Tag: Vascular
-
Vascular edge for hemodialysis
—
by
Introduction: The arteriovenous vascular area, dominated by the direct fistula, is used in preference to central venous catheters, including in children. Arteriovenous fistulas: Distal radial arteriovenous fistula: Distal cephalic arteriovenous fistula (FAV) was described by Brescia and Cimino in 1966. It remains the best vascular approach. Communication between the superficial radial vein (distal cephalic) and the…
-
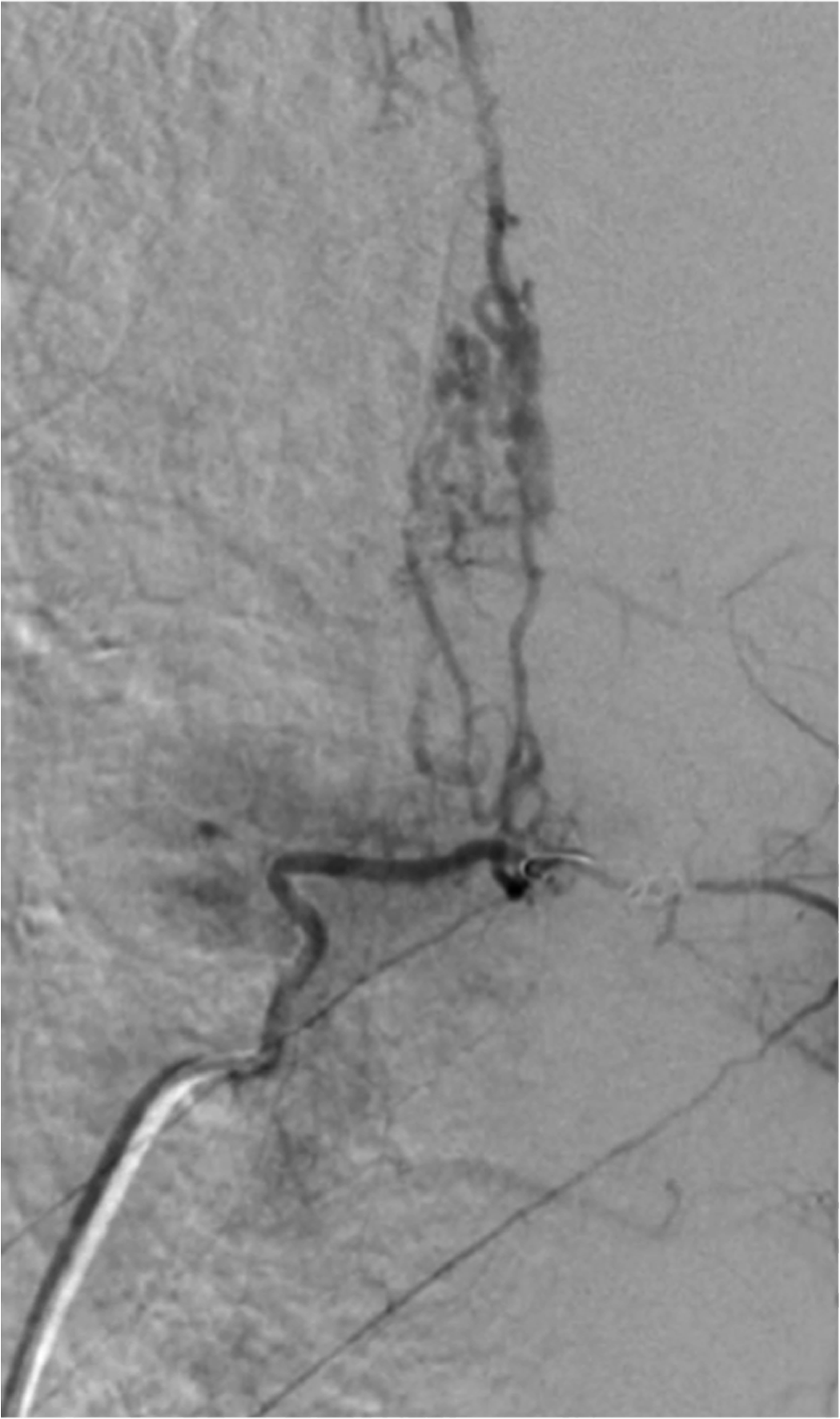
Vertebromedullary vascular malformations
—
by
SLOW MOTION CIRCULATING MELTING MALFORMATIONS: Those of the capillary compartment (telangiectasia) or the venous compartment (cavernoma) begin to be discovered today by the MRI. Rare, they are sometimes responsible for hematomyelia or spinal cord compression. The venous pockets give a heterogeneous signal in hypo- and hypersignal due to stagnant blood, and sometimes in case of bleeding the…
-
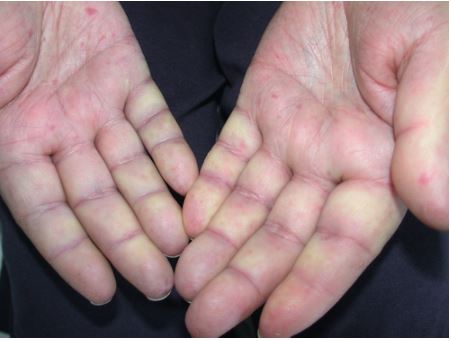
Vascular acrosyndrome
Vascular acrosyndromes are circulatory manifestations localized to the cutaneous territories of the extremities, mainly the fingers. The clinical pictures are various, the causes and the prognosis varied, the symptomatic treatment to know to relieve patients sometimes very painful. CLINIC: – The interrogation specifies the seniority of the disorders, certain toxic drugs, the smoking ++, the profession,…
-
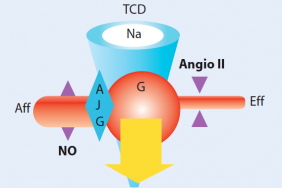
Vascular nephropathy
—
by
Introduction: Vascular nephropathy with acute renal failure have four main types: Acute necrotizing angiitis with or without associated glomerular involvement; – hemolytic and uremic syndrome, primary or secondary; – cholesterol emboli; – renal arterial thromboses. They represent a small but significant proportion of acute renal failure (ARI). Between 1986 and 1992, out of 616 patients hospitalized…
-
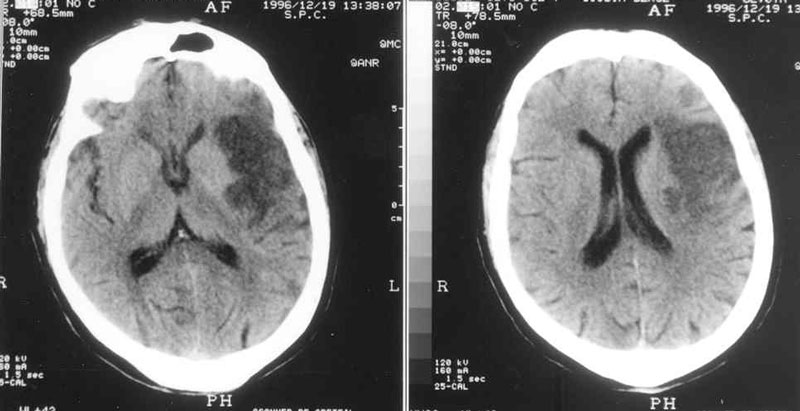
Cerebrovascular accident
—
by
1- Myocardial carotid: + Carotid: Optic-pyramidal syndrome with monocular blindness ipsilateral to the occlusion (ophthalmic artery) and contralateral hemiplegia. + Superficial Sylvian (frontal and ascending parietal convexity): – Hemiplegia contralateral to facial predominance brachiocephalic + sensory disturbances in the paralyzed area – Lateral homonymous hemianopia (HLH) often incomplete – If major or dominant hemisphere (left)…
-
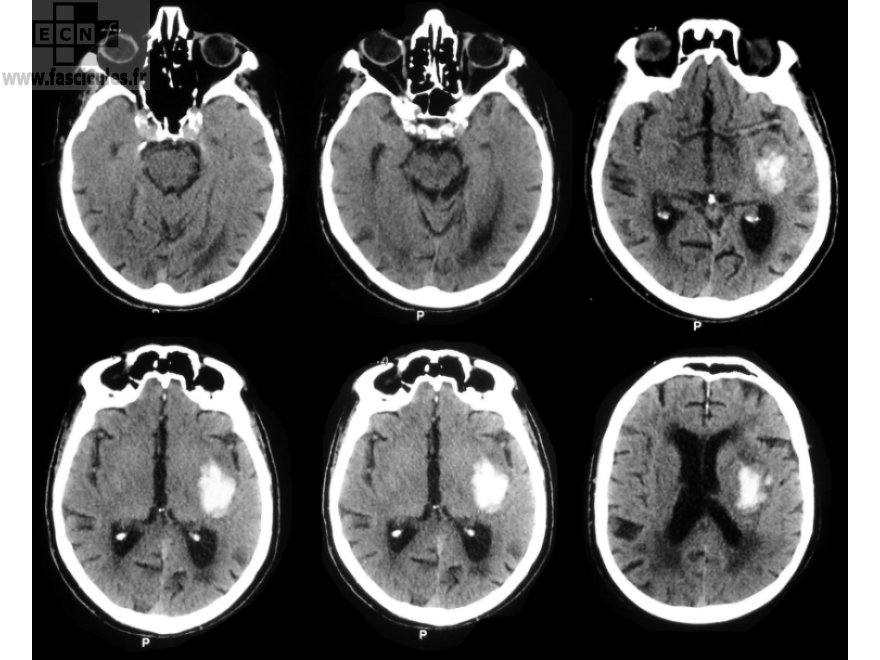
Stroke – Haemorrhagic
1- Clinical pictures: * Lens capsular hemorrhage (deep hematoma UCS): – Acute onset with headache and quickly disorders of consciousness; Hemiplegia + conjugate deviation of the head and eyes toward the lesion – Ventricular floods can occur characterized by generalized hypertension, seizures, signs decerebrate – A more gradual and less severe picture can be with:…
You must be logged in to post a comment.