Category: Additional Tests
-

Blood Lead
Indications: The main interest of the examination is to detect lead poisoning, whether occupational or environmental origin (or former habitat near an industrial site. Principle: Lead absorbed with drinks, tap water or occupational poisoning (printers, typographers old) or accidental (pieces of old paint flaking, ancient wall papers accidentally ingested) slowly into the blood and is…
-

Natremia
Indications: The review for the determination of main extracellular cation (sodium, Na), himself a good indicator of body hydration. For example, in cases of diarrhea and chronic vomiting, especially in a fragile patient as a person, the dosage of serum sodium becomes important. Principle: The stability of serum sodium is essential for a good cellular…
-
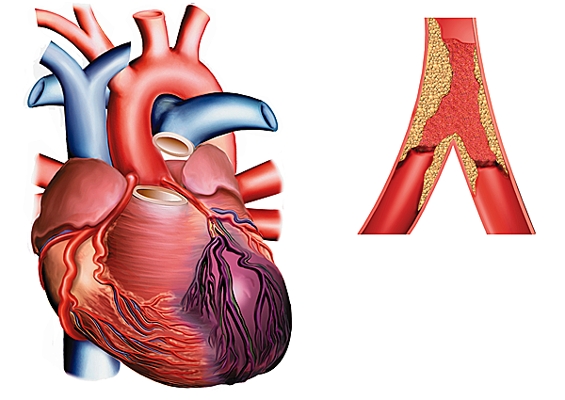
Markers infartus infarction – myoglobin, troponin and isoenzyme of creatine kinase
Indications. principle: Myocarditis necrosis first revealed by signs of suffering heart muscle and especially the myocyte that includes several types of protein: – Cytoplasmic: these are enzymes such as transaminases, creatine kinase or lacticodéshydogénase; – To metabolic function: myoglobin, involved in muscle contractility, such as troponin and myosin. When the necrosis results in cell lysis…
-

Serum Potassium
Indications: The monitoring of serum potassium can appreciate the blood level of a fundamental ke cation for muscle function like intestinal transit: potassium (K). But it also allows monitoring of treatments could cause hypokalemia (in the case of diuretics, laxatives) or hyperkalemia (ACE inhibitor, anti-aldostérones, angiotensin II antagonists). It is also an essential part of…
-
Blood Electrolytes
Indications: Before different clinical presentations that may be suspected of fluid and electrolyte disorders, the test measures the major blood anions and cations: – Cations are: sodium (Na), potassium (K), calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg); – Anions are: chlorine (Cl), bicarbonate (HCO3) and proteins. It is the clinical examination which must guide the application. The…
-
Glycosylated Hemoglobin or Glycated
Indications: The assay is useful in monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes care. Principle: hemoglobin HbA1c is a subfraction of HbA1c, which reacts with glucose. The value found in the blood, in proportion to the average plasma glucose concentration, therefore, is a good reflection of the latter. Technique: Sample of 5 mL of venous blood in…
-
Blood Culture
Indications: Before high fever with chills, it comes to detect the abnormal presence in the blood of a bacterium which can thus be identified. Then we could possibly test its resistance to contact antibiotics. Principle: The collection of blood is cultured in suitable habitat to development of germs suspected. Technique: The collection of venous blood…
-
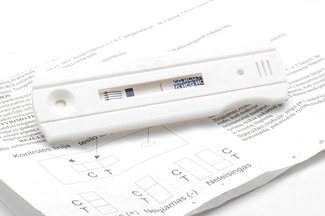
hCG and β-hCG
Indications: β-hCG of the assay allows early diagnosis of pregnancy, but mostly ectopic pregnancies. It also can diagnose secreting tumors, and early detection of trisomy 21 (in this case, the rates are unusually high compared with gestational age). Principle: The hormone choriogonadotrope is a glycoprotein secreted by the syncytiotrophobalste, which maintains during the first trimester…
-
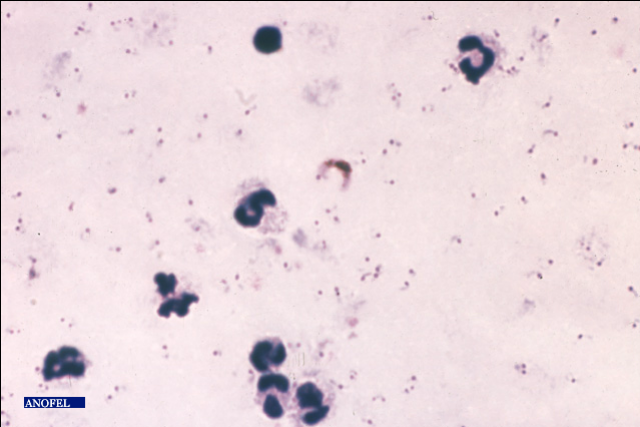
Thick Blood. Thin Smear
Indications: The examination can detect the presence in the blood of malaria parasite: Plasmodium. Principle: The realization of a thick film can concentrate the maximum noise in the minimum surface and therefore easier to detect. Technique: Levy vaccinostyle a large drop of blood from the fingertip. Placed on a slide, gout is fragmented by stirring…
-

Blood Sugar
Indications: Blood sugar assay to diagnose possible anomalies of glucose metabolism, such as pancreatic insufficiency with insulin production deficit: what is diabetes. But it is also essential in monitoring the treatment of diabetes, whether Type I or Type II. Principle: The assay of plasma glucose reflects blood sugar in the body, not related to the…
You must be logged in to post a comment.