Indications:
Take stock of not failing hearing reported by the patient or his entourage or revealed by clinical examination.
Principle:
It stimulates the hearing aid by air, with pure sounds perceived through headphones, and by the bone, with a vibrator. The patient reports the moment he begins to perceive sounds. Comparison of air and bone perceptions determines the quality of hearing and the existence of potential problems.
 Technique:
Technique:
This exam practice soundproof booth and is only possible in children after the age of 4 or 5 years.
For headphones and bone vibration, we actually “listen” pure tone. The patient reports when he begins to perceive sound.
Thus studied the functioning of the entire hearing in the inner ear, internal and external auditory pathways (nerve).
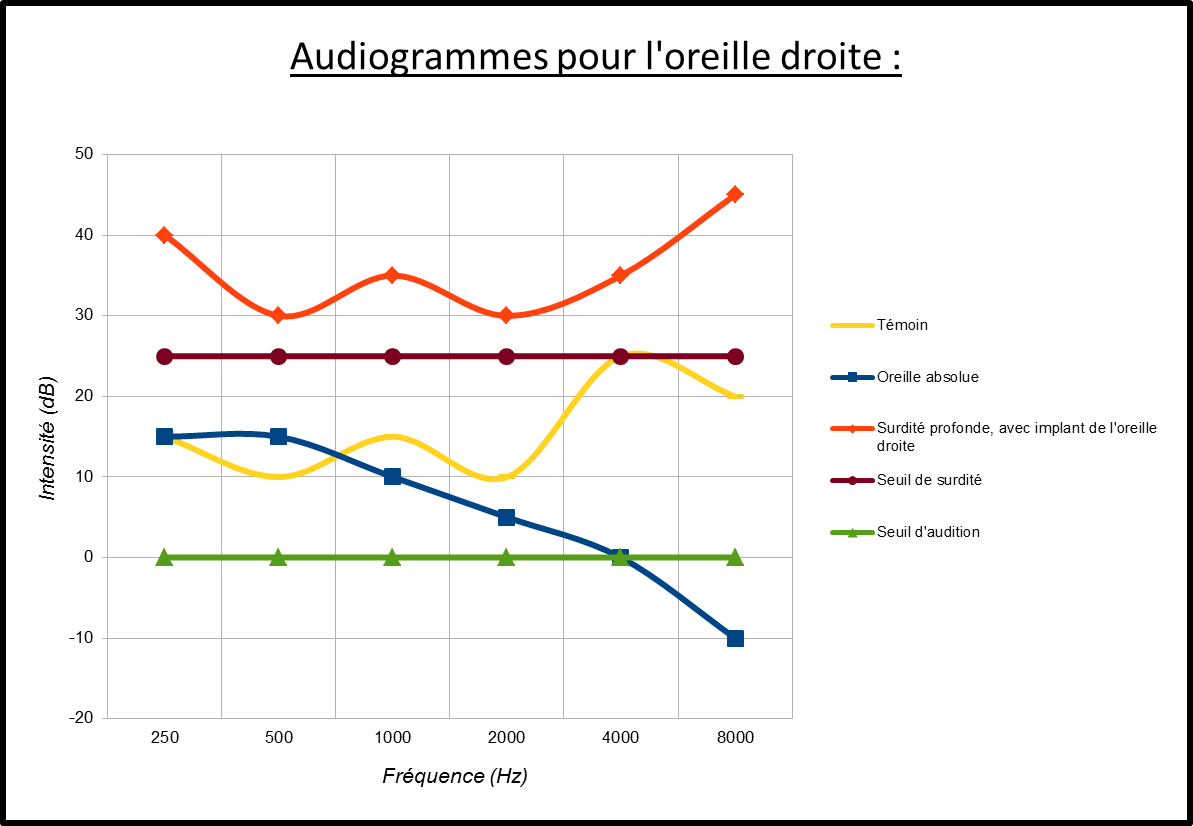
Results:
The results are expressed in decibels and should normally be comparable to those of a control population in good condition.
The air and bone perception of curves must be superimposed with a possible variation of 5 decibels.
If the loss exceeds 15 decibels, it is considered pathological; under further review is required.
If the loss affects both curves simultaneously, the hearing problem is perception.
If only the air curve is affected, loss of transmission.
Cost:
K10.
Advice practice:
Before practicing the examination, the practitioner must ensure the integrity of the external auditory canal and the absence of earwax.
Leave a Reply