Tag: Pulmonary
-
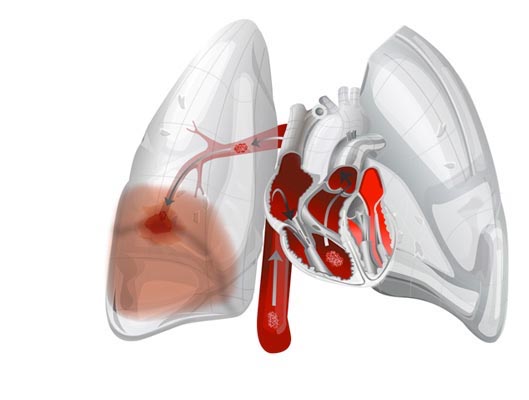
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * Difficult diagnosis because signs are not very sensitive and not very specific. * acute dyspnea of polypnea type (70%), cough (40%). * chest pain (60%) with or without hemoptysis (10%), tachycardia (30%), sometimes inaugural syncope (10%). * fever between 37.5 ° and 38.5 ° C. * the signs are frustrated in the elderly: – think about dyspnea or malaise rather than chest…
-
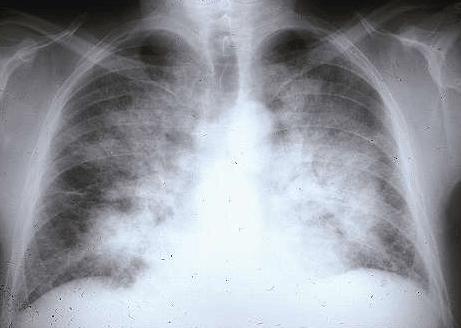
Acute Pulmonary Edema
—
by
Warning: • The PAO can be fatal (asphyxia, serious rhythm disorder) hospitalize ++. • Treatment is symptomatic and etiologic (underlying heart disease and triggering factor). • It is a turning during the development of heart disease. Clinic: – Dyspnea asphyxia often beginner night, preceded by paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea episodes with cough, laryngeal crackles, orthopnea, chest…
-
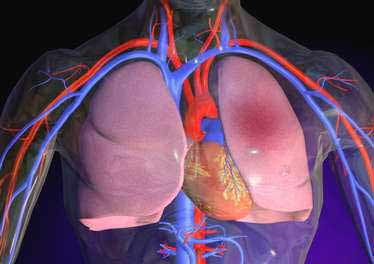
Pulmonary Embolism
—
by
Warning: • Diagnosis evoked by context and promoting the clinic. • Any suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) requires a transfer to hospital for confirmation and initiation of anticoagulation. • Do not ignore the imperfect forms, particularly without obvious phlebitis Clinic: The context is thrombophlebitis (see), but not always! functional signs: pain, sudden or increasing dyspnea, cough,…
-
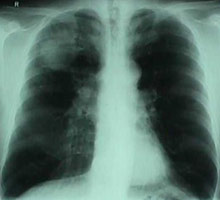
Pulmonary Emphysema
—
by
– Definition: characterized by the increase in the size (above normal) distal airspaces beyond the terminal bronchiole, or by expansion or by rupture of the alveolar walls. – Two types: diffuse emphysema panacinar and centrilobular emphysema. – Emphysema diffuse panacinar: destruction of alveolar walls; conjunctiva and parallel weft of the capillary network;expansion of all the…
-

Pulmonary Embolism
* The respiratory impact is complex, often resulting to hypoxia without carbon dioxide retention. Both there is a dead space effect (broken not perfused areas) and increased physiological shunt. This is explained by the persistence of blood flow in embolized areas and the opening of latent anastomoses under the effect of PAH. * Objective arterial…
You must be logged in to post a comment.