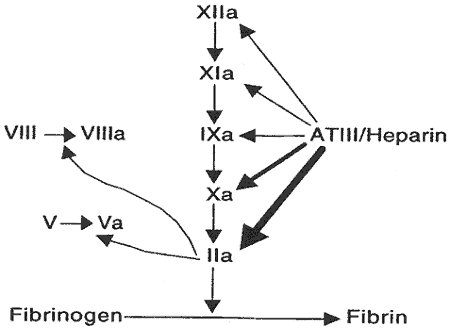
– Heparins are indirect thrombin inhibitors (IIa), acting by means of a plasma cofactor antithrombin III (AT III). The action of heparin-AT III complex is directed against thrombin (IIa) and against factor Xa (Stuart factor).
– This mode of action explains the inefficiency of heparin in patients with congenital or acquired deficiency in AT III.
– LMWHs are predominantly anti-Xa activity.
1- Unfractionated heparin:
– Heparin not reached the serous, meninges and placenta. No intestinal absorption.
– Degraded by the liver and excreted by the kidney in an inactive form. ½ life = 60-90 min.
– Curative treatment: heparin sodium => continuous venous infusion: loading dose = 50 IU / kg and infusion of 15 to 25 IU / kg / h (500 IU / kg / 24h). The first control of the TCA is made 4 to 6 hours after the start of infusion.
– Preventive treatment: Calciparine by subcutaneously every 8 hours or 12 hours (0.2 ml x3 / day)
– Biological Monitoring: TCA (1.5 to 3 times the control) 1 time a day; biweekly platelet count
– Absolute contraindications: pericarditis; aortic dissection; endocarditis; Hemorrhagic stroke; peptic ulcer recent;diabetic retinopathy; thrombocytopenia history to heparin.
– Relative contraindications: advanced age; Severe hypertension; moderate hepatic or renal impairment
– Side Effects: Heparin thrombocytopenia type 2 (immunoallergic) osteoporosis; eosinophilia; alopecia; liver enzymes; Hypoaldosteronism with hyperkalemia.
– Antidote: protamine sulphate IVL dose vis-à-vis heparin dose (last injection)
– Direct Antithrombin -> hirudin (in case of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia)
2- LMWH (low molecular weight heparin):
– LMWHs are characterized by a strong anti-factor Xa activity and low anti-factor IIa activity.
– Dosage in preventive treatment: 0.2 to 0.3 anti-Xa IU / ml.
– Dosage in curative treatment: 0.5 to 1 anti-Xa IU / ml.
– The measurement of anti-Xa activity is required in patients with moderate renal insufficiency, obesity, bleeding risk patient or use of high doses of LMWH.
– The lifetime of LMWH allows one injection every 24 hours.
– Molecules: nadroparin (Fraxiparine®) Enoxaparin (Fraxiparine®)
– Indications: Prophylaxis of thromboembolic disease; Curative treatment of venous thrombosis; pulmonary embolism low or medium severity (Inohep®) unstable angina and myocardial infarction without Q waves


Leave a Reply