Tag: Poliomyelitis
-
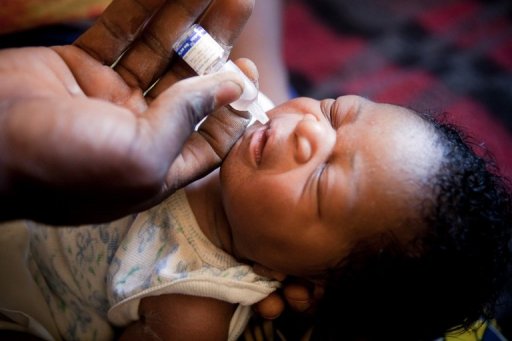
Poliomyelitis
—
by
– Acute viral infection due to a poliovirus (serotypes 1, 2 and 3). The transmission is direct (faecal-oral) or indirect (ingestion of water or food contaminated with feces). Man is the only reservoir of the virus. In principle, the disease can be eradicated by mass vaccination with oral polio vaccine (OPV). – In endemic areas,…
-
Viruses in Anatomical Pathology
• Poliomyelitis: neurotropic. Degenerative reversible first (disappearance of Nissl bodies) and final (ment-inflated or neuronal cell shrinkage). • Papillomavirus (HPV): epidermotropic. Induced epidermal hyper-plasia on the rete Malpighi with some binucleated cells; of dyskeratotic cells; Koilocytes in the surface layer. -> Condyloma; -> Papillomavirus (common wart) -> Molluscum contagiosum (crater); -> Dysplasia => carcinoma. •…
-
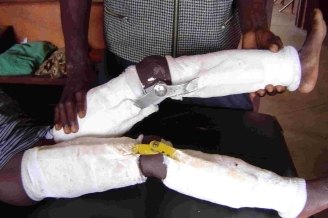
Acute Anterior Poliomyelitis
* Causal agent: due to poliovirus type 1, 2 and 3. These enteroviruses are cultivable on tissue or cellular environments and are remarkable for their strength and long survival in the environment. * Man, only virus reservoir by the nasopharynx to the initial phase of infection then the stool for several months. The attenuated vaccine…
You must be logged in to post a comment.