This is the result of a specific subacute inflammation which may be caused:
– Sarcoidosis (Besnier-Boeck disease-Schaumann or BBS)
– Crohn’s disease
– The reaction to foreign bodies
– Schistosomiasis
– Leprosy (in its tuberculoid)
– Some deep mycoses
– Tularemia
– Cat scratch disease
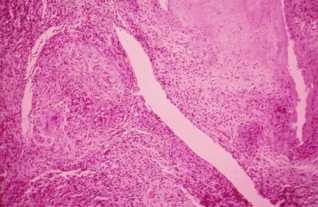
The tuberculoid granuloma is an epithelioid giant follicle
FOLLICLE epithelioid giant:
Has many epithelioid cells; few Langhans giant cells(plasmodia with more cores arranged in peripheral ring or horseshoe) -> formed from the fusion of epithelioid cells; a peripheral ring of lymphocytes.
The epithelioid cells derived from the metamorphosis of monocytes under the action of lymphokines.
1- Pathology:
Tuberculosis:
• The follicle tuberculoid forms at the subacute phase;it is not specific to tuberculosis.
The caseous follicle is specific TB
• The casein es t necrosis homogenization, eosinophilic, structureless
• The casein never subsides
• The encysted caseous lesions may persist indefinitely
• The casein softened (liquefied) can be eliminated.
* The effect of softening of casein
– Abscess -> deep location (caseum remains indefinitely)
– Ulceration -> surface tuberculosis
– Cave -> parenchyma (if removed by fistula in natural conduits)
• tubers (lungs) consist of casein encysted
• tuberculous miliary granulations are in serous and elective pulmonary location; all move at the same time -> hematogenous.
• The noncaseating follicles are the only ones able to fully heal with treatment.
• TB treatment allows the eradication of infection, healing without sequelae non caseous exudative lesions and acceleration of the fibrous scarring.
2- Other etiologies:
A- SARCOIDOSIS:
Follicular reaction without necrosis home that combines:
Giant cells containing intracytoplasmic inclusions (asteroid Schaumann bodies);epithelioid cells and lymphocytes
These follicles are usually confluent
Evolution -> fibrosis.
Diagnosis: Reaction Kveim
B- REACTION TO FOREIGN:
This is a follicular reaction around a non-absorbable material.
Granuloma consists of giant cells that include the foreign body and a polymorphic inflammatory granulation tissue.
Granuloma center can suppurating. Sometimes large granuloma -> inflammatory pseudotumor
It may regressed if the foreign body reabsorbs
The foreign body most often endogenous (mineral or vegetable, food debris, son of sutures, parasite eggs, barite, silica, asbestos …) endogenous (lipids -> lipophagic granuloma; keratin scales from dermoid cyst broken ….)
* Example: SILICOSIS
The nodule silicosis comprises a central hearth hyaline sclerosis and histiocytic crown around silica fine needles.
Progresses to fibrosis.


Leave a Reply