Tag: Measles
-
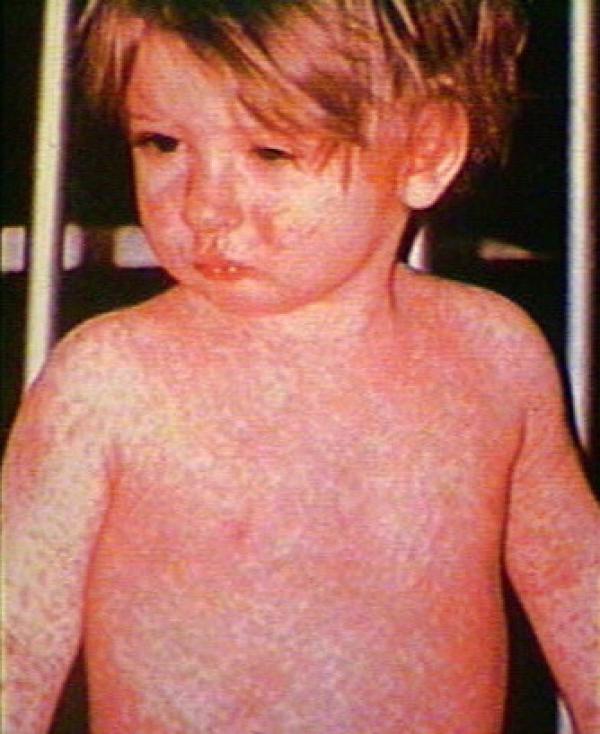
Measles
—
by
Measles is a highly contagious acute viral infection. Transmission is by air (inhalation of micro-droplets emitted by an infected person). In developing countries, it mainly affects children aged 1 to 3 years. Measles can be prevented by vaccination. For more information, refer to the Support guide of a measles outbreak, MSF. Clinical signs : –…
-
Viruses in Anatomical Pathology
• Poliomyelitis: neurotropic. Degenerative reversible first (disappearance of Nissl bodies) and final (ment-inflated or neuronal cell shrinkage). • Papillomavirus (HPV): epidermotropic. Induced epidermal hyper-plasia on the rete Malpighi with some binucleated cells; of dyskeratotic cells; Koilocytes in the surface layer. -> Condyloma; -> Papillomavirus (common wart) -> Molluscum contagiosum (crater); -> Dysplasia => carcinoma. •…
-
Incubation in Infectious Diseases
1- 2-5j: – Cholera – Chancroid – Herpes (2 to 7d) – Diphtheria – The best part of bacterial infections (scarlet fever …) 2- 10 days: – Measles – Leptospirosis (6 12j). – Pertussis (7 to 10j) – Tetanus (3 to 30d) 3- 14 days: – Rubella – Chickenpox – Malaria (10 to 20 d)…
You must be logged in to post a comment.