Tag: Thoracic
-

Acute Thoracic Pain
—
by
CLINICAL SIGNS: * suspicious signs , apart from an obvious clinical picture: – history of coronary heart disease. – pains that last for several seconds at least. – pain dependent on breathing. – Pain not reproducible by palpation and mobilization of the rib cage. – associated digestive symptoms. – risk factors for thromboembolic disease. * signs of gravity :…
-
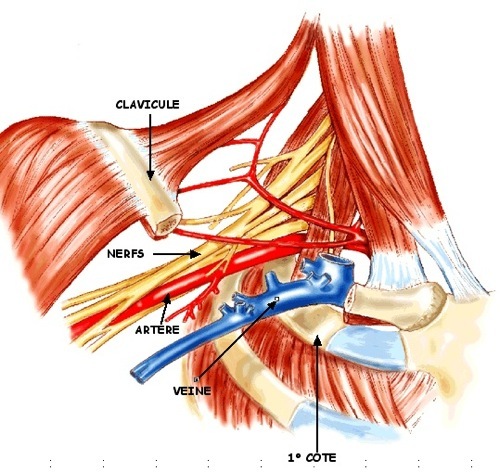
Syndrome of the thoracic outlet parade
—
by
Thoracic outlet syndrome is the more or less complete association of irritation and / or compression of the vasculo-nervous pedicle of the upper limb as it passes through the scalene parade. the costo-clavicular defile and finally, behind the pectoral small muscle before the axillary space. Depending on the level of compression, the clinical expression will…
-
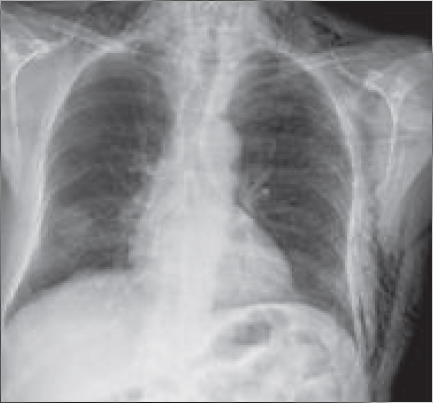
Subcutaneous Emphysema Chest
—
by
The subcutaneous emphysema corresponds to the appearance of gas in the subcutaneous tissue. It is either an air suffusion, spontaneous or during trauma, between an air cavity and the adjacent soft tissue (rupture of pleural bubble, tracheobronchial rupture, esophageal rupture) or a local production gas by anaerobic bacteria during infection (fasciitis and gas gangrene). More…
-
Chest pain
—
by
A few figures help to understand the problem that occurs most often in an emergency context: – Chest pain represents about 5% of the chief complaints in the emergency services; – Allowed to leave their homes nearly 5% of patients with chest pain is related to acute coronary symptom; – Pulmonary embolism is one of…
You must be logged in to post a comment.