Tag: Tuberculosis
-

Cough
—
by
Coughing is a reflex action in which successive inspiration, a brief closing of the glottis, and then immediately after the pressurization of the rib cage, a sudden opening of the glottis, which leads to cough shake. This cough jolt in fact corresponds to a fast flowing expiration. When the cough shakes succeed, they realize the…
-
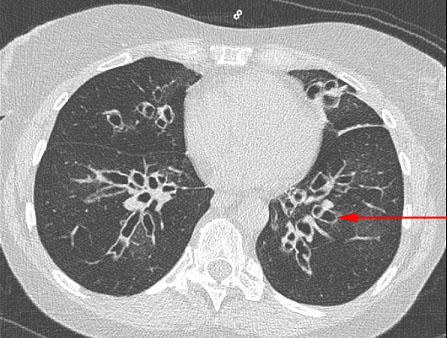
Bronchiectasis
—
by
– DDB or bronchiectasis is anatomically defined by an abnormal and irreversible dilatation of bronchial caliber associated with a destruction of the adjacent lung parenchyma. – The bronchial mucosa is the site of significant inflammation, leading to hypertrophy of mucous glands and goblet cells => bronchial hypersecretion. There is stasis of mucus favored by the…
-
Tuberculosis Bacilli
—
by
Of the many species of Mycobacteria, three are responsible for human tuberculosis. Besides Mr. tuberculosis, the most common, there are cases due to M. bovis or M. africanum. HISTORY: 1865: Villemin shows that human tuberculosis is transmissible by inoculation of rabbits and guinea pigs. 1882: Discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis currently named), clotted bovine…
-
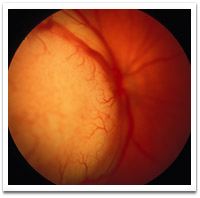
Ocular Tumors
1- Retinoblastoma: – Characterized by its early onset (children 2 to 3 years) and bilateralism and are frequent genetic trait – The development exophytic tumors do not form a protruding mass, but causes a retinal detachment – Pejorative factors: damage to the optic nerve; choroïdosclérale invasion Presentation is – Leucorie (amaurotic cat eye) – Unequal…
-
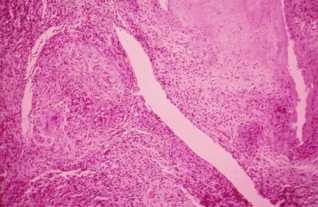
Tuberculoid Granuloma
This is the result of a specific subacute inflammation which may be caused: – Sarcoidosis (Besnier-Boeck disease-Schaumann or BBS) – Crohn’s disease – The reaction to foreign bodies – Schistosomiasis – Leprosy (in its tuberculoid) – Some deep mycoses – Tularemia – Cat scratch disease The tuberculoid granuloma is an epithelioid giant follicle FOLLICLE epithelioid…
-
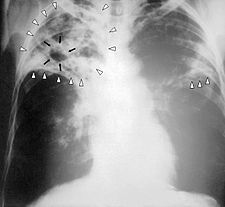
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (BK), transmitted by air. After contamination, M. tuberculosis multiplies slowly in the lungs: the primary infection. In the absence of immunosuppression, pulmonary lesion heals in 90% of cases, but 10% of patients develop active TB. There are also extrapulmonary (meningitis, miliary, lymphatic, bone, etc.). Infection…
You must be logged in to post a comment.