Indications:
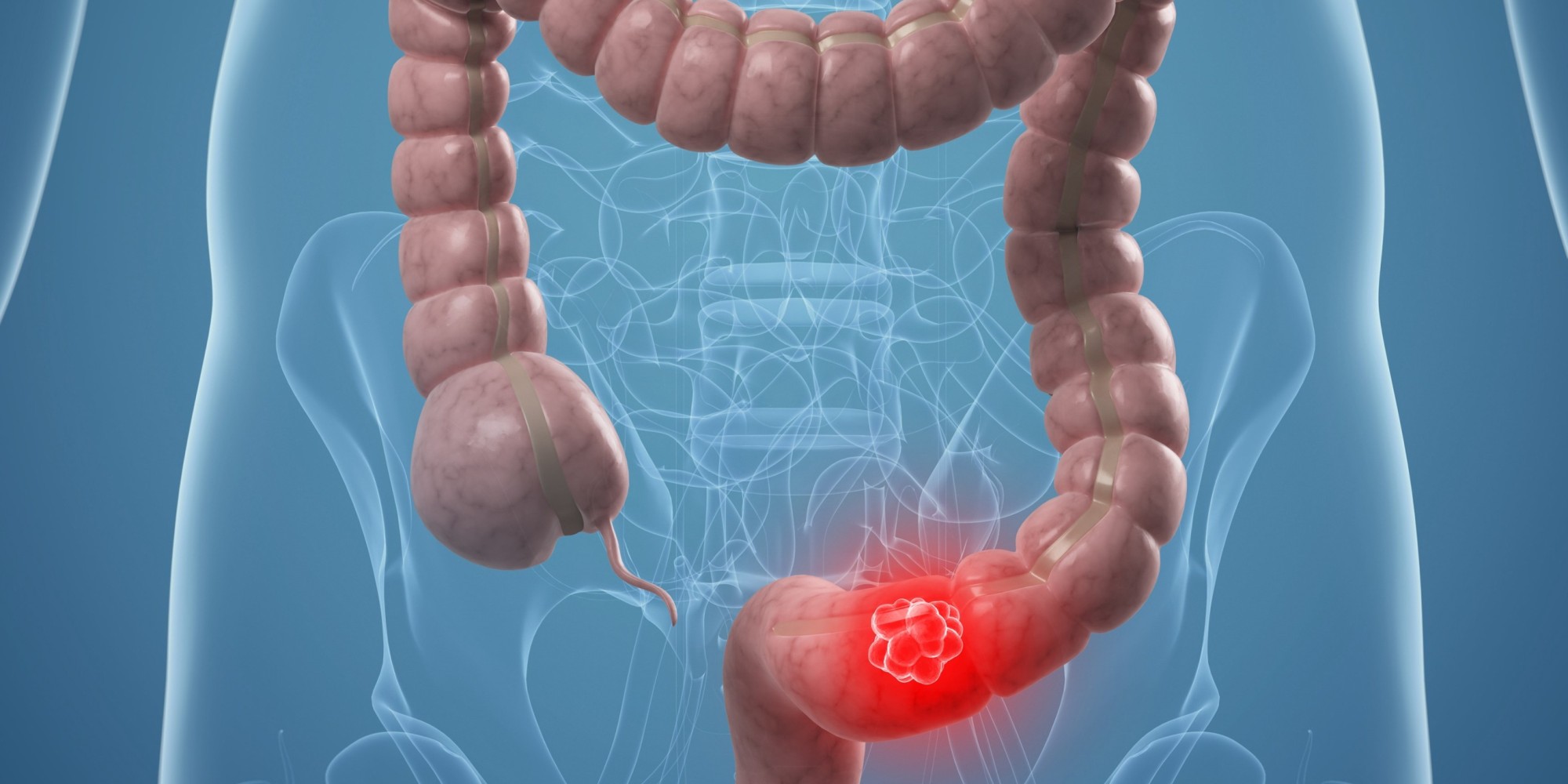
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) has an identity with an antigen of the mucous colic embryo, from which it takes its name, and is associated with colorectal cancer. This is less of a diagnostic aid as therapeutic monitoring of colorectal cancers.
Principle:
Secreted by the digestive mucosa cells, the antigen is normally present, but at very low concentrations in serum, except in cases of cancer digestive diseases.
 Technique:
Technique:
5 blood sampling mode on dry tube.
It can also include a liquid resulting from a puncture of ascites, pleural effusion or urine (for tumors of the bladder).
The assay is carried out by immuno-enzymatic method.
Results:
Normal values:
– Humans: <5 ng / mL;
For women: <7.5 ng / mL.
Pathological changes:
– The rate of ACE can rise above 25 ng / mL in the colon, but also for other digestive adenocarcinomas: esophagus and stomach, and in metastasis cancers such as breast, lung or pancreas; However, these thresholds may vary depending on the technique used;
– Its concentration also increases in cases of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatitis.
The dosage is neither specific enough nor reliable enough to serve as colon cancer screening means.
Its main use is in monitoring the progression of the disease under treatment: a rate that rises after lowering is well sign of recurrence, although a normal rate does not allow to exclude them formally.
Cost:
B70 to B105.
Practical advice:
Smoking can cause false positive ACE.
Leave a Reply