Tag: BGN
-
Leukorrhea
—
by
INTRODUCTION: Definition: The leukorrhea correspond to the flow of vaginal secretions whose abundance and appearance vary. They appear at puberty and their presence is physiological, provided they meet the following characteristics: – Odorless; – Whitish or light; – Not associated with burns, vulvovaginal itching or pelvic pain. Mechanisms: The leukorrhea is a common reason for consultation,…
-
Bacillus
—
by
GENERAL: The genus Bacillus includes rod-shaped bacteria, usually mobile, spore-forming. These bacilli are Gram-positive, facultatively aerobic or anaerobic strict. Bacillus genus includes about twenty species, but is primarily concerned with B. anthracis, due to its pathogenicity (animals, man) and B. cereus (food poisoning). However, in recent years, many publications make other Bacillus species responsible for…
-
Gram Negative bacilli difficile growth
—
by
Cardiobacterium hominis HISTORY: Slotnick and Dougherthy proposed in 1964 the name C. hominis to designate gram-negative bacilli, polymorphic slow culture, initially placed in the group II-D (related bacteria Pasteurella) responsible exclusively endocarditis.There is no andgénique kinship with Brucella, Streptobacillus, Pasteurella and Haenwphilus. I – HABITAT AND EPIDEMIOLOGY: C. hominis is part of the normal flora…
-
Acinetobacter
—
by
HISTORY: Beijerinck in 1911 described a germ isolated from the ground, Micrococcus calcoaceticus. In 1939 De Bord publishes preliminary work on a group of coccobacilli Gram (-) close Neisseria he considers the tribe Mimae (Mima polyphorma). In 1940 Audureau described a species of Moraxella close it without their nutritional requirements, under the name of Moraxella Iwoffi.…
-
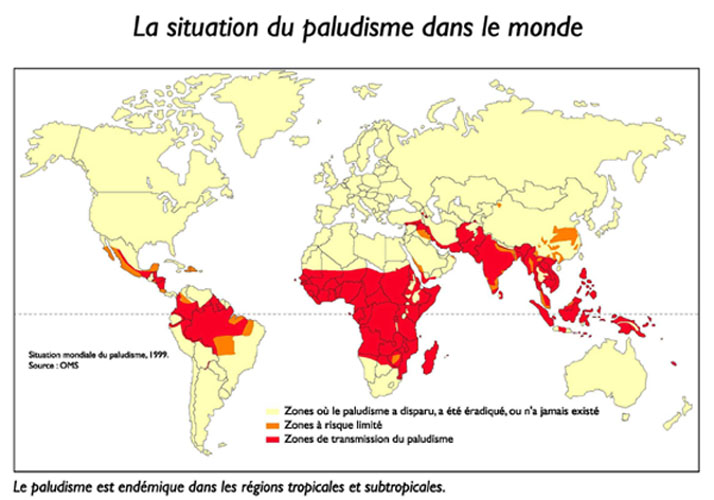
Bacterial and Parasitic Infections
* Diphtheria: it is due to the lysogénée bacteria strain that produces exotoxin. C. The diphtheria that do not produce exotoxin may be responsible for angina false membranes, but also septicemia (and secondary locations: endocarditis) but do not induce the disease diphtheria. Diphtheria is a little immunizing disease which justifies vaccination for convalescent patients. *…
You must be logged in to post a comment.