Tag: Infection
-
Acute renal failure during HIV infection
—
by
Generalities: Acute renal failure (ARF) is a common complication in HIV-positive patients for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).It occurs on average 4.5 years after the diagnosis of seropositivity. The etiologies of the IRA are multiple. Acute tubular necrosis of ischemic origin is the leading cause of ARI in HIV patients. It mainly complicates shock and sepsis. It is favored…
-
HIV Infection and AIDS
—
by
– AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is the most severe form of HIV infection (HIV). – There are two serotypes. HIV-1 is the most common. HIV-2 is found mainly in West Africa. Its virulence and its transmission are lower than those of HIV-1. – HIV affects the immune system and leads to a deficit of CD4…
-

Burns
—
by
Burns are skin trauma, produced by thermal agents, electrical, chemical or radiation. They still cause significant pain and can sometimes be life-threatening and / or functional. Classification of burns: Severe burns: one or more of the following: – Body surface area burned (SCB) greater than 10% in children and 15% in adults – Injuries by…
-

Screening for HIV infection
—
by
Diagnosis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) remains in France a city of medicine current problem.Besides the mandatory reporting of AIDS disease introduction there more than 20 years, the introduction of mandatory reporting of HIV infection from 2003 gives us precise information on the evolution of the epidemic. The estimated number of people infected…
-
Chance discovery of hepatitis B
—
by
Hepatitis B is a major public health problems worldwide. Approximately 2 billion people (one third of the world population) serological markers indicating the existence of an old infection (and healed) or chronic infection (persistent) by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), and approximately 350 million people have chronic HBV infection. Morbidity and mortality from hepatitis B…
-
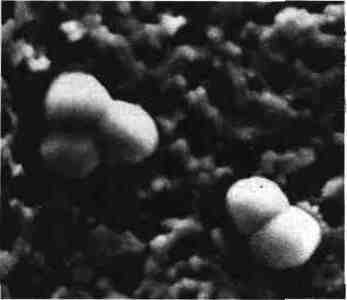
Neisseria
—
by
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: Neisseria are Gram-negative cocci, diplococci associates, sometimes tetrads and immobile. Strictly aerobic bacteria, only to respiratory metabolism (respiration of nitrate and / or nitrite is possible). They are always catalase (+) and possess a cytochrome C oxidase. Their metabolic potential is limited. These are the usual hosts of mucous membranes of humans and…
-
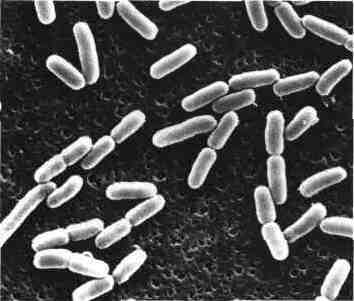
Escherichia Coli
—
by
Isolated for the first time by Escherich in 1885, is the Escherichia coli bacterial species that has been most studied by fundamentalists for physiology and genetics work. This bacterium has long been known as commensal and pathogenic digestive tube to the urinary tract. In recent decades, the role of certain categories of E. coli in…
-
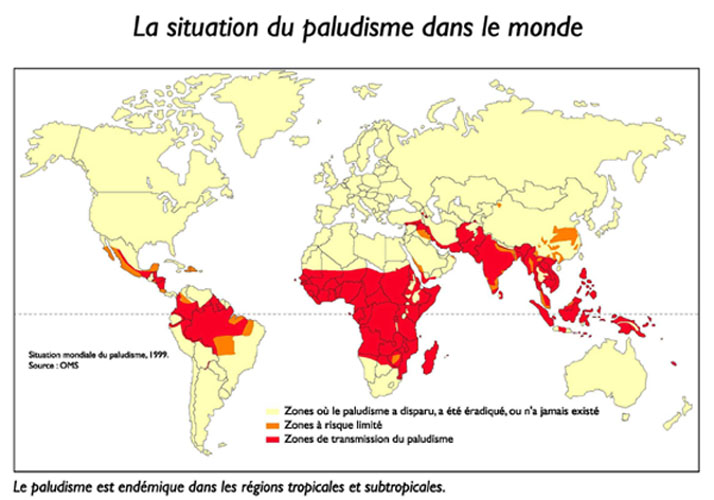
Bacterial and Parasitic Infections
* Diphtheria: it is due to the lysogénée bacteria strain that produces exotoxin. C. The diphtheria that do not produce exotoxin may be responsible for angina false membranes, but also septicemia (and secondary locations: endocarditis) but do not induce the disease diphtheria. Diphtheria is a little immunizing disease which justifies vaccination for convalescent patients. *…
-
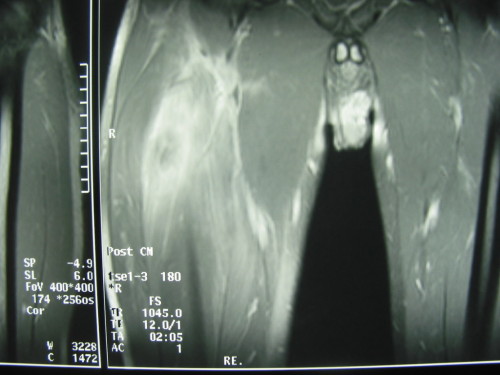
Pyomyositis
– Pyomyositis is an infection of muscle almost always due to Staphylococcus aureus, preferentially affecting the muscles of the limbs and trunk. The locations are sometimes multiple. – In the diffusion phase when the muscle is swollen, hot and painful, it is hoped that medical treatment can reduce infection. A collection phase, single-incision drainage is…
You must be logged in to post a comment.