I – Introduction:
A- Definition of emphysema and explanation of its pathology:
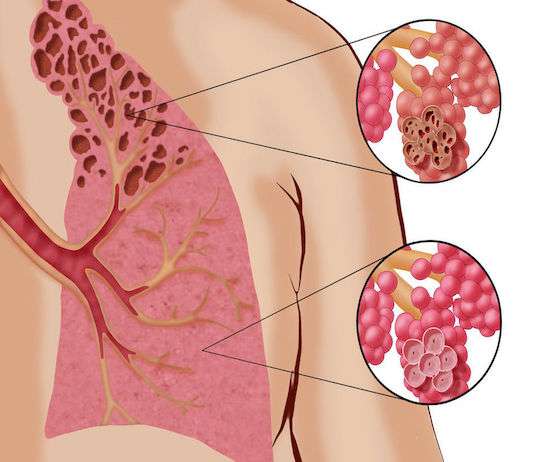
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease characterized by the progressive destruction of the alveolar walls in the lungs, which leads to a loss of elasticity in the lung tissues. This loss of elasticity leads to an increase in the air space of the lungs, thus causing a reduction in the contact surface between the air and the blood vessels. The pathology of emphysema mainly affects smokers, but it can also be caused by exposure to air pollutants, irritants or environmental toxins. Symptoms include chronic cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, fatigue, and excess mucus production. Emphysema may be a contributing factor to the onset of respiratory failure, a condition that is characterized by an inability to supply enough oxygen to the body. Treatments for emphysema may include medication to relieve symptoms, pulmonary rehabilitation, surgery, or a lung transplant. Identifying emphysema symptoms early and implementing an appropriate treatment plan can help slow the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life.
B- Importance of emphysema as a lung disease:
 Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that is of major importance due to its impact on the quality of life and life expectancy of sufferers. Indeed, this disease can seriously affect respiratory function, causing a reduction in the ability of the lungs to provide enough oxygen to the body. People with emphysema may have difficulty performing daily activities, such as climbing stairs or walking short distances, and may experience shortness of breath even at rest. Emphysema can also increase the risk of lung infections and other health complications, including respiratory failure. In addition, emphysema is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer in smokers. As is, the management of emphysema is an important public health concern, as it can have a significant impact on the quality of life of patients and on the costs of health care. Raising awareness of this disease, as well as implementing effective prevention and treatment measures, can help reduce the burden of emphysema on patients’ health and quality of life.
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that is of major importance due to its impact on the quality of life and life expectancy of sufferers. Indeed, this disease can seriously affect respiratory function, causing a reduction in the ability of the lungs to provide enough oxygen to the body. People with emphysema may have difficulty performing daily activities, such as climbing stairs or walking short distances, and may experience shortness of breath even at rest. Emphysema can also increase the risk of lung infections and other health complications, including respiratory failure. In addition, emphysema is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer in smokers. As is, the management of emphysema is an important public health concern, as it can have a significant impact on the quality of life of patients and on the costs of health care. Raising awareness of this disease, as well as implementing effective prevention and treatment measures, can help reduce the burden of emphysema on patients’ health and quality of life.
C- Objective of the article:
The goal of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of emphysema as a chronic lung disease, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We aim to raise public awareness of this disease and provide clear and precise information on its health impacts, consequences and means of prevention. We’ll also discuss the latest advances in research on this disease, as well as steps that patients with emphysema can take to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. We hope that this article will be useful for patients with emphysema, their loved ones, healthcare professionals and the general public, by providing them with accurate and reliable information about this disease. Our goal is to raise awareness of this often underdiagnosed disease, to help people understand the risks, symptoms and treatment options for emphysema. Ultimately, we hope this article helps improve the health and quality of life for people with emphysema.
II- The causes of emphysema:
A- Smokers and non-smokers: the risks associated with cigarette smoke:
Cigarette smoke can cause significant damage to health whether inhaled directly or indirectly by non-smokers. Smokers are at increased risk of developing a variety of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and respiratory disease, and emphysema. Cigarette smoke contains over 70 chemicals known to cause cancer, such as benzene and tar, as well as many other harmful chemicals, such as carbon monoxide, formaldehyde and ammonia. Non-smokers exposed to second-hand smoke, meanwhile, can develop the same diseases as smokers, including lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. Besides, pregnant women exposed to second-hand smoke may increase their risk of having a premature or low birth weight baby. It is therefore important to reduce exposure to cigarette smoke by quitting smoking or avoiding environments where smoke is present. Smokers who cannot quit should smoke outdoors to reduce non-smokers’ exposure to second-hand smoke.
B- Other causes:
Although cigarette smoke is a major cause of emphysema, there are also other factors that can contribute to the development of this disease. Long-term exposure to air pollutants such as indoor and outdoor air pollution can be a risk factor for emphysema, especially in densely populated urban areas. Exposure to toxic chemicals in the workplace, such as organic chemicals, mineral dusts, and chemical fumes, can also be a risk factor for emphysema. Additionally, certain inherited conditions, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, can increase the risk of developing emphysema, even in non-smokers. Recurrent lung infections and chronic breathing problems such as asthma can also contribute to the development of emphysema. It’s important to understand that even if you don’t smoke, you may still be at risk of developing emphysema if you are exposed to these other risk factors. Taking steps to reduce exposure to these factors can help prevent emphysema and other lung diseases.
1- Occupational exposure to toxic substances:
Occupational exposure to toxic substances can increase the risk of developing emphysema and other lung diseases. Many workers are exposed to toxic chemicals in the workplace, such as solvents, mineral dusts, metal fumes, exhaust fumes and chemical vapours. These substances can enter the lungs and cause irreversible damage to lung tissue, which can lead to chronic lung diseases such as emphysema. Workers most at risk of being exposed to these toxic substances include chemical industry workers, construction workers, miners, mechanics and automotive workers. Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe work environment and put in place safety measures to minimize exposure to toxic substances. Workers must also be trained on the potential risks to their health and the protective measures to be taken. It is important to understand the risks of occupational exposure to toxic substances and to take steps to protect yourself against potential hazards.
2- Air pollution:
Air pollution can be a significant risk factor for the development of emphysema and other lung diseases. Fine particles and toxic gases in the air can enter the lungs and cause irreversible damage to lung tissue. Air pollution is often caused by vehicle emissions, industries, power plants and forest fires. People who live in densely populated urban areas and workers who are exposed to air pollution in the workplace are particularly vulnerable to the effects of air pollution. Children, the elderly, and people with chronic respiratory diseases are also at greater risk of experiencing negative health effects from air pollution. It is important to take measures to reduce air pollution, such as promoting clean transport, reducing industrial emissions and regulating vehicle emissions. Additionally, people can reduce their exposure to air pollution by avoiding heavily polluted areas and using appropriate respirators when working in high pollution environments.
III- Symptoms of emphysema:
A- Warning signs:
The warning signs of emphysema can be difficult to identify because they develop slowly and gradually. Early symptoms may include wheezing or shortness of breath during physical exertion. People with emphysema may also experience increased fatigue and an inability to engage in normal daily activities. As the disease progresses, symptoms may become more severe, such as chronic cough with sputum, shortness of breath even during rest, persistent wheezing, and chest pain. In more severe cases, patients may need oxygen therapy to aid breathing. It is important to consult a doctor as soon as the first symptoms appear in order to quickly diagnose emphysema and put in place appropriate treatment to limit damage to the lungs. People at high risk, such as smokers and workers exposed to toxic substances, should be especially alert to the warning signs of emphysema and seek medical attention as soon as possible if symptoms persist.
B- More advanced symptoms:
Symptoms of emphysema can become more severe over time and as the disease progresses. As the lungs lose their elasticity, people with emphysema may experience a feeling of shortness of breath even at rest, increased fatigue, and an inability to perform simple daily tasks. Chronic cough with sputum may become more frequent, and wheezing may become more pronounced. Patients with emphysema may also experience chest pain and difficulty breathing during the night, which can disrupt their sleep. Advanced symptoms may also include respiratory problems such as frequent respiratory infections, cyanosis (blue discoloration of the lips or fingernails), swelling of the legs and feet, as well as disturbances in appetite and weight loss. In the most severe cases, oxygen must be continuously administered to help the patient breathe. It is important that people with emphysema receive appropriate treatment to relieve symptoms and improve their quality of life, as well as to prevent disease progression.
C- Differences with other lung diseases:
Emphysema is one of many lung diseases that affect the ability of the lungs to function properly. Although it may share some symptoms with other illnesses, it does have some key characteristics. Emphysema is caused by progressive destruction of lung tissue, particularly the small air sacs (alveoli), resulting in loss of elasticity and loss of contact surface for gas exchange. People with emphysema may experience feeling short of breath even at rest and increased fatigue, especially during physical activities. This is distinct from asthma, which is a chronic lung disease characterized by inflammation of the airways that causes wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Chronic bronchitis is another lung disease that can cause chronic coughing and mucus production. People with emphysema can also experience symptoms similar to pulmonary fibrosis, a progressive lung disease characterized by scarring of lung tissue, but the causes and treatments for these two conditions are different. Differentiating between these different lung diseases is important for accurate and effective diagnosis and treatment. a progressive lung disease characterized by scarring of lung tissue, but the causes and treatments for these two diseases are different. Differentiating between these different lung diseases is important for accurate and effective diagnosis and treatment. a progressive lung disease characterized by scarring of lung tissue, but the causes and treatments for these two diseases are different. Differentiating between these different lung diseases is important for accurate and effective diagnosis and treatment.
IV- Diagnosis and treatment of emphysema:
A- Diagnosis of emphysema:
The diagnosis of emphysema is usually based on the patient’s medical history, physical exam, and lung tests. The doctor may ask the patient to describe their symptoms, smoking history, and other risk factors, such as occupational exposure to chemicals, to assess the likelihood of emphysema. During the physical exam, the doctor may listen to the patient’s breathing with a stethoscope for signs of wheezing, coughing, and breathing problems. Lung tests, such as spirometry, measure how much air the patient can exhale and inhale and how quickly, which can help determine if the lungs are affected by emphysema. Medical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT), can also be used to visualize the lungs and detect signs of emphysema. In some cases, an arterial blood test may be done to measure blood oxygen levels, which can help assess the severity of emphysema. It is important to diagnose emphysema as early as possible to allow early treatment and symptom management to prevent disease progression and improve patients’ quality of life.
1- Spirometry:
Spirometry is a commonly used diagnostic test to assess lung function and detect lung diseases such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma. The test consists of a series of forced breaths in a device called a spirometer, which measures how much air the patient can exhale and inhale and how fast. The test is simple and non-invasive, and usually only takes a few minutes to perform. Spirometry results can help diagnose emphysema by measuring the patient’s lung capacity and identifying a reduction in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), which may indicate airway obstruction. Spirometry can also be used to monitor the progression of emphysema and to assess the effectiveness of treatments. Spirometry results can help doctors determine the stage of the disease and prescribe the most appropriate treatment. In general, spirometry is an important test for the diagnosis and monitoring of emphysema and other lung diseases.
2- Medical imaging:
Medical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) and chest X-ray, can be used to diagnose emphysema and assess its severity. CT uses X-rays to create detailed images of the lungs, showing damaged areas and how much lung tissue is affected. A chest x-ray, also known as a chest x-ray, is less accurate than CT but can be used to detect signs of emphysema and assess lung size. The images obtained from medical imaging can help doctors make an accurate diagnosis of emphysema, assess disease severity, and monitor disease progression over time. However, exposure to X-rays can be a concern for patients, especially for those who need multiple imaging tests. Healthcare professionals can explain the risks and benefits of each imaging test and discuss the best option for each patient. In general, medical imaging is an important tool for diagnosing and monitoring emphysema and other lung diseases.
B- Treatment options:
There is no cure for emphysema, but there are treatment options to slow disease progression, relieve symptoms, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment for emphysema may include smoking cessation, oxygen therapy, bronchodilator medications, pulmonary rehabilitation, and surgery. Quitting smoking is the most important measure to slow the progression of emphysema and improve lung function. Oxygen therapy may be prescribed to relieve dyspnea and improve exercise capacity. Bronchodilator medications, such as inhalers, are often used to help open the airways and make breathing easier. Pulmonary rehabilitation can help improve exercise capacity and reduce symptoms of emphysema. Surgery may be considered for the most severe cases of emphysema, such as lung volume reduction or lung transplantation. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the disease and the general health of the patient, so it is important to consult a medical professional to discuss the most appropriate treatment options.
1- Medicines:
Medications play an important role in the treatment of emphysema. Bronchodilator drugs are often used to help open the airways and make breathing easier. They can be given as inhalers or tablets. Inhalers are generally preferred because they deliver the medication directly to the lungs, allowing for quick and effective action. Bronchodilators can be divided into two types: beta-agonists and anticholinergics. Beta-agonists are often used to relieve acute symptoms of emphysema, such as dyspnea, by relaxing airway muscles and improving airflow. Anticholinergics are often used to reduce mucus production in the airways and to reduce spasms of airway muscles. Corticosteroids can also be used to reduce inflammation in the airways. They are often given in the form of inhalers or tablets. However, corticosteroids should be used with caution, as they can have serious long-term side effects, including decreased bone density, increased blood sugar, and immune system suppression.
2- Pulmonary rehabilitation:
Besides medication, other treatment options are available for people with emphysema, including pulmonary rehabilitation and surgery. Pulmonary rehabilitation is a program that aims to improve quality of life by helping patients better manage their disease. It includes breathing exercises, physical exercise, dietary advice and psychological advice. Surgery may also be considered for patients with advanced emphysema. The most common surgical procedure is lung volume reduction, which involves removing part of the lungs to reduce the size of the air space and improve breathing. Lung transplantation is also an option for patients with advanced emphysema who have not responded to other treatments. However, lung transplantation is a complex and invasive procedure that carries significant risks, including rejection of the transplanted organ and infections. The choice of treatment method will depend on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the age and the general state of health of the patient.
3- Surgery:
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that can be difficult to treat. Although non-surgical treatments such as medications, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation can be helpful, some patients may need surgery. Surgery is considered a treatment option for patients with severe emphysema who have not responded to conventional treatments. Surgery may involve removing part of the lungs to improve lung function or installing bronchial valves to improve lung expansion. These procedures can help reduce symptoms of emphysema such as shortness of breath and coughing, as well as improving patients’ quality of life. However, surgery can have risks and side effects, and it is not suitable for all patients with emphysema. Patients should discuss the benefits and risks of surgery with their doctor to determine if this treatment option is right for them.
C- Importance of early diagnosis and treatment:
It is essential to diagnose and treat emphysema early because the disease is progressive and can cause permanent damage to the lungs. Patients with advanced emphysema can experience extreme breathing difficulties and their quality of life can be significantly affected. Early diagnosis can help patients start treatment before the disease progresses, which can help prevent or slow further lung damage. Early treatment can also help patients better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. It is important to remember that the damage caused to the lungs by emphysema cannot be completely cured, but treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and prevent serious complications. It is therefore recommended that people with symptoms see their doctor as soon as possible for early diagnosis and treatment.
V- Tips for patients with emphysema:
A- How to prevent the worsening of emphysema:
Emphysema is a progressive lung disease characterized by the destruction of the walls of the alveoli, the air sacs in the lungs. This disease causes a decrease in breathing capacity, which can make daily activities more difficult. However, there are steps people with emphysema can take to prevent the condition from getting worse. First of all, quitting smoking is crucial. Smoking is the main cause of emphysema and quitting smoking can slow the progression of the disease. It is also important to avoid lung irritants such as air pollution, chemicals, dusts and allergens. People with emphysema should also maintain a healthy, balanced diet and exercise regularly to improve their breathing capacity. Finally, it is important to follow the advice of your doctor and take the prescribed medications regularly to control the symptoms of emphysema and prevent exacerbations. By taking these steps, it is possible to prevent emphysema from worsening and maintain a satisfactory quality of life.
B- Tips for managing the symptoms of emphysema:
Emphysema is a lung disease that can cause difficulty breathing and reduce quality of life. However, there are practical tips for managing the symptoms of this disease and improving your quality of life. First, it is important to follow a treatment plan established by your doctor. This may include medication to relieve symptoms, inhalers, or steroids. It is also recommended that you follow a breathing exercise program to improve your lung capacity. Deep breathing exercises, directed coughing, and relaxation can help improve respiratory function and reduce anxiety. It’s also important to maintain a healthy, balanced diet to promote overall health and maintain a healthy weight. Avoid lung irritants such as smoke, chemicals, pollution, and allergens as much as possible. Finally, seek emotional support to help you cope with the difficulties of the illness, whether through a support group or mental health professionals. By taking these steps, you can help manage emphysema symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
C- Importance of quitting smoking:
Quitting smoking is one of the most important choices a person can make to improve their health. Smoking tobacco is the leading cause of preventable disease and premature death worldwide. The health risks associated with smoking are numerous and serious, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, lung disease, and other chronic health problems. When one quits smoking, the body begins to repair itself immediately. The health risks of smoking gradually decrease over time, helping to reduce the risk of serious illnesses. Quitting smoking can also improve quality of life by reducing respiratory symptoms, such as cough and shortness of breath, and improving smell and taste. Moreover, quitting smoking can have economic benefits, as the cost of smoking can be considerable, and it can save money. In sum, quitting smoking is crucial to maintaining health, improving quality of life and saving money in the long run.
VI- Conclusion:
A- Summary of the key points of the article:
In this article, we have discussed emphysema and the steps you can take to prevent it from getting worse. First, we highlighted the importance of quitting smoking, as smoking is the main cause of disease. Next, we suggested avoiding lung irritants such as air pollution, chemicals, and allergens, and maintaining a healthy, balanced diet and regular physical activity. We also explained how to manage the symptoms of emphysema by following a treatment plan from a medical professional, practicing breathing exercises, avoiding lung irritants, and seeking emotional support. Finally, we highlighted the importance of quitting smoking to improve overall health and reduce the risk of serious illness.
B- Reaffirmation of the importance of emphysema awareness and disease prevention:
It is essential to reaffirm the importance of emphysema awareness and disease prevention. Emphysema is a lung disease that can be prevented by avoiding risk factors such as smoking and exposure to irritating substances. It is crucial to raise awareness about the risks of smoking and the importance of quitting smoking to reduce the number of people affected by emphysema. In addition, disease prevention can be achieved by improving air quality in indoor and outdoor environments and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Efforts to raise awareness and prevent emphysema can also improve disease management, as early detection will allow for prompt intervention and more effective treatments.
Leave a Reply