I – Introduction:
A- Definition of Progeria:
Progeria is a rare and genetic disease that affects children and is characterized by accelerated aging. Children with this condition have similar symptoms to premature aging, such as hair loss, thin, wrinkled skin, and joint changes. Progeria is caused by a specific genetic mutation in the LMNA gene, which codes for a protein called laminin A. This protein plays a key role in the structure and stability of cell nuclei. When the protein is altered by the genetic mutation, cell nuclei become unstable, leading to accelerated aging and associated medical complications. Children with Progeria often develop premature cardiovascular problems and have a very limited life expectancy. usually only about 13 years old. Progeria is extremely rare, occurring in approximately 1 in 4 to 8 million newborn babies.
B- Statistics on the frequency of the disease:
 The frequency of Progeria varies widely around the world due to the rarity of the disease. It is estimated that there are around 200 children with Progeria worldwide. However, these estimates are difficult to establish with precision due to the rarity of the disease and the difficulty in diagnosing Progeria. Progeria is considered an orphan disease, meaning it affects an extremely small population. The disease is genetic and occurs randomly, with no known connection to family history or environmental factors. Although Progeria is rare, it is recognized as a unique model for the study of premature aging and vascular degeneration.
The frequency of Progeria varies widely around the world due to the rarity of the disease. It is estimated that there are around 200 children with Progeria worldwide. However, these estimates are difficult to establish with precision due to the rarity of the disease and the difficulty in diagnosing Progeria. Progeria is considered an orphan disease, meaning it affects an extremely small population. The disease is genetic and occurs randomly, with no known connection to family history or environmental factors. Although Progeria is rare, it is recognized as a unique model for the study of premature aging and vascular degeneration.
C- Purpose of the article:
The aim of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of Progeria, a rare disease that affects children and is characterized by accelerated aging. We will discuss the definition of Progeria, statistics on the frequency of the disease and the associated symptoms. We will also look at the causes of Progeria and the medical complications that can occur. Finally, we will discuss the importance of the study of Progeria for the understanding of premature aging and age-related diseases. The article aims to educate people about Progeria, raise awareness about this rare disease, and encourage initiatives for research and development of treatments. It is aimed at all those who are interested in rare diseases, premature aging and medical advances. We hope this article will be helpful for patients, families, and healthcare professionals looking to learn more about Progeria.
II- Causes of Progeria:
A- Theories on the causes of Progeria:
There are several theories about the causes of Progeria, but the exact cause of this rare disease remains largely unknown. Progeria is caused by a genetic mutation in the LMNA gene, which codes for a protein called laminin A. This protein plays a key role in the structure and stability of cell nuclei. When the protein is altered by the genetic mutation, cell nuclei become unstable, leading to accelerated aging and associated medical complications. Some theories suggest that the genetic mutation in the LMNA gene can trigger an immune response that damages healthy cells and accelerates aging. Other theories suggest that the mutation may impair normal metabolic and cellular function, leading to premature aging. It is also possible that several environmental and genetic factors are involved in the development of Progeria. Studies to understand the exact causes of Progeria continue to expand and focus on the mechanisms underlying the accelerated aging associated with this disease.
B- Genetic factors involved:
Genetic factors are a key component of Progeria. The disease is caused by a specific mutation in the LMNA gene, which codes for a protein called laminin A. This protein plays an important role in the structure and stability of cell nuclei. The genetic mutation in the LMNA gene alters the protein laminin A, which can lead to instability of cell nuclei and accelerated aging. Progeria is considered a dominant genetic disease, which means that people with Progeria have a mutant copy of this gene from each parent. As a result, children who inherit the genetic mutation are at risk of developing Progeria. However, the majority of Progeria cases are caused by sporadic mutations, who appear for the first time in the family with no family history. Genetic studies of Progeria can help understand the mechanisms underlying the accelerated aging associated with this disease and can also provide insight into the genetic factors involved in aging in general.
C- Role of the environment in the development of the disease:
Although Progeria is widely believed to be a genetic disease caused by a specific mutation in the LMNA gene, some researchers suggest that the environment may also play a role in the development of the disease. Some studies have shown that environmental factors such as air pollution, high-fat diets, and exposures to toxins can affect genetic stability and increase the risk of genetic mutations. Other studies have also suggested that factors such as oxidative stress and alterations in cell damage repair mechanisms may contribute to accelerated aging and the development of Progeria. However, the scientific evidence as to the impact of the environment on the development of Progeria remains limited and requires more research to establish definitive conclusions. Future studies could also help determine whether environmental interventions, such as improving air and water quality, can reduce the risk of developing Progeria or other age-related diseases.
III- Symptoms of Progeria:
A- The most common physical signs:
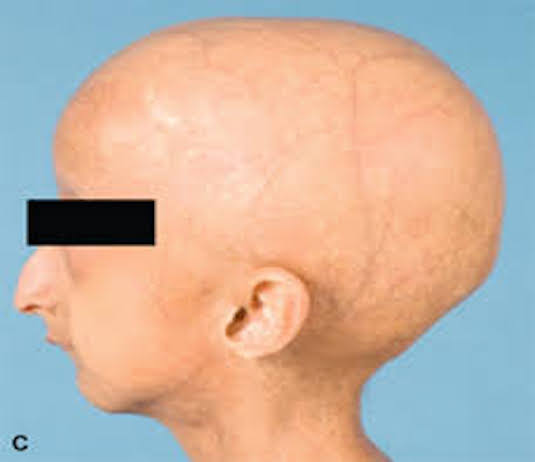
The most common physical signs of Progeria are associated with accelerated aging and include reduced height and weight growth, an angular face, and short, skinny limbs. Children with Progeria often have scanty hair and skin defects, along with loss of subcutaneous fat and altered skin texture. Additionally, patients may suffer from heart conditions, such as arteriosclerotic lesions, blood clotting disorders, and arterial aneurysms. People with Progeria may also develop bone disorders, such as osteoporosis, and may have abnormal teeth and eyes. The physical signs of Progeria can begin to appear within the first few months of life and gradually worsen over time. However, it is important to note that each case of Progeria is unique and the severity and course of symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
B- Associated medical complications:
Medical complications associated with Progeria can include cardiovascular disorders, joint disorders, and bone disorders. Children with Progeria are often affected by early arteriosclerotic damage, which can lead to blood flow abnormalities and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. Additionally, patients may experience joint pain and stiffness, as well as osteoporosis and frequent fractures. Bone disorders can also make patients more vulnerable to falls and injuries. Additionally, people with Progeria may develop breathing disorders, such as sleep apnea, as well as digestive problems and abdominal pain. The medical complications of Progeria can seriously affect the quality of life of patients and reduce their life expectancy. Therefore, it is important to carefully monitor patients with Progeria and treat them promptly to minimize medical complications.
C- Evolution of the disease over time:
The course of the disease over time in patients with Progeria is usually progressive and may lead to loss of functionality and deterioration in health status over time. The physical signs of Progeria, such as reduced height and weight growth and skin abnormalities, may worsen over time. In addition, patients can develop serious medical complications, such as arteriosclerotic lesions and cardiac disorders, which can affect their quality of life and reduce their life expectancy. Patients with Progeria may also develop mental and emotional disorders, such as depression, which can worsen symptoms of the disease. However, it is important to note that the progression of the disease can vary widely from person to person and that some patients may live longer than others. Finally, it is important to emphasize that medical treatments can help control the symptoms of Progeria and improve the quality of life of patients.
IV- Diagnosis of Progeria:
A- Medical examinations used for diagnosis:
Diagnosing Progeria can be difficult because of the rarity of the disease and the similarity of its symptoms to other medical conditions. However, medical examinations can help establish an accurate diagnosis. Tests commonly used for the diagnosis of Progeria include:
1- Physical examination: A careful physical examination can reveal the typical physical signs of Progeria, such as short stature, skin abnormalities and craniofacial abnormalities.
2- Genetic testing: Genetic testing can be used to detect genetic abnormalities associated with Progeria.
3- Laboratory tests: Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and urine tests, can help assess the general health of the patient and detect any abnormalities.
4- Medical imaging: Medical imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can be used to visualize internal abnormalities and to assess the condition of the arteries, bones and other organs.
Ultimately, diagnosing Progeria requires a multidisciplinary approach and a combination of medical tests to make an accurate diagnosis. Progeria patients should be seen regularly by a team of doctors to monitor their condition and to address any medical complications that may arise over time.
B- Importance of early diagnosis:
Early diagnosis of Progeria is extremely important for patient well-being. This can allow treatment to be started quickly and maximize the chances of survival. Additionally, early diagnosis can help avoid potential medical complications and improve patients’ quality of life.
Early diagnosis can also allow doctors to better understand disease progression and tailor treatment accordingly. Patients may also benefit from earlier access to supportive care and therapy to manage the physical and emotional challenges associated with Progeria.
Finally, early diagnosis can also help provide valuable information to families of Progeria patients to help them better understand the disease and make the best care decisions.
In conclusion, early diagnosis of Progeria is essential for patients, their families and physicians. It can help maximize chances of survival, improve patients’ quality of life, and provide valuable information for future care.
C- Difficulties associated with the diagnosis of Progeria:
Diagnosing Progeria can be difficult due to its rarity and variability in symptoms. Indeed, Progeria is a very rare disease that affects only about one in twenty million children worldwide. Additionally, symptoms can vary widely from patient to patient, which can make diagnosis more difficult.
Also, Progeria can be confused with other medical conditions such as juvenile osteoporosis or disorders of bone development, which can make diagnosis even more difficult. Doctors may need additional tests, such as blood work and genetic testing, to make a diagnosis of Progeria.
The rarity of the condition can also pose challenges for families seeking a diagnosis, as it can be difficult to find a doctor who has experience with the condition. Families may need to see multiple doctors to get a correct diagnosis.
Finally, Progeria can be difficult to diagnose due to the lack of knowledge and awareness about this disease. Doctors may not be aware of this condition or know what to look for, which can lead to a late or inaccurate diagnosis.
In conclusion, diagnosing Progeria can be difficult due to its rarity, variability in symptoms, confusion with other medical conditions, and lack of knowledge about this disease. Families may need to persevere to get a correct diagnosis.
V- Treatment of Progeria:
A- Current therapeutic approaches:
There is currently no cure for Progeria. However, doctors can help manage medical complications associated with the disease and improve patients’ quality of life. Current therapeutic approaches include:
1- Symptomatic treatment: Doctors can prescribe medication to manage joint pain, heart problems and other medical complications associated with Progeria.
2- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Patients can benefit from regular exercise to maintain mobility and muscle strength.
3- Palliative care: Doctors can provide palliative care to improve the quality of life of patients and relieve their pain.
4- Ongoing research: Several studies on potential treatments for Progeria are underway. Researchers are studying approaches such as gene therapy and the use of drugs to slow premature aging.
Although current therapeutic approaches cannot cure Progeria, they can help patients better manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Families can also be helped by the support of support groups for Progeria patients and their families.
B- Role of personalized medicine:
Personalized medicine is a growing field in the treatment of Progeria and many other rare diseases. The goal of personalized medicine is to provide treatments tailored to the individual needs of each patient, based on their genetics and medical history. This approach can help maximize treatment results and minimize side effects.
For Progeria, personalized medicine can help to better understand the causes of the disease and the mechanisms underlying premature aging. It can also help identify patients who are most at risk of developing serious medical complications and develop a personalized treatment plan for each patient.
Using techniques such as genome analysis and computer modeling, doctors can evaluate the most promising treatment options for each patient with Progeria. This approach can also help to identify patients who are most receptive to existing therapeutic approaches and to develop new targeted therapies.
In sum, the role of personalized medicine in the treatment of Progeria is to provide treatments that are more effective and more suited to the individual needs of each patient. This approach can help improve patients’ quality of life and extend their life expectancy.
C- Current limits of the treatment of Progeria:
Despite recent advances in the field of personalized medicine, the treatment of Progeria remains largely limited. The main difficulty lies in the complex nature of the disease and the difficulty in identifying the underlying causes.
Lack of knowledge about the biology of Progeria means that treatment options remain limited. Current therapies often focus on managing symptoms and associated medical complications, rather than curing the disease itself.
Additionally, since Progeria is an extremely rare disease, it can be difficult to find suitable patients for clinical trials and to develop effective therapies. The costs associated with researching and developing new therapies can also pose significant financial challenges.
Finally, Progeria can cause serious and life-threatening complications, which can make treatment difficult and require constant medical supervision. Progeria patients may also face social and emotional challenges due to their distinct physical appearance.
In conclusion, the current limitations of the treatment of Progeria are largely related to the complexity of the disease and the challenges associated with the research and development of new therapies. However, continued advances in the field of personalized medicine offer hope for the future, and it is important to continue supporting research to develop new treatment options for patients with Progeria.
VI- Perspective on the future of research on Progeria:
A- Recent advances in the understanding of the disease:
Recent advances in the understanding of Progeria have been considerable. Through the use of advanced genetic analysis techniques, scientists have identified the gene responsible for the disease, known as LMNA. This discovery has led to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of Progeria and has paved the way for new avenues of research to develop potential treatments. Additionally, the use of animal models to study Progeria has allowed scientists to observe the effects of different treatments and assess their effectiveness. Finally, clinical trials on patients with Progeria have also provided new knowledge about the disease and have made it possible to develop better targeted treatments.
B- Future objectives of research on Progeria:
Future goals for Progeria research are to develop more effective treatments for the disease. This includes continuing to understand the underlying mechanisms of Progeria in order to target treatments more effectively. Scientists are also working on genetic approaches to correct the disease-causing mutation. Additionally, efforts are focused on improving care for patients with Progeria, ensuring that treatments are better tailored to their individual needs. Other goals include identifying new markers for early diagnosis and developing methods to assess treatment outcomes. Finally, Progeria research also focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with the disease and creating ways to support them. In summary, the future goals of Progeria research are to provide a better quality of life for patients and to find a definitive cure for the disease.
C- Importance of awareness and research on Progeria:
Progeria awareness and research is extremely important for patients with this rare and devastating disease. Raising awareness about Progeria can help break down stereotypes and educate people about the realities of the disease, which can lead to better understanding and support for patients and their families. Progeria research can also help develop more effective treatments for patients, which can improve their quality of life and extend their lifespan. Additionally, advances in understanding Progeria may have implications for other age-related diseases, such as heart disease and inflammation-related disorders. Finally, Progeria awareness and research can help bring attention to rare diseases in general, which have often been overlooked by funding and research, and spur governments and organizations to devote more resources to research and raising awareness for rare diseases. In summary, Progeria awareness and research is crucial for patients with the disease, for the medical community, and for efforts to understand and treat rare diseases.
VII- Conclusion:
A- Summary of key information about Progeria:
Progeria is a rare genetic disease that causes accelerated aging in children. Children with Progeria often show physical signs such as hair loss, thin, wrinkled skin, brittle bones, and stunted growth. This disease can also lead to serious medical complications such as heart disease and stroke. The causes of Progeria are complex and are currently believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Medical tests, such as genetic tests and blood tests, can help diagnose the condition. However, diagnosis can be difficult due to the rarity of the disease and the associated difficulties in identifying its signs. Current treatment approaches for Progeria are limited and aim to relieve symptoms and prolong life. Progeria research is constantly evolving and recent advances have led to a better understanding of the disease. Future research goals include the development of more effective treatments and prevention strategies. Awareness and research on Progeria is extremely important for children with this disease and their families. Future research goals include the development of more effective treatments and prevention strategies. Awareness and research on Progeria is extremely important for children with this disease and their families. Future research goals include the development of more effective treatments and prevention strategies. Awareness and research on Progeria is extremely important for children with this disease and their families.
B- Final message on the importance of awareness and research on Progeria:
The final message on the importance of awareness and research on Progeria is crucial for the medical community, patients and their families. Progeria is a rare disease that affects children and young people, causing accelerated aging and premature tissue degeneration. Unfortunately, few people know about this disease and the resources available to patients and their families are limited. This is why awareness and research are so important to the community. By raising awareness about this disease, we can help patients receive the support and care they need to improve their quality of life. At the same time, research can bring important advances in understanding the disease and developing more effective treatments for patients with Progeria. It is therefore vital to continue to support awareness and research on this disease in order to advance medicine for patients with Progeria.
C- Final thoughts on the future of Progeria research and treatment:
Progeria is a rare and devastating disease that affects children all over the world. Although recent advances in the understanding of the disease have led to the development of promising therapeutic approaches, there is still a long way to go to find an effective treatment for Progeria. The current limitations of treatment are often due to the lack of sufficient data on the biology of the disease and the rarity of this condition. However, personalized medicine can play an important role in finding more effective treatments for patients with Progeria. It is also important to continue education and research efforts to support patients and their families, as well as to advance the understanding of Progeria and future treatments.
Leave a Reply