Tag: fever
-
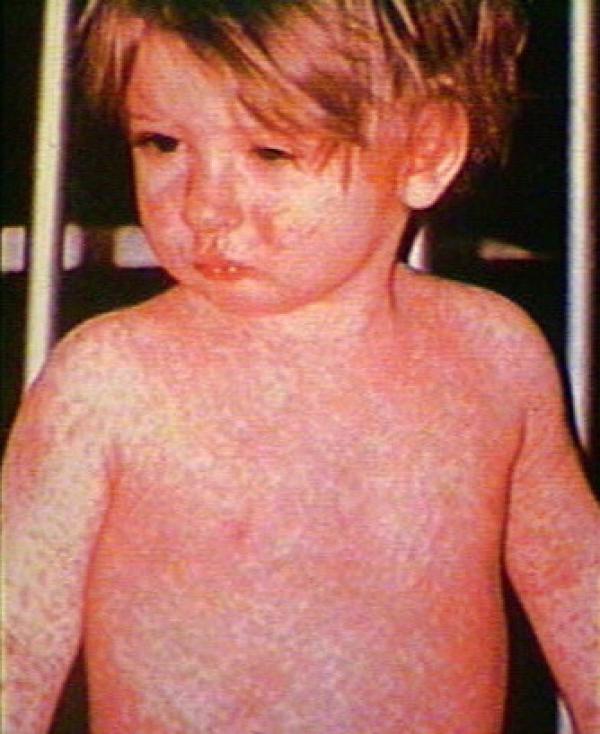
Measles
—
by
Measles is a highly contagious acute viral infection. Transmission is by air (inhalation of micro-droplets emitted by an infected person). In developing countries, it mainly affects children aged 1 to 3 years. Measles can be prevented by vaccination. For more information, refer to the Support guide of a measles outbreak, MSF. Clinical signs : –…
-

Fever
—
by
Fever is defined as a temperature higher than 37.5 ° C axillary and 38 ° C rectally. It is usual to consider that taking axillary temperature underestimates 0.5 ° C core temperature but this is very approximate. Use an electronic thermometer if possible (The temperature must be taken for 5 minutes when using a mercury…
-

Recurrent fever (Borreliosis)
—
by
Relapsing fever (FR) are caused by spirochetes of the genus Borrelia, transmitted to humans by arthropod vectors. Relapsing fever (FRP): FRP is caused by Borrelia recurrentis. The disease develops in epidemic when conditions favorable to the spread of body lice are met: cold weather, overcrowding and poor hygiene (eg refugee camps, prisons..). Endemic foci are…
-

Prolonged fever
—
by
We deal here that prolonged unexplained fevers. The diagnostic approach to acute fever is bad schématisable effect. It depends too associated symptoms, and would amount to treat each other of all infectious diseases. Although the possible causes prolonged fever are multiple, the diagnostic process is fairly stereotypical: – Ensure that it is a fever; –…
-

Malaria
—
by
The French carried about 8 million stays in the tropics each year, many opportunities to be exposed to malaria. In this context, the role of Field Operations is twofold: to correctly advise consultants to reduce as far as possible, the risk of malaria during or subsequent to a journey in endemic areas, but also know…
-
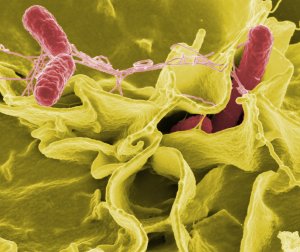
Salmonella – Citrobacter
—
by
HISTORY: – In 1820, Bretonneau showed the contagiousness of typhoid fever that was called dothiénentérite. – In 1880, Eberth bacillus first observed in the organs of a dead sick of typhoid. – In 1884, Graffky successful culture of this bacillus. – In 1896, Widal showed that the serum of patients with typhoid fever agglutinated cultures…
-
Borrelia
—
by
Borrelia are responsible for borreliosis, usually called recurrent fevers. These are diseases transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. According to the arthropod vector is conventionally divided into two groups of borreliosis: – The borreliosis transmitted by lice, – The tick-borne borreliosis. This bacterial genus experiencing a revival since the isolation of B. burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme…
-
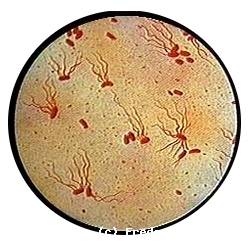
Typhoid Fever
* This is a septicemic poisoning (S. enterica / Typhi) at the point of departure mesenteric lymph caused by the bacillus of Eberth. The germ of the reservoir is represented by the man. * S. Typhi and Paratyphi The C can carry said Vi capsular Ag (used in the vaccination). Facultative intracellular bacterium. * The…
-
Q fever ( coxiellosis )
* Due to an intracellular bacteria (macrophages) Coxiella burnetii. * This is a ubiquitous zoonosis; human contamination is mainly by domestic animals (sheep, goats, cattle) inhalation of contaminated aerosols; contamination by ingestion of dairy products possible; and by the policy. * Acute Q fever: the average incubation period is 3 weeks; febrile hepatitis is the…
-
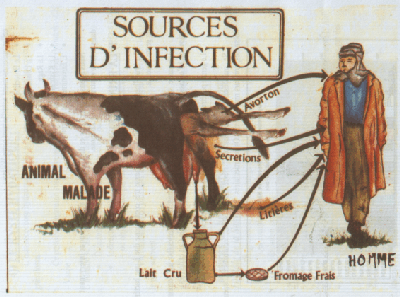
Brucellosis ( undulant fever , undulant fever )
* Brucella: bacillus gram-negative aerobic and spore forming; Brucella intracellular situation makes the total sterilization almost impossible with a risk of relapse (3-10%). Hypersensitivity of State for chronic functional disorders. * In animal, brucellosis is a genital disorder whose dominant expression is abortion. * The seed won the first lymph node and multiplies it; the…
You must be logged in to post a comment.