Category: Additional Tests
-
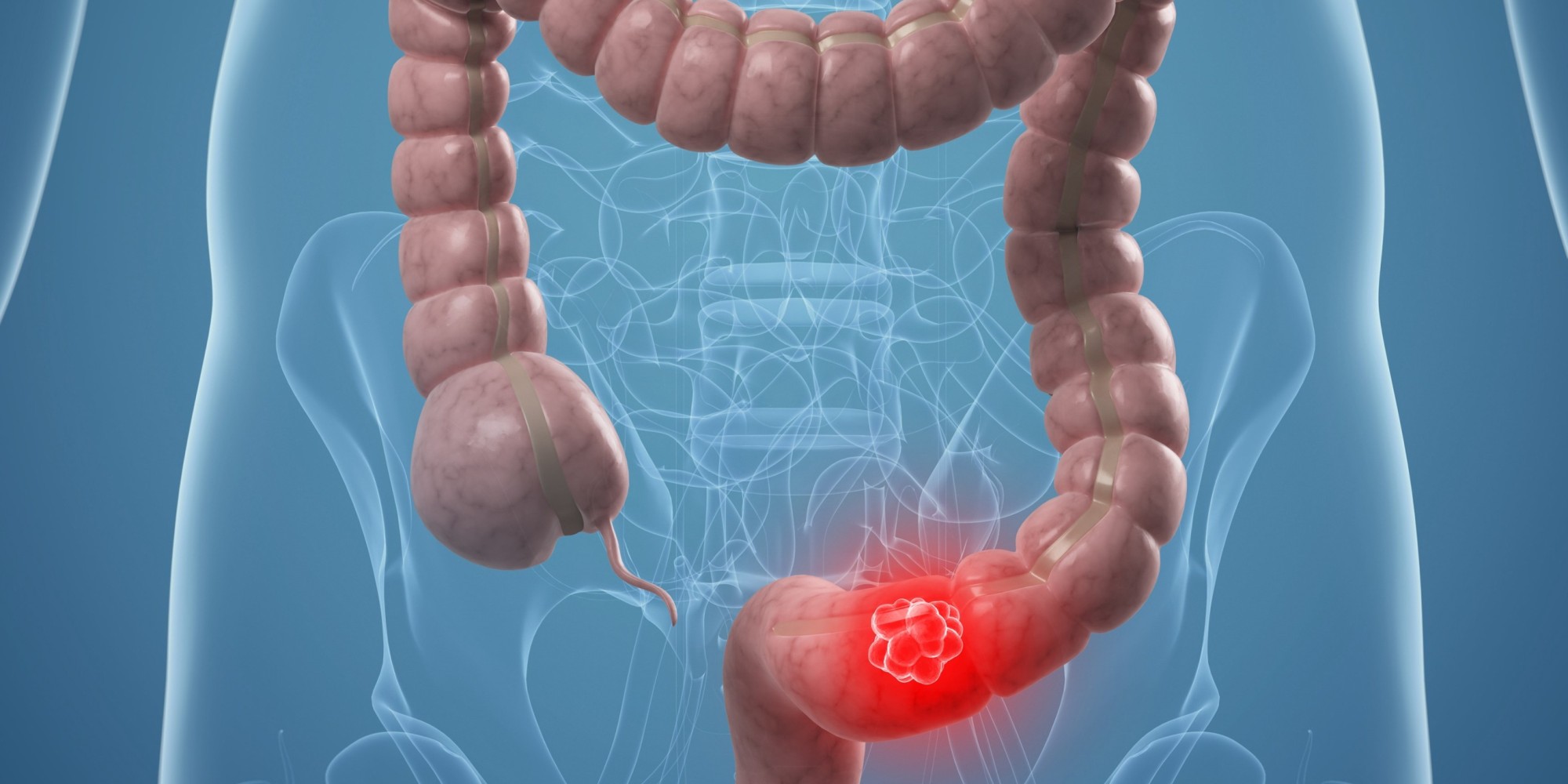
Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA)
Indications: CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) has an identity with an antigen of the mucous colic embryo, from which it takes its name, and is associated with colorectal cancer. This is less of a diagnostic aid as therapeutic monitoring of colorectal cancers. Principle: Secreted by the digestive mucosa cells, the antigen is normally present, but at very…
-
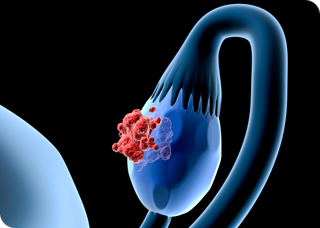
CA 125 Antigen
Indications: This is not a diagnostic test, the purpose to review the monitoring of epithelial ovarian cancer. Principle: A monoclonal antibody allows to highlight an antigen not normally present in the blood released in the genital epithelial tissue is in the serum by tumor cells. Technique: Sampling 5 mL of blood in a dry tube.…
-
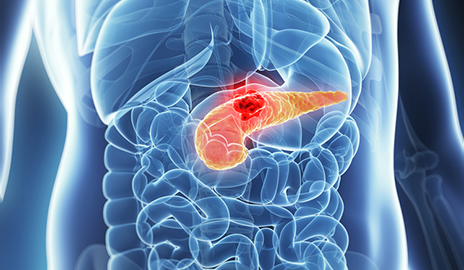
Antigen CA 19.9
Indications: CA 19.9 is a circulating antigen associated with gastrointestinal cancer, especially the pancreas and colon. Principle: This is detected in the serum antigen not normally present and produced by gastrointestinal tumor cells. Technique: Sampling 5 mL of blood in a dry tube. The assay is radioimmunoassay or enzyme immunoassay with double antibodies. Results: normal…
-
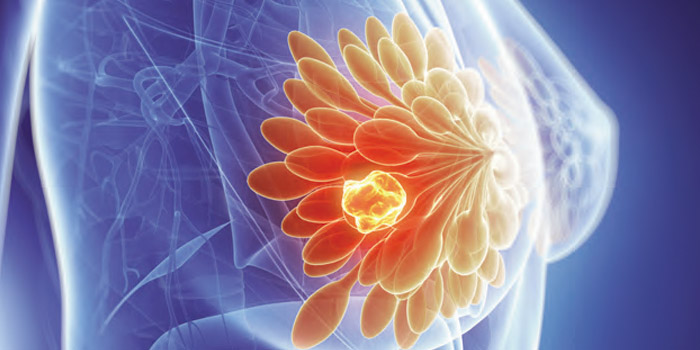
Antigen CA 15.3
Indications: The blood test CA 15.3 is useful in the effective control of an antitumor treatment. Principle: Circulating antigen, CA 15-3 is associated with breast cancer: it is recognized by monoclonal antibodies against membrane antigens of breast tumors. Technique: Levy of 2 mL of blood in a dry tube. The assay method is radioimmunoassay or…
-

Antithyroid Antibodies
Indications: if the review is essentially practical suspected thyroid autoimmune diseases (such as Hashimoto thyroiditis, for example), but When it evoked the diagnosis of neonatal hyperthyroidism. Apart from the diagnostic indication, the examination will follow, during treatment or stage of pregnancy, treated hyperthyroidism Graves. Principle: The antibodies are directed essentially against thyroglobulin, microsomes and the…
-

Anti-Sperm Antibodies
Indications: The examination allows to find an immunological cause infertility: the presence of iso-antibodies in women and autoantibodies in humans. Principle: The antibodies cause infertility with sperm agglutination. Technique: In humans: taking 5 mL of blood in a dry tube and seminal fluid. For women: 5 mL sample of blood and mucus. The agglutination of…
-
Gliadin Antibodies
Indications: The dosage of anti-gliadin antibodies provides help diagnose celiac disease (gluten intolerance) in children. Principle: A blood test can detect the presence of blood antibodies against gliadin component of the immune response in celiac disease. These antibodies disappear when gluten free diet. Technique: Blood sample to detect IgA and IgG: – IgA are found…
-

Anti-dsDNA Antibodies. Farr Assay
Indications: The presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies is observed that in case of lupus. In contrast, anti-DNA antibodies denatured, less specific, are found in several autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma and also hepatitis. Principle: The Farr assay consists in bringing the patient’s serum with the DNA labeled with carbon 14. It then precipitated proteins by…
-
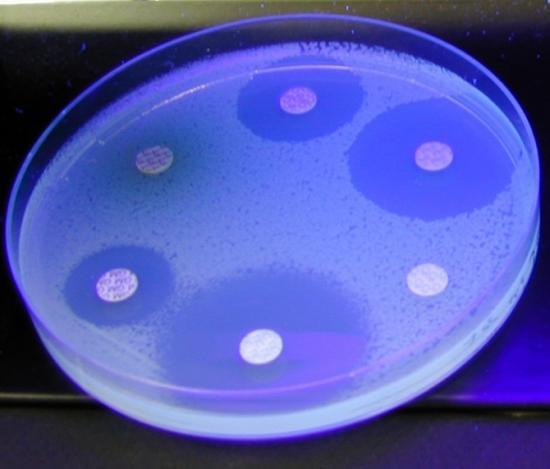
Antibiogram
Indications: This test assesses the antibiotic susceptibility of a bacterial strain believed to be responsible for infection. Principle: The antibiotic tested, if effective, to inhibit microbial growth on ke levy cultured. Results: They can be obtained in a few hours up to 24 hours after isolation of the strain (total duration of the examination on…
-

Amylase
Indications: The measurement of plasma amylase evidence to suggest or confirm the diagnosis of pancreatitis in acute attack These enzymes, which cleave the starch, are secreted by the pancreas and salivary glands. For they pass in serum, where it is normally absent, it is necessary that there be either ductal obstruction or tissue necrosis. Serum…
You must be logged in to post a comment.