Tag: ECG
-
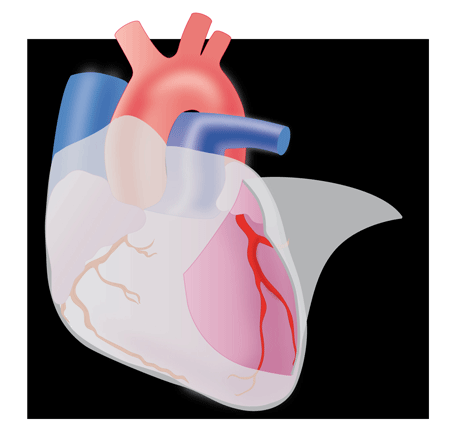
Acute Pericarditis
—
by
Warning: • Any pericarditis may be complicated by tamponade. • Viral acute pericarditis may recur in the short term. • Link to aspirin or anti-inflammatory oral gastric protector. Clinic: – Prolonged chest pain, continuous, non triggered by stress, increased by deep inspiration or supine, relieved by sitting insensitive nitroglycerin. – Moderate dyspnea. – Background influenza…
-

Stable Angina
—
by
Warning: • Angina is only one manifestation of coronary insufficiency (which may itself be the cause of ischemic heart failure, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia supraventricular and ventricular, or sudden death). • Ischemia can be painless, “silent” (the symptoma¬tologie is unfaithful). • Interest additional tests such as stress testing and stress echo to assess the existence and…
-
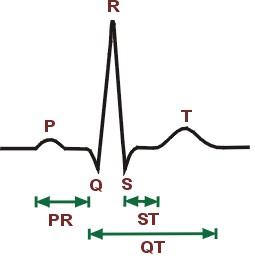
Electrocardiogram – ECG
Speed = 25mm / sec => 1cm = 0.4 sec (x-axis) Amplitude of 1 cm / mV => 1cm = 1mV (ordinate) Normal values: P wave -> 0.08 to 0.10 s; <0.25 cm PR space -> from 0.12 to 0.20 s QRS -> <0.08 s General: PR: – Prolongation of the PR interval reflects the…
-
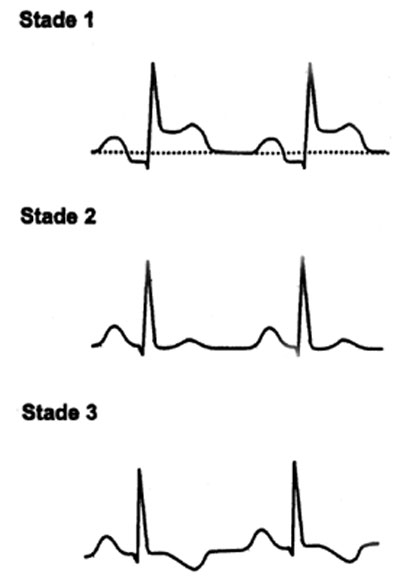
Pericarditis ECG
Developments in 4 stages: Stage I: Subepicardial injury: ST segment elevation in upper concavity, early, fleeting, not including the T wave, positive. Stage II (2nd week): ST return to the isoelectric line with flattened T waves Stage III: Negativity of the T wave, which can persist for several weeks (most constant sign and most durable:…
-
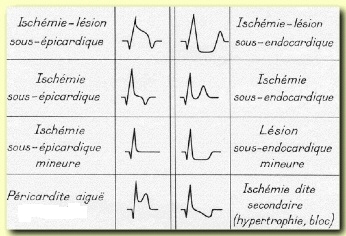
Myocardial Infarction ECG
* The non-Q wave infarction: IDM Nontransmural, has no Q-wave Contains intense as ST depression or T wave ischemia (sustainable). With increase in cardiac enzymes. Timeline & morphology: In the March 1 H: Giant waves symmetrical T (subendocardial ischemia) By the fourth hour: STEMI ST convex upwards encompassing the T wave -> is the wave…
-
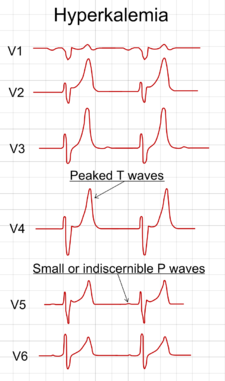
Electrolyte Disorders ECG
Dyskaliémies: Hypokalemia (<3.5 meq / l): * Increased wave U (nonspecific sign) * Flattening and negativity of the T wave (T + U draws a lying S) * ST cupuliforme Depression Hyperkalemia: * Wave symmetrical and sharp T, narrow base, tent (serum potassium of 5.5 to 6.4 meq) * The T waves are diffuse and…
-

Digitalis ECG
– Also called cardiac glycosides – Digitalis are in fact only small positive inotropic with some peripheral vascular effects. – At the level of myocardial cell, digitalis bind to membrane receptors and inhibit Na + / K + ATPase membrane. This blocks the outlet of extracellular Na + => [Ca2 +] int high (Na +…
-
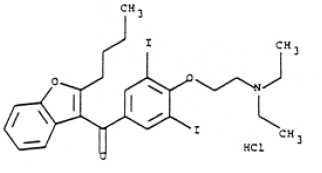
Drug Actions ECG
1- cardiac drugs: A- Digitalis (impregnation): * PR Elongation * ST cup Aspect * Flattening or negativity of the T wave * A moderately increased amplitude U * QT shortening B- Quinidine: * PR Elongation * Moderate Expansion of QRS * Sub-ST segment elevation; Flat or negative T * Increased U * QT Prolongation C-…
-
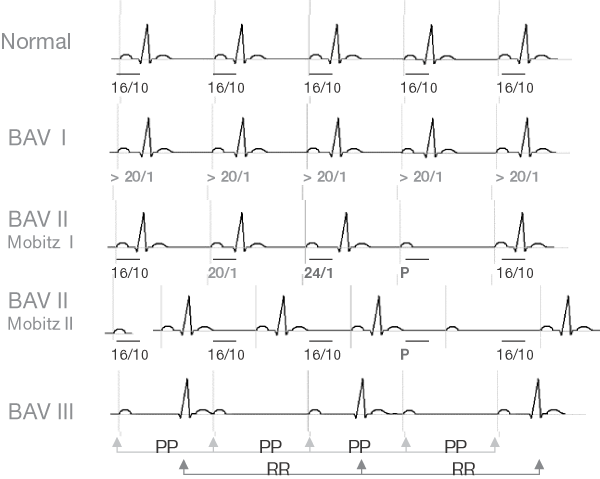
Atrioventricular block ECG
AVB I: It results in a prolongation of the PR interval (> 0.20 sec) AVB II: – Mobitz 1: Luciani-Wenckebach rate (progressive enlargement of the space PR -> P wave blocked). The headquarters of this block is usually supra-hissien (nodal) – Mobitz 2: paroxysmal AV conduction block. The block of the seat is usually sub-hissien…
-
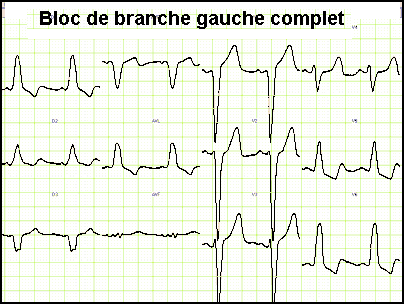
ECG branch block
1- complete left bundle branch block: – The electrical impulses will go from right to left – QRS> 0.12 s (incomplete block -> 0.10 to 0.12) – Deflection intrinsécoïde Delay (DIS) V6> 0,08s – In V6 characteristic morphology: no wave q; Wide QRS with top tray or crocheted (RR ‘) – In V1-V3: negativity wide…
You must be logged in to post a comment.