* Connected to the free silica dust accumulation crystalline form of silicon dioxide
* The characteristic anatomical lesion is silicosis nodule: up in the center of collagen fibers and hyalinized on the outskirts of a fiborconiotique crown (Dust seat)
* Exposed Professions Off-road work (mining, tunnel); abrasives industry; etching; exterior surfaces; ceramics manufacturing; dental technician
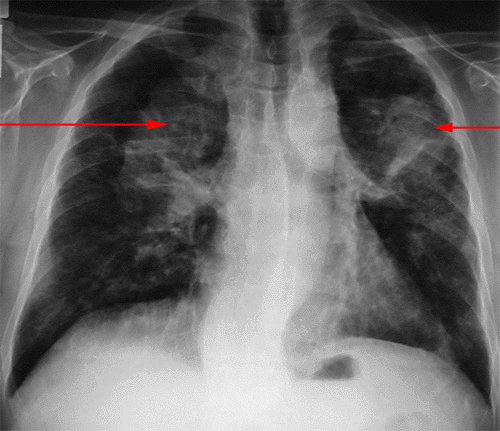
* Two types of opacities silicosis characteristics: small rounded opacities (<10 mm); extended opacity (> 1 cm); -> See ILO classification
Hilar lymphadenopathy * calcified in periphery “eggshell”
* Other: deformations of diaphragmatic; lucency bases (emphysema) …
* The scanner is useful (especially at an early stage)
* There is typically a restrictive syndrome often associated with the spread of disorder and obstructive syndrome.
* The first manifestations appear after a professional dustiness of 15 to 20 years
* Complications: tuberculosis; Aseptic necrosis of the tumor-like mass responsible for an array of mélanoptysie; transplant aspergillosis; spontaneous pneumothorax; chronic bronchial suppuration
* The scleroderma: systemic sclerosis silicosis +
* Syndrome Caplan: silicosis + RA
CLASSIFICATION ILO:
* Small rounded opacities: micro (between 1.5-3 mm);nodular (between 3 and 10 mm); punctate (<1.5 mm)
* These small opacities are always bilateral
– Category 1: few; visible in the sup parties. and Avg.
– Category 2: Many opacities, invading both lung fields
– Category 3: opacities very numerous, invading two lung fields
* Extended opacities; usually bilateral and roughly symmetrical
– Category A: single opacity <5 cm or more> 1 cm but the sum is <5 cm
– Category B: one or more opacities whose area does not exceed 1/3 of the right lung field.
– Category C: surface sum exceeds ⅓ of the right lung field

Leave a Reply