sneezing. It is also important not to share personal items, such as towels or toothbrushes, with someone who has TB. In addition, people should avoid crowded places and regularly ventilate indoor spaces. It is also advisable to consult a doctor as soon as symptoms of tuberculosis appear to minimize the risk of transmission to other people. Finally, it is recommended to receive a vaccination against tuberculosis if one is exposed to a high risk of contracting the disease.
C- Importance of vaccination against tuberculosis:
Vaccination against tuberculosis is an important way to prevent the disease in people at risk. There is currently a vaccine called Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) that is given to some people to prevent tuberculosis. This vaccine is not 100% effective, but can help reduce the risk of contracting the disease or alleviate symptoms in the event of contamination. It is especially recommended for children who live in areas where tuberculosis is common and for people at high risk of contracting the disease, such as healthcare workers and people with weakened immune systems. Vaccination against tuberculosis is also important for vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, who are more at risk of serious complications in the event of contamination. Finally, vaccination can help reduce the spread of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis in the population, which can help reduce the burden of disease on health care systems.
VII- Conclusion:
A- Summary of key points:
The Summary of Key Points on Tuberculosis includes the following information: Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is spread by coughing and exhaling airborne droplets. Symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and weight loss, and diagnosis can be made by tests such as chest x-ray and tuberculin skin test. Treatment involves taking antibiotic medications for several months, and prevention includes vaccination, avoiding transmission of the bacteria, and prompt treatment of the disease. It is important to diagnose and treat TB early to prevent its progression and transmission to others.
B- Importance of raising awareness about tuberculosis:
Raising awareness about TB is important for several reasons. First, it is important that people understand the seriousness of the disease and the dangers of its spread. By knowing the symptoms, risk factors and means of prevention, people can be more alert and act quickly if necessary. Additionally, raising awareness can help break down the stereotypes and misconceptions that often surround TB, which can deter people from getting diagnosed and receiving appropriate treatment. Finally, by raising awareness, we can strengthen the fight against tuberculosis and eliminate the stigmatization of people with the disease.
C- Final message for readers:
In conclusion, tuberculosis is a serious disease that can have serious health consequences if not diagnosed and treated in time. It is important to know the symptoms, the risk factors and the means of prevention to protect your own health as well as that of others. Medicines exist to treat tuberculosis, but it is crucial to follow the doctor’s recommendations to ensure complete and effective treatment. Finally, raising awareness about TB is an important aspect of the fight against this disease, as it can help break down stereotypes and inspire people to seek timely diagnosis and treatment.
Leave a Reply