Indications:
The goal is to repeat, by examining a large number of chromosomal abnormalities in the unborn child, if it shows malformation risk factors or signs making fear: nuchal thickening of the neck to ultrasonography or hCG levels too high.
With a mother aged (over 38 years with a positive test HT21) for example, it allows to perform a fetal karyotype.
Cons-indications:
A practical limitation in case of risk of spontaneous abortion and placental malabsorption.
 Principle:
Principle:
20 mL sample of amniotic fluid to analyze and can be cultured amniocytes.
Technique:
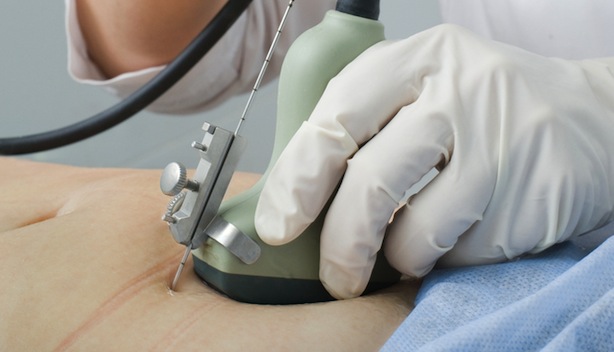
Without anesthesia, outpatient examination begins with an ultrasound location of the placenta and verification of fetal vitality.
Possible from the 15th week of gestation, the puncture is transabdominal ultrasound-guided needle in.
20 ml liquid enough for the exam.
The collected amniotic fluid is cultured, and amniocytes are analyzed.
Results:
The karyotype is established by the cytogenetics laboratory within 15 to 20 days, and a map of the observed genetic abnormalities.
Incidents:
There are rare under ultrasound but may exist as:
– A white puncture bringing not liquid;
– A bloody puncture wound through the placenta;
– Especially a risk of miscarriage: 0.5 to 1% of cases.
Cost:
K15 + K10 + B120 and B1300 for additional dosage of alpha-fetoprotein.
Practical advice:
On suspicion of spina bifida (malformation family history or as Depakine mother during pregnancy) may be added a dose of alpha-fetoprotein, alkaline phosphatase and its isoenzymes for research of cystic fibrosis.
Determining the sex of the fetus is also possible for conditions related to fetal sex.
Leave a Reply