Category: Additional Tests
-
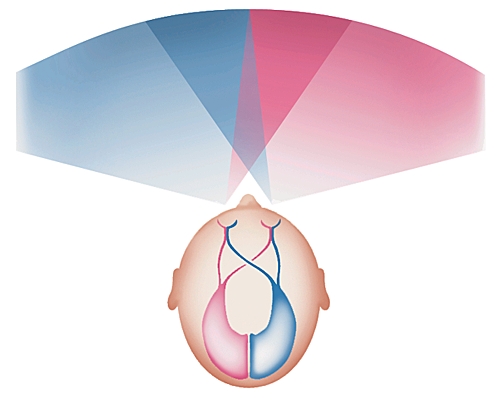
Visual Field
Indications: The determination of the visual field is used to diagnose glaucoma and intracranial tumors. Principle: It determines the field width seen by the patient making him secure a point straight ahead. The doctor sets curves connecting the equal retinal sensitivity point (isopter). Technique: The seated patient, a masked eye, fixed centrally. He is presented…
-
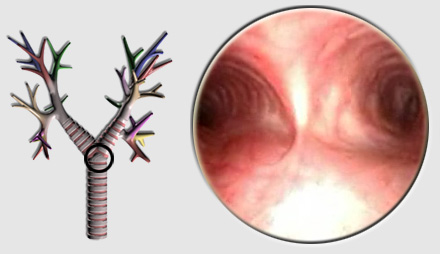
Bronchoscopy
Indications: This is a flinch-diagnose lung disease before clinical symptoms unexplained or a radiological image to be determined. Principle: The flexible endoscope to visualize the bronchial tree; he can practice aspirations in case of obstructions and biopsies guided by the vision of abnormal areas or systematic in doubt bronchial hull. Endoscopy can be used to…
-
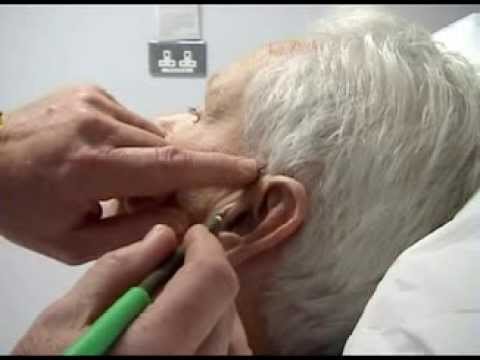
Temporal Biopsy
Indications: The biopsy is performed in case of suspicion of temporal arteritis, either in a temporal arteritis or polymyalgia rheumatica. Cons-indications: anticoagulant therapy. Principle: The histological analysis of samples of arterial wall can diagnose temporal arteritis or polymyalgia rheumatica. Technique: The gesture is performed under local anesthesia without requiring hospitalization. Local anesthesia is obtained using…
-
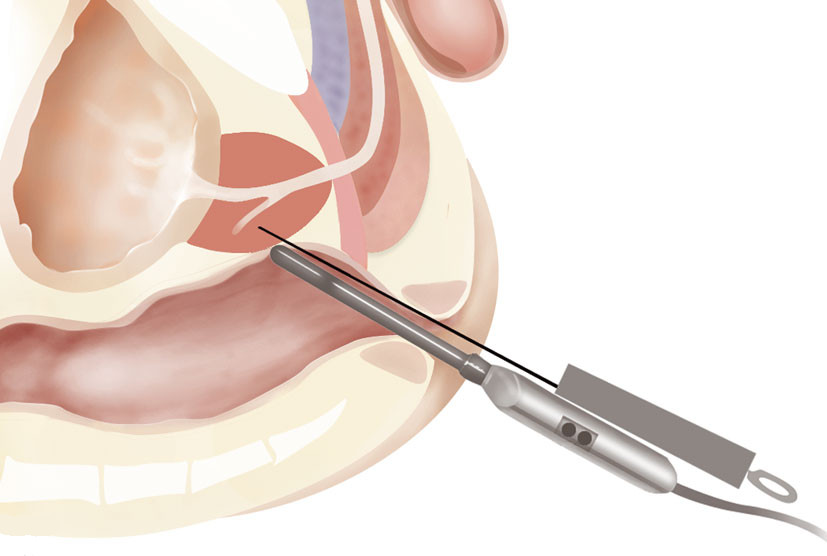
Prostate Biopsy
Indications: The review serves to confirm or before treatment for prostate cancer and type. Principle: This is to clarify a doubt, clinical or ultrasound, realizing a sampling of the radio-controlled area possible. Technique: There are two techniques: – Transperitoneal under general anesthesia; – Transrectal without anesthesia. The collection of samples is entrusted to a cytologist,…
-
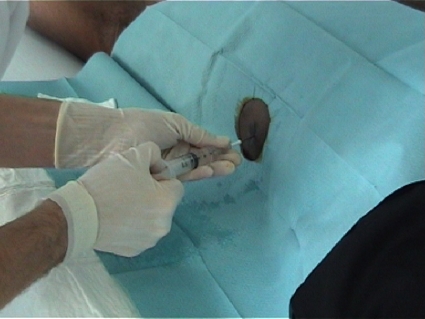
Liver Biopsy
Indications: The interest of the biopsy should be carefully weighed before the risks. This is thanks to a liver tissue sampling to know the liver condition, information that can be useful in case of chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis scalable. Cons-indications: cholestatic liver disease (obstruction of the bile duct blocking the functioning of the liver). Patient…
-
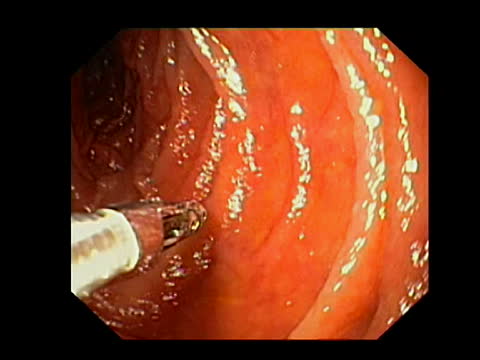
Biopsy of the Small Intestine
Indications: This is to detect diseases of the small intestine such as celiac disease, lymphoma, or Whipple’s disease. Cons-indications: Hemostasis disorders and against any indication to general anesthesia. Technique: There are two techniques: – High biopsies are done by gastroesophageal endoscopic examination; – Distal biopsies are done through a flexible endoscope that can cross the…
-
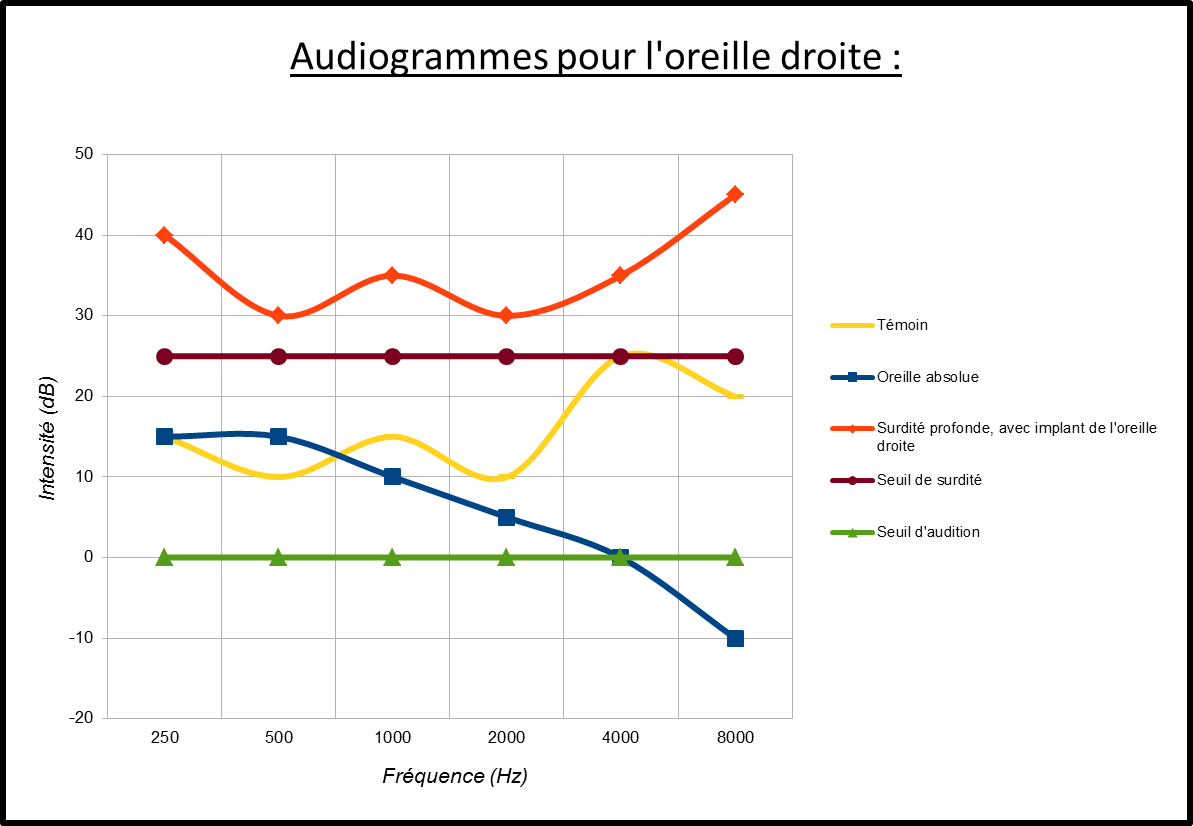
Audiogram
Indications: Take stock of not failing hearing reported by the patient or his entourage or revealed by clinical examination. Principle: It stimulates the hearing aid by air, with pure sounds perceived through headphones, and by the bone, with a vibrator. The patient reports the moment he begins to perceive sounds. Comparison of air and bone perceptions…
-
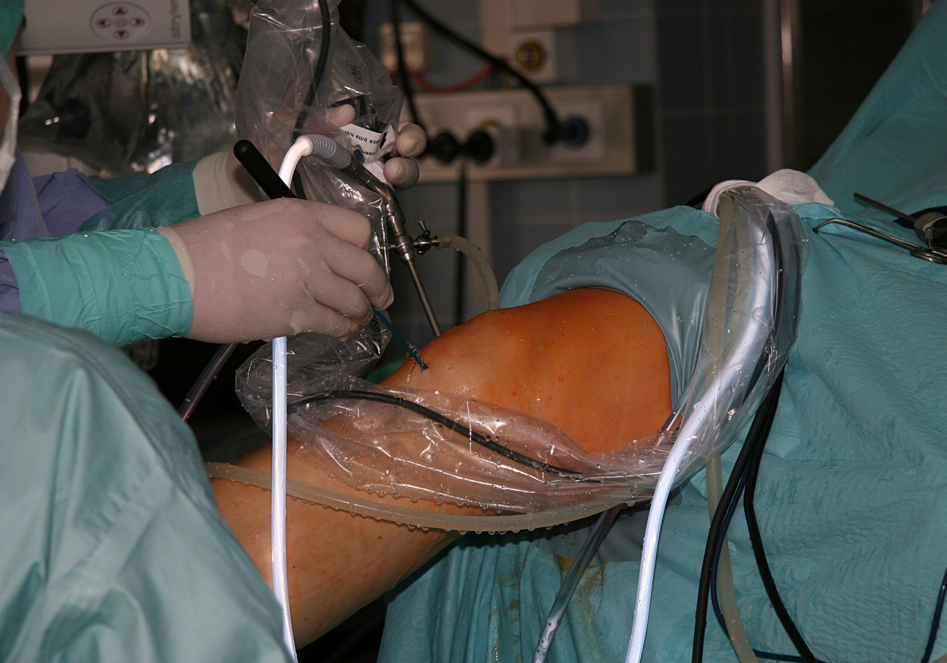
Knee Arthroscopy
Indications: Any injury suspected meniscus or ligaments requires an arthroscopy. The review is required if a suspect knee meniscal tear, partial or complete, or if serious doubt exists on a ligament injury and in case of suspicion of an intra-articular foreign body. Another indication is infectious arthritis, when adequate medical treatment is not enough to…
-
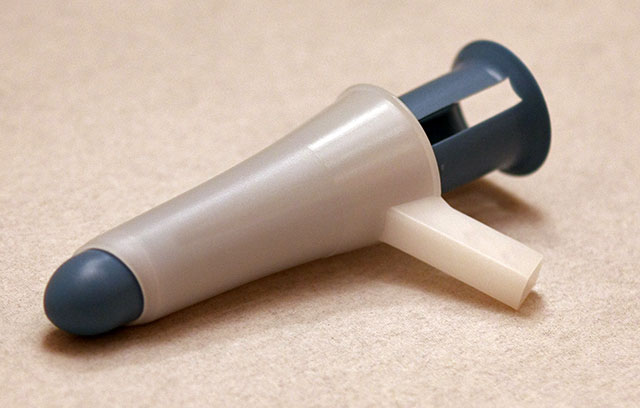
Anoscopy
Indications: The test checks the state of the anus, rectum and its walls; it allows to take stock of the presence and importance of hemorrhoids, treat, but also to detect anal fissures, rectal polyps, to find the cause of rectal bleeding (polyp, ulcerative colitis). Cons-indications: It is difficult to conduct the examination if the patient…
-
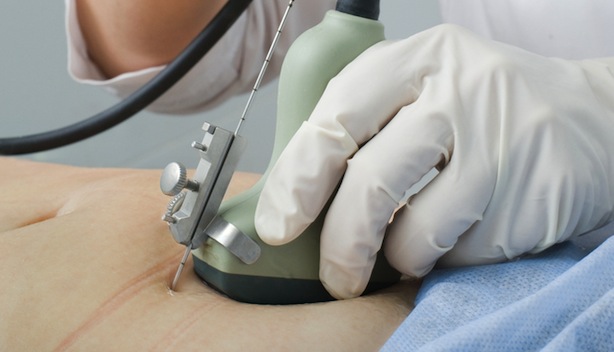
Amniocentesis
Indications: The goal is to repeat, by examining a large number of chromosomal abnormalities in the unborn child, if it shows malformation risk factors or signs making fear: nuchal thickening of the neck to ultrasonography or hCG levels too high. With a mother aged (over 38 years with a positive test HT21) for example, it…
You must be logged in to post a comment.