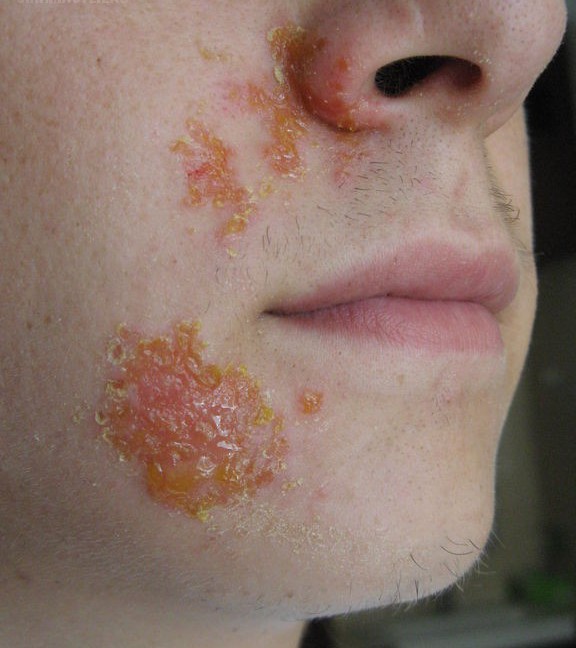
* Superficial skin infection ß-hemolytic streptococcus A and / or Staphylococcus aureus; self-inoculated and not immunizing; It affects mainly children; it is contagious. In adults almost always reflects pre-existing skin lesions (ectoparasites).
* The elementary lesion is a superficial bubble, sub-stratum, flabby and very fragile. Evolves rapidly to erosion covered with crusts of mélicériques centrifugal extension. At the beginning often periorificial -> dissemination
* Bullous Impetigo: characteristic of the newborn (Staphylococcus); at the stage of higher gravity is the staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (or SSS)
* Ecthyma: burrowing form of impetigo, usually located in the NCI-laughing members; especially immunocompromised; it is due to Streptococcus pyogenes
* The potential risk of GNA leads to control proteinuria three weeks after the infectious episode. This risk is exceptional
* Local treatment may be sufficient in form of small extent (preferably oily ointments to soften and break down the crust).
* Antibiotics (oral) are required for large lesions: oxacillin; pristinamycin (Pyostacine)

Leave a Reply