I – Introduction:
A- Definition of Pneumothorax:
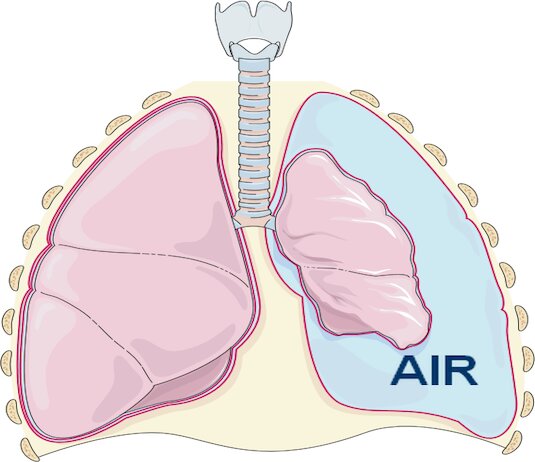
Pneumothorax is a potentially serious medical condition in which air collects in the pleural cavity, which separates the lungs from the chest wall. This can cause negative pressure on the lung, which can cause it to partially or completely collapse. Pneumothorax can be caused by various factors such as chest injuries, lung diseases, invasive medical treatments, etc. Symptoms usually include sharp chest pain, labored breathing, dry cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The diagnosis of pneumothorax can be made from a physical exam, chest X-ray, chest CT scan, or blood test. Treatment for pneumothorax may include careful observation, drainage of the pneumothorax, oxygen therapy and thoracic surgery. Preventing pneumothorax can include avoiding chest injuries, carefully following medical treatments, monitoring for lung disease, and avoiding high-risk activities.
B- Frequency of Pneumothorax:
 Pneumothorax is a relatively common problem that can occur at any age. According to data, about 20-25% of the general population may develop pneumothorax in their lifetime. The frequency of pneumothorax depends on several factors, such as age, gender, medical history, and lifestyle. Men are generally more likely to develop pneumothorax than women, especially at a young age. However, women can also develop pneumothorax later in life due to factors such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Smokers are also at greater risk of developing pneumothorax than non-smokers.
Pneumothorax is a relatively common problem that can occur at any age. According to data, about 20-25% of the general population may develop pneumothorax in their lifetime. The frequency of pneumothorax depends on several factors, such as age, gender, medical history, and lifestyle. Men are generally more likely to develop pneumothorax than women, especially at a young age. However, women can also develop pneumothorax later in life due to factors such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Smokers are also at greater risk of developing pneumothorax than non-smokers.
C- Importance of understanding Pneumothorax:
Understanding pneumothorax is important because it is a potentially serious condition that can lead to serious complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly. A pneumothorax can affect the ability of the lung to function properly, which can lead to reduced oxygen delivery to the blood and increased work of breathing. This can lead to heart failure, hypoxemia, failure of other organs and even shock. Additionally, pneumothorax can be complicated by issues such as recurrent air leakage, pleurisy, or infection, which may require surgery. Understand the causes, Symptoms and ways to prevent pneumothorax can help minimize risk and quickly diagnose and treat the condition when needed. Finally, understanding pneumothorax can help raise awareness about the importance of prevention and proper management of pulmonary medical conditions.
II- Causes of Pneumothorax:
A- Chest injuries:
Chest injuries can be defined as any damage sustained to chest structures such as ribs, breastbone, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. Chest injuries can be caused by a variety of factors such as traffic accidents, falls, punches, gunshot wounds, contact sports, and work accidents. Chest injuries can lead to a variety of potentially serious complications, including pneumothorax, cardiac rupture, internal bleeding, respiratory nerve damage, and ruptured spleen. Diagnosis of chest injuries may include a physical exam, chest X-ray, chest CT scan, or positron emission tomography. Treatment for chest injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but may include careful monitoring, drainage, surgery, physical therapy, and respiratory rehabilitation. It is important to consider chest injuries when caring for patients and monitor them carefully to minimize the risk of serious complications.
B- Lung diseases:
Lung disease refers to a wide range of conditions affecting the lungs and airways. Some of the most common lung diseases include asthma, chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. Causes of lung disease can include cigarette smoke, exposure to environmental pollutants, respiratory infections, genetics, and certain lifestyle factors. Symptoms of lung disease can include coughing, sputum production, wheezing, fatigue, and weight loss. Diagnosis of lung disease may include physical examination, diagnostic tests such as chest X-ray, positron emission tomography or bronchoscopy. Treatment for lung disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but can include medications, surgeries, breathing therapies, and lifestyle changes to improve lung function. It is important to consider lung diseases when caring for patients and monitor them carefully to minimize the risk of serious complications.
C- Invasive medical treatments:
Invasive medical treatments refer to a variety of medical procedures involving physical intervention in the body to diagnose or treat a medical condition. Invasive medical treatments can include surgical procedures such as cardiac surgery, imaging procedures such as positron emission tomography (PET) or bronchoscopy, as well as invasive treatment techniques such as pleural drainage therapy or thoracoscopy. Invasive medical treatments can provide greater access to internal body structures for more accurate diagnosis or more effective treatment. However, these procedures can also carry risks such as infections, bleeding, anesthesia-related complications, and allergic reactions.
III- Symptoms of Pneumothorax:
A- Acute chest pain:
Acute chest pain is a form of pain that occurs suddenly and can be felt in the chest. It can be described as a dull, oppressive, sharp or burning pain and can spread to other parts of the body, such as the arm, neck or jaw. Acute chest pain can have many causes, including heart disease such as angina or myocardial infarction, lung disease such as pneumonia or pneumothorax, and other causes such as musculoskeletal disorders. -skeletal, gastrointestinal or nervous disorders. Symptoms associated with acute chest pain may include cold sweats, nausea, shortness of breath, weakness, or dizziness. If you experience sharp chest pain, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible, as this can be a potentially serious condition requiring immediate treatment. An accurate diagnosis is crucial to establish an effective treatment plan and to minimize the risk of serious complications.
B- Difficult breathing:
Labored breathing is a condition in which it is difficult to breathe normally. It can occur due to a variety of factors, such as lung disease, breathing problems, infections, allergies, chest injuries, heart problems, or side effects from medications. Symptoms associated with labored breathing may include rapid or shallow breathing, feeling short of breath or gasping for air, chest pain, or persistent cough. The severity of labored breathing can vary greatly, from simple discomfort to a life-threatening condition. It is important to consult a doctor if you are having difficulty breathing, as it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires treatment. The doctor may perform a physical exam and order diagnostic tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or blood tests to determine the cause of labored breathing and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
C- Dry cough:
A dry cough is a type of cough that does not produce mucus or sputum. It is the body’s natural reaction to eliminate irritants from the throat and respiratory tract. Dry cough can be caused by a variety of factors, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, allergies, upper respiratory infections, lung diseases such as bronchitis or asthma, and certain medications . Symptoms associated with a dry cough may include a persistent cough, chest pain or discomfort, difficulty breathing, fatigue, or headache. If you experience a persistent dry cough, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions and to develop an effective treatment plan.
D- Fatigue and shortness of breath:
Fatigue and shortness of breath are symptoms frequently associated with a variety of medical conditions. Fatigue is a feeling of tiredness or lack of energy, while shortness of breath is a feeling of discomfort or difficulty in breathing. Both can be caused by factors such as stress, depression, sleep disturbances, heart disease, lung disease, infections, and circulatory system disorders. Additionally, some medications can also cause fatigue and shortness of breath. If you experience persistent symptoms of fatigue and shortness of breath, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatments may include medications, lifestyle modifications, therapies such as physiotherapy or psychotherapy, as well as medical interventions such as heart or lung procedures. It is important to work with a doctor to understand the causes of fatigue and shortness of breath and to put in place an effective treatment plan to improve quality of life.
IV- Diagnosis of Pneumothorax:
A- Physical examination:
Physical examination is a crucial step in assessing a patient’s general health and determining the presence of any medical conditions. It is a visual, tactile, and auditory process performed by a physician to inspect the body and assess vital signs such as temperature, heart rate, and respiration. The physical exam may include tests such as auscultation of the lungs to listen for breath sounds, assessment of muscle strength and mobility, and measurement of blood pressure. In addition to the physical exam, the doctor may also perform laboratory tests, such as blood or urine tests, to get a more complete picture of the patient’s health. The results of the physical exam can help the doctor diagnose a medical condition, develop an effective treatment plan and monitor the progression of the condition over time. It is important to participate in regular physical examinations to maintain good general health and to detect any possible medical problems early.
B- X-rays of the thorax:
Chest x-rays are x-ray images of the torso that help doctors visualize the internal structures of the chest, including the lungs, ribs, heart, and major blood vessels. They can help diagnose a variety of medical conditions, such as pneumothorax, lung infections, chronic lung disease, lung tumors and heart abnormalities. Chest X-rays can also help track the progression of an existing medical condition and assess the effectiveness of treatment. Chest X-rays are usually simple, quick, and minimally invasive, and usually don’t require special preparation. However, some people may be sensitive to x-rays and may need additional protective measures to minimize radiation exposure. It is important to work with a doctor to determine if chest X-rays are needed and what is the best approach for you. Chest x-rays can be an important tool to help maintain lung and chest health and diagnose potential problems early.
C- Thoracic scanner:
A chest CT scan is a medical imaging test that uses high frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the chest. It is often used to diagnose lung problems, such as pneumothorax, lung infections, lung tumors, and heart abnormalities. Chest CT can also help assess the extent of damage caused by chest injuries such as rib cage fractures. The examination is generally painless and requires no special preparation. However, some patients may need to receive contrast fluid to improve image quality. Chest CT is generally considered safe and minimally invasive, but rare side effects, such as allergic reactions, can occur. It is important to speak with a doctor to determine if a chest CT scan is necessary and what is the best approach for you. Chest CT can be an important tool to help diagnose lung and chest problems and assess the progression of an existing medical condition.
D- Blood test:
Blood tests are tests frequently used to assess a person’s general health and detect potential health problems. They can help diagnose a variety of medical conditions, including lung problems such as pneumothorax. Blood tests can measure different elements of blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Blood tests can also detect specific markers for diseases such as emphysema, pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Blood test results can help doctors make a diagnosis and determine the most appropriate treatment. Blood tests are usually simple and painless, and results can be available within days. Blood tests can be an important part of the diagnostic process for patients with symptoms of lung and chest problems, as well as a way to monitor disease progression.
V- Treatment of Pneumothorax:
A- Careful observation:
Careful observation is an important aspect of health management and patient treatment. This involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms and clinical signs to determine the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment. For patients with symptoms of pneumothorax, careful observation may include assessment of breathing, coughing, chest pain, and fatigue or shortness of breath. Doctors can also observe skin and mucous membrane color, heart rate, and blood pressure to determine the severity of the condition. Careful observation may also include tests such as physical exams and chest X-rays. At the end of the day,
B- Drainage of the pneumothorax:
Pneumothorax drainage is an invasive medical treatment that involves removing accumulated air or gas from the pleural cavity using a small tube called a chest tube. This treatment is generally recommended for patients with spontaneous pneumothorax or severe traumatic pneumothorax. Chest drainage can be done through an incision or through a needle inserted into the pleural cavity through the chest. This procedure removes accumulated air, reduces pressure on the lungs and allows the wound to heal. The chest tube can be left in place for several days, until the symptoms have subsided and the air leak has completely stopped. After removing the drain, patients are generally subject to close medical follow-up to monitor healing and prevent recurrences. Ultimately, pneumothorax drainage is a crucial procedure to treat this respiratory disorder and ensure a full and healthy recovery.
C- Oxygen therapy:
Oxygen therapy is a treatment used to treat patients with pneumothorax. It involves providing supplemental oxygen to a patient through a nasal mask or a catheter inserted into the nose. This therapy is recommended for patients suffering from symptoms such as labored breathing and increased fatigue. Oxygen therapy can help increase blood oxygen levels and improve blood flow to the lungs, which can help reduce chest pain and improve breathing. However, it is important to note that oxygen therapy can only be used under the supervision of a doctor, as prolonged use can lead to potentially serious side effects such as burns to the airways and increased intracranial pressure. Ultimately, oxygen therapy is an effective treatment for patients with pneumothorax, but it should be used with caution and under the supervision of a competent physician.
D- Thoracic surgery:
Chest surgery is a medical procedure that may be needed to treat some cases of pneumothorax. This procedure may involve opening the chest to access the lung and repair the damage caused by the pneumothorax. Thoracic surgery can include thoracoscopic surgery or thoracotomy, both of which are surgical techniques that can visualize the lungs and repair damage.
Chest surgery may be recommended for patients with recurrent pneumothorax or for those who have not responded to noninvasive medical treatments. This procedure may also be necessary to treat patients with underlying lung diseases that may contribute to the development of pneumothorax.
Although chest surgery can be effective in treating pneumothorax symptoms, it can also lead to potential complications, including bleeding, infection, and persistent chest pain. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of chest surgery with a doctor to determine if this procedure is the best option for treating pneumothorax. Ultimately, chest surgery is an important treatment for patients with pneumothorax, but it’s important to understand the potential risks and benefits before making a decision.
VI- Prevention of Pneumothorax:
A- Avoid chest injuries:
It is important to take steps to avoid chest injuries, as these can lead to serious complications, including the development of pneumothorax. Some of the most important measures to avoid chest injuries include:
1- Wear adequate protective equipment during sports or professional activities that involve a risk of chest injury.
2- Avoiding activities that can lead to chest injuries, such as high-risk outdoor activities or contact sports.
3- Use a seat belt when driving or traveling by car.
4- Avoid smoking, as smoking can increase the risk of lung diseases which can lead to the development of pneumothorax.
5- Consult a doctor if you have symptoms of lung disease, such as dry cough, fatigue and shortness of breath, as these symptoms may indicate an increased risk of chest injury.
Finally, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding the measures to be taken to avoid chest injuries. By working together, patients can minimize the risk of chest injury and avoid potential complications such as pneumothorax.
B- Follow medical treatments with care:
Following medical treatments carefully is crucial for the successful treatment of pneumothorax and to prevent potential complications. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions regarding prescribed medications, the duration of oxygen therapy and the follow-up of medical appointments. Patients should also inform their doctor of any changes in their medical condition or any side effects observed following medical treatment.
It is also important to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding activities to avoid during the treatment period, such as sports activities or activities involving sudden movements or major physical exertion. Patients may also need to follow a healthy, balanced diet to help prevent complications and support their recovery.
Finally, it is important not to ignore the symptoms of pneumothorax and to consult a doctor immediately if the state of health deteriorates or if new symptoms appear. By following medical treatments carefully, patients can maximize their chances of a quick recovery and minimize the risk of potential complications.
C- Monitor lung diseases:
It is important to monitor lung disease to prevent the development of pneumothorax. Lung diseases can include chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis, tuberculosis and emphysema, all of which can damage the walls of the air cells and increase the risk of pneumothorax. Therefore, it is crucial to regularly monitor lung health status and follow recommended medical treatments for existing lung diseases. Patients should also tell their doctor immediately if they experience symptoms such as cough, fatigue, and labored breathing, which may indicate a lung complication. Finally, it is important to adopt a healthy lifestyle,
D- Avoid high-risk activities:
It is important to avoid high-risk activities to prevent chest injuries and the development of pneumothorax. High-risk activities can include contact sports such as football, basketball, and hockey, as well as extreme activities such as bungee jumping and paragliding. People who engage in these activities should wear proper protective gear to reduce the risk of chest injury. It’s also important to avoid activities that can lead to chest trauma, such as traffic accidents and falls. Finally, it is important not to smoke or be exposed to cigarette smoke, as this can damage the lungs and increase the risk of chest injury. In general,
VII- Conclusion:
A- Summary of key information about Pneumothorax:
Pneumothorax is a serious medical condition that occurs when air builds up in the pleural cavity, causing increased pressure on the lung and heart. It can be caused by chest injuries, lung disease, invasive medical treatments, or even no known cause. Symptoms include sharp chest pain, labored breathing, dry cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The diagnosis can be confirmed by physical examination, chest x-rays, chest CT scan, or blood tests. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and may include pneumothorax drainage, oxygen therapy, chest surgery, or careful observation. To prevent pneumothorax, it is important to monitor lung disease, avoid high-risk activities, follow medical treatment carefully, and avoid chest injuries. It is important to see a doctor if you think you have this condition for prompt and effective treatment.
B- Importance of prevention and rapid treatment:
Prevention and prompt treatment of pneumothorax are critically important to chest health. If pneumothorax is not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications such as respiratory distress, heart failure, and even death. That’s why it’s important to watch carefully for symptoms like sharp chest pain, labored breathing, and dry cough. A physical exam, chest X-rays, chest scans, and blood tests can all help diagnose pneumothorax and assess its severity. Treatments for pneumothorax include drainage, oxygen therapy, and chest surgery. It is also important to avoid chest injuries, carefully follow medical treatment and monitor lung disease to minimize the risk of pneumothorax. Ultimately, prevention and timely treatment of pneumothorax can save lives and help patients return to healthy, active lives.
C- Encouragement to consult a health professional in case of suspicious symptoms:
It is very important to consult a medical professional in case of suspicious symptoms of pneumothorax. Symptoms may include sharp chest pain, labored breathing, dry cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor right away for a physical exam and diagnostic tests such as chest x-rays, chest CT scan, or blood tests. Prompt prevention and treatment of pneumothorax can prevent serious complications and improve the chances of recovery. It is also important to watch for lung diseases and follow medical treatments carefully, as well as to avoid high-risk activities and protect against chest injuries.
Leave a Reply